International Education Guide - Enterprise and Advanced Education ...
International Education Guide - Enterprise and Advanced Education ...
International Education Guide - Enterprise and Advanced Education ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
INTERNATIONAL EDUCATION GUIDE for the assessment of education from the Islamic Republic of Pakistan<br />
.3<br />
The most common first language in Pakistan is Punjabi<br />
(spoken by 44.2 per cent of the population), followed by<br />
Pashto/Pakhtu (15.2 per cent), Sindhi (14.1 per cent),<br />
Siraiki (10.5 per cent), Urdu (7.8 per cent) <strong>and</strong> Balochi<br />
(3.8 per cent). As provincial boundaries are linguistically<br />
based, each of the four provinces has one dominant ethnolinguistic<br />
group:<br />
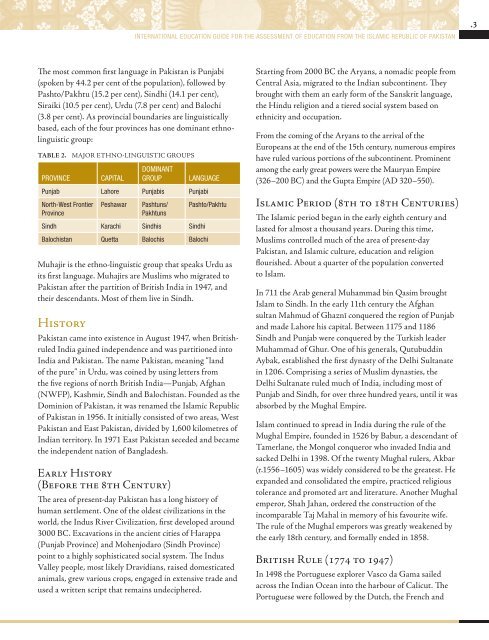
Table 2. Major Ethno-Linguistic Groups<br />
Province<br />
Capital<br />
Dominant<br />
Group<br />
Language<br />
Punjab Lahore Punjabis Punjabi<br />
North-West Frontier<br />
Province<br />
Peshawar<br />
Pashtuns/<br />
Pakhtuns<br />
Sindh Karachi Sindhis Sindhi<br />
Pashto/Pakhtu<br />
Balochistan Quetta Balochis Balochi<br />
Muhajir is the ethno-linguistic group that speaks Urdu as<br />
its first language. Muhajirs are Muslims who migrated to<br />
Pakistan after the partition of British India in 1947, <strong>and</strong><br />
their descendants. Most of them live in Sindh.<br />
History<br />
Pakistan came into existence in August 1947, when Britishruled<br />
India gained independence <strong>and</strong> was partitioned into<br />
India <strong>and</strong> Pakistan. The name Pakistan, meaning “l<strong>and</strong><br />
of the pure” in Urdu, was coined by using letters from<br />
the five regions of north British India—Punjab, Afghan<br />
(NWFP), Kashmir, Sindh <strong>and</strong> Balochistan. Founded as the<br />
Dominion of Pakistan, it was renamed the Islamic Republic<br />
of Pakistan in 1956. It initially consisted of two areas, West<br />
Pakistan <strong>and</strong> East Pakistan, divided by 1,600 kilometres of<br />
Indian territory. In 1971 East Pakistan seceded <strong>and</strong> became<br />
the independent nation of Bangladesh.<br />
Early History<br />
(Before the 8th Century)<br />
The area of present-day Pakistan has a long history of<br />
human settlement. One of the oldest civilizations in the<br />
world, the Indus River Civilization, first developed around<br />
3000 BC. Excavations in the ancient cities of Harappa<br />
(Punjab Province) <strong>and</strong> Mohenjodaro (Sindh Province)<br />
point to a highly sophisticated social system. The Indus<br />
Valley people, most likely Dravidians, raised domesticated<br />
animals, grew various crops, engaged in extensive trade <strong>and</strong><br />
used a written script that remains undeciphered.<br />
Starting from 2000 BC the Aryans, a nomadic people from<br />
Central Asia, migrated to the Indian subcontinent. They<br />
brought with them an early form of the Sanskrit language,<br />
the Hindu religion <strong>and</strong> a tiered social system based on<br />
ethnicity <strong>and</strong> occupation.<br />
From the coming of the Aryans to the arrival of the<br />
Europeans at the end of the 15th century, numerous empires<br />
have ruled various portions of the subcontinent. Prominent<br />
among the early great powers were the Mauryan Empire<br />
(326–200 BC) <strong>and</strong> the Gupta Empire (AD 320–550).<br />
Islamic Period (8th to 18th Centuries)<br />
The Islamic period began in the early eighth century <strong>and</strong><br />
lasted for almost a thous<strong>and</strong> years. During this time,<br />
Muslims controlled much of the area of present-day<br />
Pakistan, <strong>and</strong> Islamic culture, education <strong>and</strong> religion<br />
flourished. About a quarter of the population converted<br />
to Islam.<br />
In 711 the Arab general Muhammad bin Qasim brought<br />
Islam to Sindh. In the early 11th century the Afghan<br />
sultan Mahmud of Ghaznī conquered the region of Punjab<br />
<strong>and</strong> made Lahore his capital. Between 1175 <strong>and</strong> 1186<br />
Sindh <strong>and</strong> Punjab were conquered by the Turkish leader<br />
Muhammad of Ghur. One of his generals, Qutubuddin<br />
Aybak, established the first dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate<br />
in 1206. Comprising a series of Muslim dynasties, the<br />
Delhi Sultanate ruled much of India, including most of<br />
Punjab <strong>and</strong> Sindh, for over three hundred years, until it was<br />
absorbed by the Mughal Empire.<br />
Islam continued to spread in India during the rule of the<br />
Mughal Empire, founded in 1526 by Babur, a descendant of<br />
Tamerlane, the Mongol conqueror who invaded India <strong>and</strong><br />
sacked Delhi in 1398. Of the twenty Mughal rulers, Akbar<br />
(r.1556–1605) was widely considered to be the greatest. He<br />
exp<strong>and</strong>ed <strong>and</strong> consolidated the empire, practiced religious<br />
tolerance <strong>and</strong> promoted art <strong>and</strong> literature. Another Mughal<br />
emperor, Shah Jahan, ordered the construction of the<br />
incomparable Taj Mahal in memory of his favourite wife.<br />
The rule of the Mughal emperors was greatly weakened by<br />
the early 18th century, <strong>and</strong> formally ended in 1858.<br />
British Rule (1774 to 1947)<br />
In 1498 the Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama sailed<br />
across the Indian Ocean into the harbour of Calicut. The<br />
Portuguese were followed by the Dutch, the French <strong>and</strong>