PDF 1.938kB
PDF 1.938kB
PDF 1.938kB
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 5<br />
Results<br />
To better examine the methods presented in Chapter 4 a simulation framework was developed which<br />
allows the modelling of component-based systems with the elements presented in Section 4.3. The<br />
framework was implemented using the Mobile Robot Programming Toolkit (MRPT) 1 which provides<br />
methods to do matrix calculation and to visualize 3D data.<br />
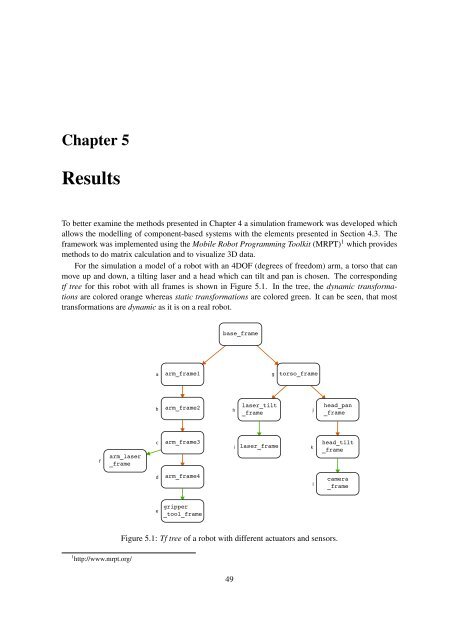
For the simulation a model of a robot with an 4DOF (degrees of freedom) arm, a torso that can<br />
move up and down, a tilting laser and a head which can tilt and pan is chosen. The corresponding<br />
tf tree for this robot with all frames is shown in Figure 5.1. In the tree, the dynamic transformations<br />
are colored orange whereas static transformations are colored green. It can be seen, that most<br />
transformations are dynamic as it is on a real robot.<br />
a<br />
g<br />
b<br />
h<br />
j<br />
c<br />
i<br />
k<br />
f<br />
d<br />
l<br />
e<br />
Figure 5.1: Tf tree of a robot with different actuators and sensors.<br />
1 http://www.mrpt.org/<br />
49