TRENDS AND IMPACTS OF FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN DEVELOPING COUNTRY AGRICULTURE
TRENDS AND IMPACTS OF FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN DEVELOPING COUNTRY AGRICULTURE
TRENDS AND IMPACTS OF FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN DEVELOPING COUNTRY AGRICULTURE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
UG<strong>AND</strong>A<br />
Trends and impacts of foreign investment in<br />
developing country agriculture<br />
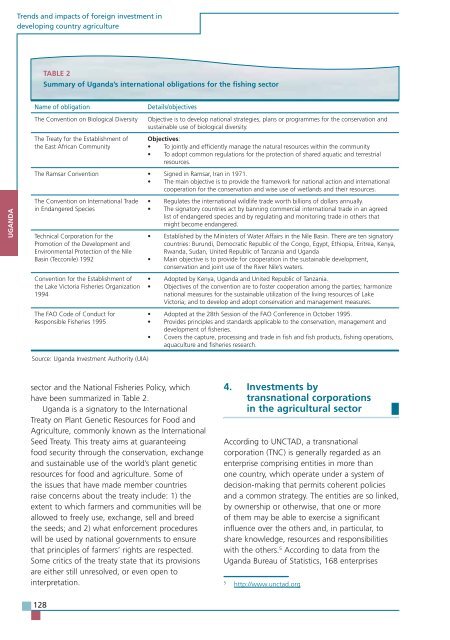
sector and the National Fisheries Policy, which<br />
have been summarized in Table 2.<br />
Uganda is a signatory to the International<br />
Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and<br />
Agriculture, commonly known as the International<br />
Seed Treaty. This treaty aims at guaranteeing<br />
food security through the conservation, exchange<br />
and sustainable use of the world’s plant genetic<br />
resources for food and agriculture. Some of<br />
the issues that have made member countries<br />
raise concerns about the treaty include: 1) the<br />
extent to which farmers and communities will be<br />
allowed to freely use, exchange, sell and breed<br />
the seeds; and 2) what enforcement procedures<br />
will be used by national governments to ensure<br />
that principles of farmers’ rights are respected.<br />
Some critics of the treaty state that its provisions<br />
are either still unresolved, or even open to<br />
interpretation.<br />
128<br />
TABLE 2<br />
Summary of Uganda’s international obligations for the fishing sector<br />
Name of obligation Details/objectives<br />
The Convention on Biological Diversity Objective is to develop national strategies, plans or programmes for the conservation and<br />
sustainable use of biological diversity.<br />
The Treaty for the Establishment of<br />
the East African Community<br />
Source: Uganda Investment Authority (UIA)<br />
Objectives:<br />
To jointly and efficiently manage the natural resources within the community<br />
To adopt common regulations for the protection of shared aquatic and terrestrial<br />
resources.<br />
The Ramsar Convention Signed in Ramsar, Iran in 1971.<br />
The main objective is to provide the framework for national action and international<br />
cooperation for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources.<br />
The Convention on International Trade<br />
in Endangered Species<br />
Technical Corporation for the<br />
Promotion of the Development and<br />
Environmental Protection of the Nile<br />
Basin (Tecconile) 1992<br />
Convention for the Establishment of<br />
the Lake Victoria Fisheries Organization<br />
1994<br />
The FAO Code of Conduct for<br />
Responsible Fisheries 1995<br />
Regulates the international wildlife trade worth billions of dollars annually.<br />
The signatory countries act by banning commercial international trade in an agreed<br />
list of endangered species and by regulating and monitoring trade in others that<br />
might become endangered.<br />
Established by the Ministers of Water Affairs in the Nile Basin. There are ten signatory<br />
countries: Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Kenya,<br />
Rwanda, Sudan, United Republic of Tanzania and Uganda<br />
Main objective is to provide for cooperation in the sustainable development,<br />
conservation and joint use of the River Nile’s waters.<br />
Adopted by Kenya, Uganda and United Republic of Tanzania.<br />
Objectives of the convention are to foster cooperation among the parties; harmonize<br />
national measures for the sustainable utilization of the living resources of Lake<br />
Victoria; and to develop and adopt conservation and management measures.<br />
Adopted at the 28th Session of the FAO Conference in October 1995.<br />
Provides principles and standards applicable to the conservation, management and<br />
development of fisheries.<br />
Covers the capture, processing and trade in fish and fish products, fishing operations,<br />
aquaculture and fisheries research.<br />
4. Investments by<br />
transnational corporations<br />
in the agricultural sector <br />
According to UNCTAD, a transnational<br />
corporation (TNC) is generally regarded as an<br />
enterprise comprising entities in more than<br />
one country, which operate under a system of<br />
decision-making that permits coherent policies<br />
and a common strategy. The entities are so linked,<br />
by ownership or otherwise, that one or more<br />
of them may be able to exercise a significant<br />
influence over the others and, in particular, to<br />
share knowledge, resources and responsibilities<br />
with the others. 5 According to data from the<br />
Uganda Bureau of Statistics, 168 enterprises<br />
5 http://www.unctad.org