FPGA based Hardware Accleration for Elliptic Curve Cryptography ...
FPGA based Hardware Accleration for Elliptic Curve Cryptography ...
FPGA based Hardware Accleration for Elliptic Curve Cryptography ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3.4. FINITE FIELD ARITHMETIC 23<br />
Thus, we can calculate the number of gates of an+ -bit CKM with the following recurrences:<br />
e)'U 3 K+ˆ<br />
6+*<br />
I + 6 c<br />
3 K+ˆ†¦«+ ´ c e('U 8 K+ˆ<br />
6+*<br />
I + 6 c<br />
c:)?þe('U 8 K+ˆ†¦ + ´ c<br />
+¢)Wþe)'pU<br />
<br />
€ 3 K+ˆ<br />
6+* c + 6 c<br />
þ v<br />
<br />
€ 3 K+ˆ†¦«+ ´ c e)'U $ K+ˆ<br />
6+*<br />
I + 6 c<br />
+ _ ¨)?þe)'pU-$PK+ˆ†¦ + ´ c<br />
v<br />
With the master method [19] it can easily be shown that all of these recurrences belong to the complexity<br />
õ7K+¨öø÷Cù 8 class . The ofv<br />
<br />
€ 3 number gates exactly+¨öø÷Cù 8 is . By substituting a 3-input XOR by<br />
e('U 3<br />
two<br />
and a 4-input XOR threee)'pU 3 by gates, an upper bound on requirede('U 3 the count is be given<br />
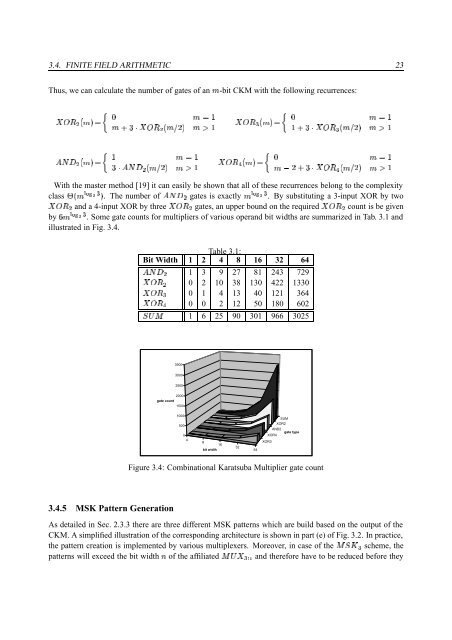
k+Nöø÷Cù 8 by . Some gate counts <strong>for</strong> multipliers of various operand bit widths are summarized in Tab. 3.1 and<br />
illustrated in Fig. 3.4.<br />
v<br />
<br />
€ 3<br />
e('U 3<br />
e('U 8 e('U-$<br />
Table 3.1:<br />
Bit Width 1 2 4 8 16 32 64<br />
1 3 9 27 81 243 729<br />
0 2 10 38 130 422 1330<br />
0 0 2 12 50 180 602<br />
0 1 4 13 40 121 364<br />
,! 1 6 25 90 301 966 3025<br />
3500<br />
3000<br />
2500<br />
2000<br />
gate count<br />
1500<br />
1000<br />
500<br />
0<br />
4<br />
8<br />
16<br />
bit width<br />
32<br />
64<br />
AND2<br />
gate type<br />
XOR4<br />
XOR3<br />
SUM<br />
XOR2<br />
Figure 3.4: Combinational Karatsuba Multiplier gate count<br />
3.4.5 MSK Pattern Generation<br />
As detailed in Sec. 2.3.3 there are three different MSK patterns which are build <strong>based</strong> on the output of the<br />
CKM. A simplified illustration of the corresponding architecture is shown in part (e) of Fig. 3.2. In practice,<br />
the pattern creation is implemented by various multiplexers. Moreover, in case of the& œ" 8<br />
scheme, the<br />
patterns will exceed the bit width( of the affiliated"!ƒe<br />
8 #Y and there<strong>for</strong>e have to be reduced be<strong>for</strong>e they