Abstract Book of EAVLD2012 - eavld congress 2012
Abstract Book of EAVLD2012 - eavld congress 2012
Abstract Book of EAVLD2012 - eavld congress 2012
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
S3 - O - 02<br />
25 YEARS OF PASSIVE SURVEILLANCE OF BATS IN THE NETHERLANDS. MOLECULAR<br />
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND EVOLUTION OF EBLV-1.<br />
Introduction<br />
Since 1986 a reactive surveillance program is running in the<br />
Netherlands to investigate the presence <strong>of</strong> European Bat<br />
Lyssavirusses (EBLV-1 and EBLV-2) in bats. In this program all<br />
contact cases, with human or pets, are send to the laboratory in<br />
Lelystad and tested for EBLV with a EU prescribed immune<br />
fluorescence test (IFT). Up to date almost 5000 samples have<br />
been tested. The main reservoir for EBLV is Eptesicus serotinus,<br />
334 positive cases so far which is about 22% <strong>of</strong> the samples<br />
tested, second species is Myotis dasycneme, with almost 4%<br />
positive thus far (Table 1). EBLV-2 has not been detected in the<br />
Netherlands since 1993.<br />
Materials & methods<br />
Bat brains were tested using the prescribed fluorescent antibody<br />
test (FAT). For conformation a real time PCR test on the N-gene<br />
was used. On the same nucleic acid isolation used for the realtime<br />
PCR N and G-gene sequencing was performed on an ABI<br />
sequencer according to the manufacturers protocol. The species<br />
<strong>of</strong> all submissions were determined by a bat expert.<br />
The MCC phylogenetic tree, estimates <strong>of</strong> the rate <strong>of</strong> molecular<br />
evolution (substitutions per site per year) and the TMRCA for the<br />
alignments were inferred using a Bayesian MCMC method in the<br />
BEAST package.<br />
B. Kooi, A. Vogel and E. Van Weezep<br />
Central Veterinary Institute <strong>of</strong> Wageningen UR, Lelystad, The Netherlands.<br />
Lyssavirus, EBLV, bats, surveillance, molecular epidemiology<br />
Results & Discussion<br />
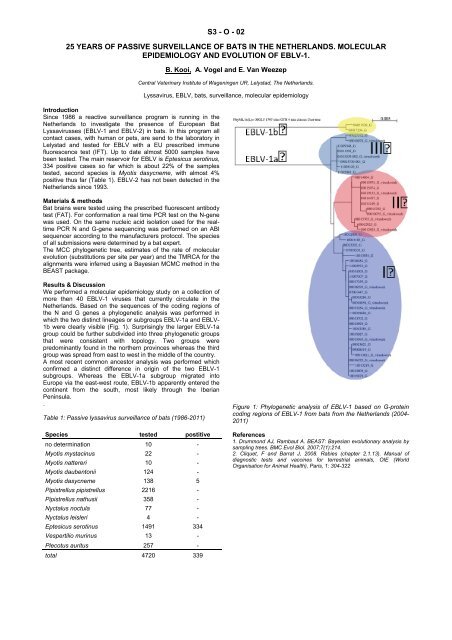
We performed a molecular epidemiology study on a collection <strong>of</strong><br />
more then 40 EBLV-1 viruses that currently circulate in the<br />
Netherlands. Based on the sequences <strong>of</strong> the coding regions <strong>of</strong><br />
the N and G genes a phylogenetic analysis was performed in<br />
which the two distinct lineages or subgroups EBLV-1a and EBLV-<br />
1b were clearly visible (Fig. 1). Surprisingly the larger EBLV-1a<br />
group could be further subdivided into three phylogenetic groups<br />
that were consistent with topology. Two groups were<br />
predominantly found in the northern provinces whereas the third<br />
group was spread from east to west in the middle <strong>of</strong> the country.<br />
A most recent common ancestor analysis was performed which<br />
confirmed a distinct difference in origin <strong>of</strong> the two EBLV-1<br />
subgroups. Whereas the EBLV-1a subgroup migrated into<br />
Europe via the east-west route, EBLV-1b apparently entered the<br />
continent from the south, most likely through the Iberian<br />
Peninsula.<br />
.<br />
Table 1: Passive lyssavirus surveillance <strong>of</strong> bats (1986-2011)<br />
Species tested postitive<br />
no determination 10 -<br />
Myotis mystacinus 22 -<br />
Myotis nattereri 10 -<br />
Myotis daubentonii 124 -<br />
Myotis dasycneme 138 5<br />
Pipistrellus pipistrellus 2216 -<br />
Pipistrellus nathusii 358 -<br />
Nyctalus noctula 77 -<br />
Nyctalus leisleri 4 -<br />
Eptesicus serotinus 1491 334<br />
Vespertilio murinus 13 -<br />
Plecotus auritus 257 -<br />
total 4720 339<br />
Figure 1: Phylogenetic analysis <strong>of</strong> EBLV-1 based on G-protein<br />
coding regions <strong>of</strong> EBLV-1 from bats from the Netherlands (2004-<br />
2011)<br />
References<br />
1. Drummond AJ, Rambaut A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by<br />
sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol. 2007;7(1):214.<br />
2. Cliquet, F and Barrat J, 2008. Rabies (chapter 2.1.13). Manual <strong>of</strong><br />
diagnostic tests and vaccines for terrestrial animals, OIE (World<br />
Organisation for Animal Health), Paris, 1: 304-322