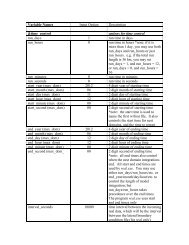
Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
From the reference temperature and pressure, the reference potential temperature is then defined<br />
as<br />
<br />
θd = T0 + A ln pd p0<br />
p0<br />
and the reciprocal of the reference density using (5.4) and (5.5) is given by<br />
αd = 1<br />
ρ d<br />
= Rd θd<br />
p0<br />
pd<br />
p0<br />
p d<br />
R d<br />
Cp<br />
, (5.5)<br />
− Cv<br />
Cp<br />
. (5.6)<br />
The base state difference of the dry surface pressure from (5.3) and the model top is given as<br />
µ d = pdhs − pdht. (5.7)<br />
From (5.6) and (5.7), the reference state geopotential defined from the hydrostatic relation is<br />
δηφ = −αd µ d.<br />
One of the total fields provided to the real-data cases by the SI is µd. The perturbation field<br />
given the reference value (5.7) is<br />
µ ′ d = µd − µ d. (5.8)<br />
Starting with the reference state fields (5.4, 5.6, and 5.7) and the dry surface pressure perturbation<br />
(5.8), the perturbation fields for pressure and inverse density are diagnosed. The pressure<br />
perturbation includes moisture and is diagnosed from the hydrostatic equation<br />
<br />
1 + qv η<br />
<br />
+ qv η µ d,<br />
δηp ′ = µ ′ d<br />
which is integrated down from at the model top (where p ′ = 0) to recover p ′ . The total dry<br />
inverse density is given as<br />
αd = Rd<br />
p0<br />
<br />
θ<br />
1 + Rv<br />
qv<br />
Rd<br />
which defines the perturbation field for inverse density<br />
α ′ d = αd − αd.<br />
p ′ d + p d<br />
p0<br />
− Cv<br />
Cp<br />
,<br />
The perturbation geopotential is diagnosed from the hydrostatic relation<br />
δηφ ′ = − µdα ′ d + µ ′ <br />
dαd<br />
by upward integration using the terrain elevation as the lower boundary condition. In future<br />
versions of the real-data pre-processor, p ′ will be re-diagnosed consistent with the method used<br />
in the model (2.21) as a final step. No modifications to the original µd, u, v, qv, or θ from the<br />
SI are performed. The vertical component of velocity is initialized to zero.<br />
37