Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Technical Note - MMM - University ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
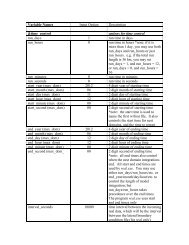
List of Figures<br />
1.1 <strong>WRF</strong> system components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2<br />
2.1 <strong>ARW</strong> η coordinate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5<br />
3.1 Time step integration sequence. Here n represents the number of acoustic time<br />
steps for a given substep of the RK3 integration, and ns is the ratio of the RK3<br />
time step to the acoustic time step for the second and third RK3 substeps. . . . 14<br />
3.2 Horizontal and vertical grids of the <strong>ARW</strong> . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17<br />
5.1 Schematic showing the data flow and program components in the SI, and how<br />
the SI feeds initial data to the <strong>ARW</strong>. Letters in the rectangular boxes indicate<br />
program names. GRID GEN: defines the model domain and creates static files<br />
of terrestrial data. GRIB PREP: decodes GriB data. HINTERP: interpolates<br />
meteorological data to the model domain. VINTERP: vertically interpolates<br />
data to model coordinate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36<br />
6.1 Specified and relaxation zones for a grid with a single specified row and column,<br />
and four rows and columns for the relaxation zone. These are typical values used<br />
for a specified lateral boundary condition for a real-data case. . . . . . . . . . . 41<br />
7.1 1-way and 2-way nesting options in the <strong>ARW</strong>. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44<br />
7.2 Various nest configurations for multiple grids. (a) Telescoping nests. (b) Nests at<br />
the same level with respect to a parent grid. (c) Overlapping grids: not allowed<br />
(d) Inner-most grid has more than one parent grid: not allowed . . . . . . . . . 45<br />
7.3 Arakawa-C grid staggering for a portion of a parent domain and an imbedded<br />
nest domain with a 3:1 grid size ratio. The solid lines denote coarse grid cell<br />
boundaries, and the dashed lines are the boundaries for each fine grid cell. The<br />
horizontal components of velocity (“U” and “V”) are defined along the normal cell<br />
face, and the thermodynamic variables (“θ”) are defined at the center of the grid<br />
cell (each square). The bold typeface variables along the interface between the<br />
coarse and the fine grid define the locations where the specified lateral boundaries<br />
for the nest are in effect. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46<br />
7.4 Similar to Fig. 7.3, but with a 2:1 grid-distance ratio. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48<br />
7.5 Nest grid integration sequence. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49<br />
9.1 Sketch showing the relationship between datasets (circles), and algorithms (rectangles)<br />
of the <strong>ARW</strong> system. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66<br />
v