PhD Fekete - SZIE version - 2.2 - Szent István Egyetem
PhD Fekete - SZIE version - 2.2 - Szent István Egyetem
PhD Fekete - SZIE version - 2.2 - Szent István Egyetem
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Literature review<br />
2.1.2. Structural build-up of the knee and the major bones<br />
The knee joint is a closed system, built up from ligaments and muscles. This system is generally<br />
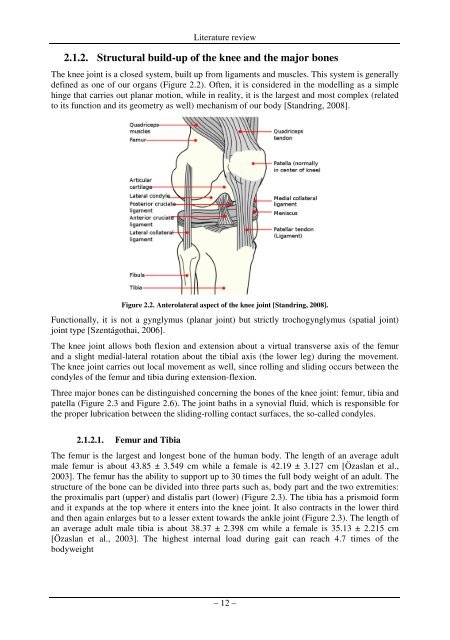
defined as one of our organs (Figure <strong>2.2</strong>). Often, it is considered in the modelling as a simple<br />
hinge that carries out planar motion, while in reality, it is the largest and most complex (related<br />
to its function and its geometry as well) mechanism of our body [Standring, 2008].<br />
Figure <strong>2.2</strong>. Anterolateral aspect of the knee joint [Standring, 2008].<br />
Functionally, it is not a gynglymus (planar joint) but strictly trochogynglymus (spatial joint)<br />
joint type [<strong>Szent</strong>ágothai, 2006].<br />
The knee joint allows both flexion and extension about a virtual transverse axis of the femur<br />
and a slight medial-lateral rotation about the tibial axis (the lower leg) during the movement.<br />
The knee joint carries out local movement as well, since rolling and sliding occurs between the<br />
condyles of the femur and tibia during extension-flexion.<br />
Three major bones can be distinguished concerning the bones of the knee joint: femur, tibia and<br />
patella (Figure 2.3 and Figure 2.6). The joint baths in a synovial fluid, which is responsible for<br />
the proper lubrication between the sliding-rolling contact surfaces, the so-called condyles.<br />
2.1.2.1. Femur and Tibia<br />
The femur is the largest and longest bone of the human body. The length of an average adult<br />
male femur is about 43.85 ± 3.549 cm while a female is 42.19 ± 3.127 cm [Özaslan et al.,<br />
2003]. The femur has the ability to support up to 30 times the full body weight of an adult. The<br />
structure of the bone can be divided into three parts such as, body part and the two extremities:<br />
the proximalis part (upper) and distalis part (lower) (Figure 2.3). The tibia has a prismoid form<br />
and it expands at the top where it enters into the knee joint. It also contracts in the lower third<br />
and then again enlarges but to a lesser extent towards the ankle joint (Figure 2.3). The length of<br />
an average adult male tibia is about 38.37 ± 2.398 cm while a female is 35.13 ± <strong>2.2</strong>15 cm<br />
[Özaslan et al., 2003]. The highest internal load during gait can reach 4.7 times of the<br />
bodyweight<br />
– 12 –