Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1-Way <strong>ARW</strong> <strong>WRF</strong> Simulation<br />
Two Consecutive<br />
<strong>ARW</strong> simulations<br />
(using ndown)<br />
1) Run coarse grid<br />
(CG) simulation<br />
2) Process CG for<br />
initial condition (IC)<br />
for fine grid (FG)<br />
3) Process CG for<br />
lateral boundary<br />
condition (LBC) for<br />
FG<br />
4) Run FG simulation<br />
Concurrent <strong>ARW</strong><br />
simulation with two<br />
domains<br />
1) Both CG and FG<br />
simulations run within<br />
the same <strong>WRF</strong><br />
2) FG LBC from CG<br />
at each coarse time<br />
step<br />
3) CG integrates one<br />
time step, then the<br />
FG integrates up to<br />
the same time<br />
2-Way <strong>ARW</strong> Simulation<br />
Concurrent <strong>ARW</strong><br />
simulation with two<br />
domains<br />
Both CG and FG<br />
simulations run within<br />
the same <strong>WRF</strong><br />
2) FG LBC from CG<br />
at each coarse time<br />
step<br />
3) CG integrates one<br />
time step, then the<br />
FG integrates up to<br />
the same time<br />
4) Feedback FG to CG<br />
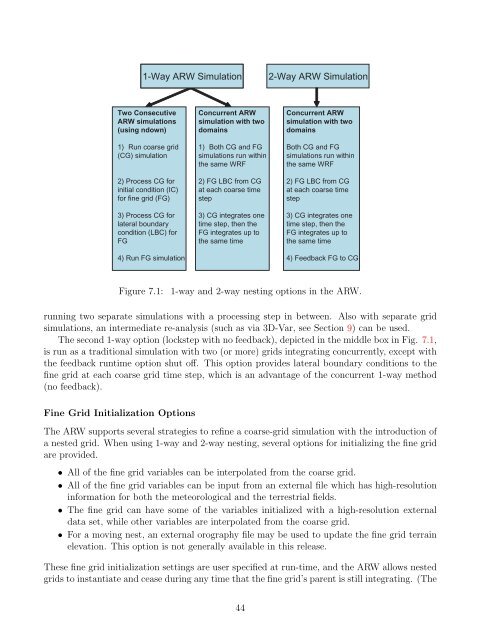
Figure 7.1: 1-way and 2-way nesting options in the <strong>ARW</strong>.<br />
running two separate simulations with a processing step in between. Also with separate grid<br />
simulations, an intermediate re-analysis (such as via 3D-Var, see Section 9) can be used.<br />
The second 1-way option (lockstep with no feedback), depicted in the middle box in Fig. 7.1,<br />
is run as a traditional simulation with two (or more) grids integrating concurrently, except with<br />
the feedback runtime option shut off. This option provides lateral boundary conditions to the<br />
fine grid at each coarse grid time step, which is an advantage of the concurrent 1-way method<br />
(no feedback).<br />
Fine Grid Initialization Options<br />
The <strong>ARW</strong> supports several strategies to refine a coarse-grid simulation with the introduction of<br />
a nested grid. When using 1-way and 2-way nesting, several options for initializing the fine grid<br />
are provided.<br />
• All of the fine grid variables can be interpolated from the coarse grid.<br />
• All of the fine grid variables can be input from an external file which has high-resolution<br />
information for both the meteorological and the terrestrial fields.<br />
• The fine grid can have some of the variables initialized with a high-resolution external<br />
data set, while other variables are interpolated from the coarse grid.<br />
• For a moving nest, an external orography file may be used to update the fine grid terrain<br />
elevation. This option is not generally available in this release.<br />
These fine grid initialization settings are user specified at run-time, and the <strong>ARW</strong> allows nested<br />
grids to instantiate and cease during any time that the fine grid’s parent is still integrating. (The<br />
44