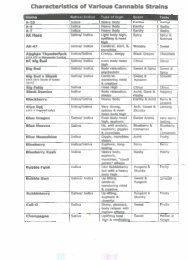
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Cannabinoid targets for pain therapeutics 159<br />
characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 34: 605–613<br />
6 Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI (1990) Structure of a cannabinoid<br />
receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 346: 561–564<br />
7 Munro S, Thomas KL, Abu-Shaar M (1993) Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor<br />
for cannabinoids. Nature 365: 61–65<br />
8 Devane WA, Hanusˇ L, Breuer A, Pertwee RG, Stevenson LA, Griffin G, Gibson D, Mandelbaum<br />
A, Etinger A, Mechoulam R (1992) Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the<br />
cannabinoid receptor. Science 258: 1946–1949<br />
9 Pertwee RG (1997) Pharmacology of cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharmacol Ther 74:<br />
129–180<br />
10 Palmer SL, Thakur GA, Makriyannis A (2002) Cannabinergic ligands. Chem Phys Lipids 121:<br />
3–19<br />
11 Walker JM, Krey JF, Chu CJ, Huang SM (2002) Endocannabinoids and related fatty acid derivatives<br />
in pain modulation. Chem Phys Lipids 121: 159–172<br />
12 Dixon WE (1899) The pharmacology of Cannabis indica. Br Med J 2: 1354–1357<br />
13 Bicher HI, Mechoulam R (1968) Pharmacological effects of two active constituents of marihuana.<br />
Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 172: 24–31<br />
14 Kosersky DS, Dewey WL, Harris LS (1973) Antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects<br />
of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 24: 1–7<br />
15 Bloom AS, Dewey WL, Harris LS, Brosius KK (1977) 9-nor-9beta-hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol,<br />
a cannabinoid with potent antinociceptive activity: comparisons with morphine. J Pharmacol Exp<br />
Ther 200: 263–270<br />
16 Buxbaum DM (1972) Analgesic activity of 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the rat and mouse.<br />
Psychopharmacologia 25: 275–280<br />
17 Martin BR, Compton DR, Thomas BF, Prescott WR, Little PJ, Razdan RK, Johnson MR, Melvin<br />
LS, Mechoulam R, Ward SJ (1991) Behavioral, biochemical, and molecular modeling evaluations<br />
of cannabinoid analogs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40: 471–478<br />
18 Hohmann AG, Martin WJ, Tsou K, Walker JM (1995) Inhibition of noxious stimulus-evoked<br />
activity of spinal cord dorsal horn neurons by the cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2. Life Sci 56:<br />
2111–2118<br />
19 Hohmann AG, Tsou K, Walker JM (1998) Cannabinoid modulation of wide dynamic range neurons<br />
in the lumbar dorsal horn of the rat by spinally administered WIN55,212-2. Neurosci Lett<br />
257: 119–122<br />
20 Hohmann AG, Tsou K, Walker JM (1999) Cannabinoid suppression of noxious heat-evoked activity<br />
in wide dynamic range neurons in the lumbar dorsal horn of the rat. J Neurophys 81: 575–583<br />
21 Martin WJ, Hohmann AG, Walker JM (1996) Suppression of noxious stimulus-evoked activity in<br />
the ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus by a cannabinoid agonist: correlation between<br />
electrophysiological and antinociceptive effects. J Neurosci 16: 6601–6611<br />
22 Strangman NM, Walker JM (1999) The cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 inhibits the activity-dependent<br />
facilitation of spinal nociceptive responses. J Neurophys 81: 472–477<br />
23 Drew LJ, Harris J, Millns PJ, Kendall DA, Chapman V (2000) Activation of spinal cannabinoid 1<br />
receptors inhibits C-fibre driven hyperexcitable neuronal responses and increases<br />
[ 35 S]GTPgammaS binding in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord of noninflamed and inflamed rats.<br />
Eur J Neurosci 12: 2079–2086<br />
24 Kelly S, Chapman V (2001) Selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor activation inhibits spinal nociceptive<br />
transmission in vivo. J Neurophysiol 86: 3061–3064<br />
25 Hunt SP, Pini A, Evan G (1987) Induction of c-fos-like protein in spinal cord neurons following<br />
sensory stimulation. Nature 328: 632–634<br />
26 Farquhar-Smith WP, Jaggar SI, Rice AS (2002) Attenuation of nerve growth factor-induced visceral<br />
hyperalgesia via cannabinoid CB(1) and CB(2)-like receptors. Pain 97: 11–21<br />
27 Hohmann AG, Tsou K, Walker JM (1999) Intrathecal cannabinoid administration suppresses noxious-stimulus<br />
evoked Fos protein-like immunoreactivity in rat spinal cord: comparison with morphine.<br />
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 20: 1132–1136<br />
28 Martin WJ, Loo CM, Basbaum AI (1999) Spinal cannabinoids are anti-allodynic in rats with persistent<br />
inflammation. Pain 82: 199–205<br />
29 Nackley AG, Makriyannis A, Hohmann AG (2003) Selective activation of cannabinoid CB2 receptors<br />
suppresses spinal Fos protein expression and pain behavior in a rat model of inflammation.<br />
Neuroscience 119: 747–757