Use of Models and Facility-Level Data in Greenhouse Gas Inventories
Use of Models and Facility-Level Data in Greenhouse Gas Inventories
Use of Models and Facility-Level Data in Greenhouse Gas Inventories
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Use</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Models</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Facility</strong>-<strong>Level</strong> <strong>Data</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Greenhouse</strong> <strong>Gas</strong> <strong>Inventories</strong><br />
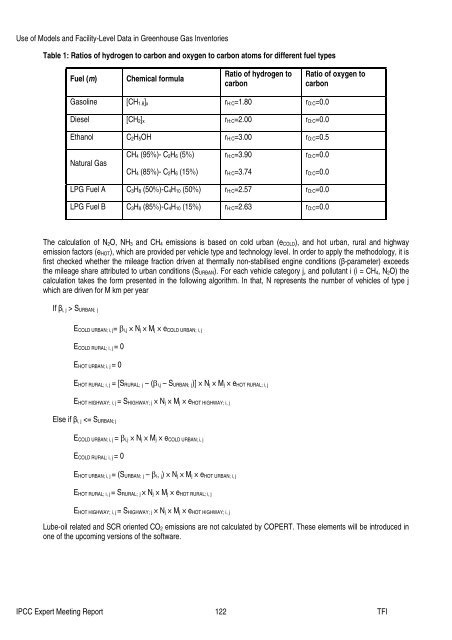
Table 1: Ratios <strong>of</strong> hydrogen to carbon <strong>and</strong> oxygen to carbon atoms for different fuel types<br />
Fuel (m)<br />
Chemical formula<br />
Ratio <strong>of</strong> hydrogen to<br />
carbon<br />
Ratio <strong>of</strong> oxygen to<br />
carbon<br />
<strong>Gas</strong>ol<strong>in</strong>e [CH 1.8] x r H:C=1.80 r O:C=0.0<br />
Diesel [CH 2] x r H:C=2.00 r O:C=0.0<br />
Ethanol C 2H 5OH r H:C=3.00 r O:C=0.5<br />
Natural <strong>Gas</strong><br />
CH 4 (95%)- C 2H 6 (5%) r H:C=3.90 r O:C=0.0<br />
CH 4 (85%)- C 2H 6 (15%) r H:C=3.74 r O:C=0.0<br />
LPG Fuel A C 3H 8 (50%)-C 4H 10 (50%) r H:C=2.57 r O:C=0.0<br />
LPG Fuel B C 3H 8 (85%)-C 4H 10 (15%) r H:C=2.63 r O:C=0.0<br />
The calculation <strong>of</strong> N 2O, NH 3 <strong>and</strong> CH 4 emissions is based on cold urban (e COLD), <strong>and</strong> hot urban, rural <strong>and</strong> highway<br />
emission factors (e HOT), which are provided per vehicle type <strong>and</strong> technology level. In order to apply the methodology, it is<br />
first checked whether the mileage fraction driven at thermally non-stabilised eng<strong>in</strong>e conditions (β-parameter) exceeds<br />
the mileage share attributed to urban conditions (S URBAN). For each vehicle category j, <strong>and</strong> pollutant i (i = CH 4, N 2O) the<br />
calculation takes the form presented <strong>in</strong> the follow<strong>in</strong>g algorithm. In that, N represents the number <strong>of</strong> vehicles <strong>of</strong> type j<br />
which are driven for M km per year<br />
If β i, j > S URBAN; j<br />
E COLD URBAN; i, j= β i,j × N j × M j × e COLD URBAN; i, j<br />
E COLD RURAL; i, j = 0<br />
E HOT URBAN; i, j = 0<br />
E HOT RURAL; i, j = [S RURAL; j – (β i,j – S URBAN; j)] × N j × M j × e HOT RURAL; i, j<br />
E HOT HIGHWAY; i, j = S HIGHWAY; j × N j × M j × e HOT HIGHWAY; i, j<br />
Else if β i, j