primary prevention of coeliac disease - Associazione Italiana ...
primary prevention of coeliac disease - Associazione Italiana ...
primary prevention of coeliac disease - Associazione Italiana ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
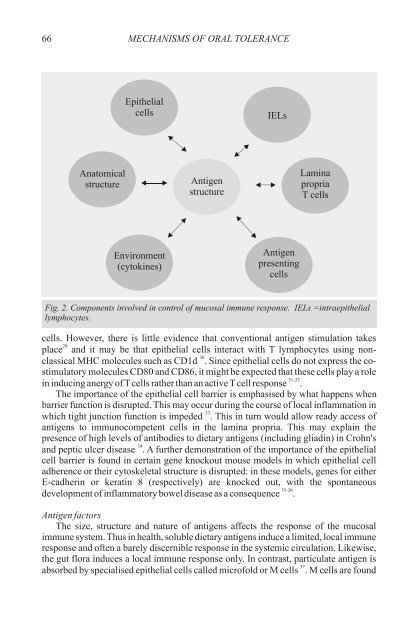
66 MECHANISMS OF ORAL TOLERANCE<br />
Epithelial<br />
cells<br />
IELs<br />
Anatomical<br />
structure<br />
Antigen<br />
structure<br />
Lamina<br />
propria<br />
T cells<br />
Environment<br />
(cytokines)<br />
Antigen<br />
presenting<br />
cells<br />
Fig. 2. Components involved in control <strong>of</strong> mucosal immune response. IELs =intraepithelial<br />
lymphocytes.<br />
cells. However, there is little evidence that conventional antigen stimulation takes<br />
29<br />
place and it may be that epithelial cells interact with T lymphocytes using non-<br />
30<br />
classical MHC molecules such as CD1d . Since epithelial cells do not express the costimulatory<br />
molecules CD80 and CD86, it might be expected that these cells play a role<br />
31-32<br />
in inducing anergy <strong>of</strong> T cells rather than an active T cell response .<br />
The importance <strong>of</strong> the epithelial cell barrier is emphasised by what happens when<br />
barrier function is disrupted. This may occur during the course <strong>of</strong> local inflammation in<br />
33<br />
which tight junction function is impeded . This in turn would allow ready access <strong>of</strong><br />
antigens to immunocompetent cells in the lamina propria. This may explain the<br />
presence <strong>of</strong> high levels <strong>of</strong> antibodies to dietary antigens (including gliadin) in Crohn's<br />
34<br />
and peptic ulcer <strong>disease</strong> . A further demonstration <strong>of</strong> the importance <strong>of</strong> the epithelial<br />
cell barrier is found in certain gene knockout mouse models in which epithelial cell<br />
adherence or their cytoskeletal structure is disrupted: in these models, genes for either<br />
E-cadherin or keratin 8 (respectively) are knocked out, with the spontaneous<br />
35-36<br />
development <strong>of</strong> inflammatory bowel <strong>disease</strong> as a consequence .<br />
Antigen factors<br />
The size, structure and nature <strong>of</strong> antigens affects the response <strong>of</strong> the mucosal<br />
immune system. Thus in health, soluble dietary antigens induce a limited, local immune<br />
response and <strong>of</strong>ten a barely discernible response in the systemic circulation. Likewise,<br />
the gut flora induces a local immune response only. In contrast, particulate antigen is<br />
37<br />
absorbed by specialised epithelial cells called micr<strong>of</strong>old or M cells . M cells are found