primary prevention of coeliac disease - Associazione Italiana ...
primary prevention of coeliac disease - Associazione Italiana ...
primary prevention of coeliac disease - Associazione Italiana ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
76<br />
GENETICALLY DETOXIFIED GRAINS<br />
molecular weight proteins. High-molecular weight proteins (x - and y-type subunits)<br />
comprise the HMW subunits <strong>of</strong> glutenins; glutamine, glycine, and proline represent<br />
70% <strong>of</strong> total residues. Medium-molecular weight group consists <strong>of</strong> w-gliadins; 80% <strong>of</strong><br />
the amino acids is due to glutamine, proline, and phenylalanine, but cysteine and<br />
methionine, i.e. sulphur containing amino acids, are almost absent. Low-molecular<br />
weight proteins consist <strong>of</strong> a-, b-, g-gliadins and LMW subunits <strong>of</strong> glutenins; they are<br />
rich in sulphur containing amino acids.<br />
Functional properties <strong>of</strong> gluten proteins<br />
Although the only known function <strong>of</strong> these proteins is to act as storage proteins, by<br />
releasing nitrogen for the germinating seed, their biochemistry structure has a crucial<br />
2,6<br />
role in providing the unique baking quality <strong>of</strong> wheat . Both LMW and HMW have not<br />
only intrachain but also interchain disulphide bonds allowing them to crosslink other<br />
glutenin and gliadin peptides, which results in the formation <strong>of</strong> beta-spirals. During the<br />
baking process, CO<br />
2<br />
is produced by yeast fermentation and is trapped in the beta-spiral<br />
three dimensional net. Glutenins spirals become extended but maintain the capacity to<br />
return to the colloid state. So, elasticity and cohesivity <strong>of</strong> the dough system are due to<br />
the cross-linked nature <strong>of</strong> the glutenin subunits, mainly the high molecular weight<br />
glutenins. On the other hand, soluble monomeric gliadins guarantee extensibility and<br />
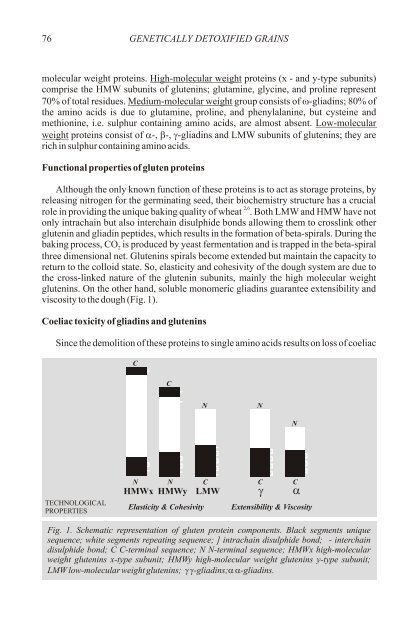
viscosity to the dough (Fig. 1).<br />
Coeliac toxicity <strong>of</strong> gliadins and glutenins<br />
Since the demolition <strong>of</strong> these proteins to single amino acids results on loss <strong>of</strong> <strong>coeliac</strong><br />
C<br />
C<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
TECHNOLOGICAL<br />
PROPERTIES<br />
N N C C C<br />
HMWx HMWy LMW g a<br />
Elasticity & Cohesivity<br />
Extensibility & Viscosity<br />
Fig. 1. Schematic representation <strong>of</strong> gluten protein components. Black segments unique<br />
sequence; white segments repeating sequence; ] intrachain disulphide bond; - interchain<br />
disulphide bond; C C-terminal sequence; N N-terminal sequence; HMWx high-molecular<br />
weight glutenins x-type subunit; HMWy high-molecular weight glutenins y-type subunit;<br />
LMW low-molecular weight glutenins; g-gliadins; a-gliadins.