Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
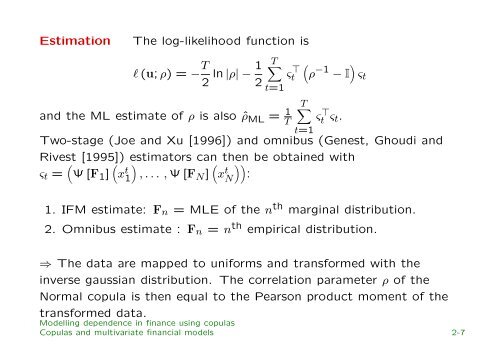
Estimation<br />
The log-likelihood function is<br />
l (u; ρ) = − T 2 ln |ρ| − 1 2<br />
T∑<br />
ςt<br />
⊤<br />
t=1<br />
(<br />
ρ −1 − I ) ς t<br />
and the ML estimate of ρ is also ˆρ ML = 1 T<br />
T∑<br />
t=1<br />
ς ⊤ t ς t.<br />
Two-stage (Joe and Xu [1996]) and omnibus (Genest, Ghoudi and<br />
Rivest [1995]) estimators can then be obta<strong>in</strong>ed with<br />
ς t = ( Ψ [F 1 ]<br />
(<br />
x<br />
t<br />
1<br />
)<br />
, . . . , Ψ [FN ]<br />
(<br />
x<br />
t<br />
N<br />
))<br />
:<br />
1. IFM estimate: F n = MLE of the n th marg<strong>in</strong>al distribution.<br />
2. Omnibus estimate : F n = n th empirical distribution.<br />
⇒ The data are mapped to uniforms and transformed with the<br />
<strong>in</strong>verse gaussian distribution. The correlation parameter ρ of the<br />
Normal copula is then equal to the Pearson product moment of the<br />
transformed data.<br />
<strong>Modell<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>dependence</strong> <strong>in</strong> f<strong>in</strong>ance us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>copulas</strong><br />
Copulas and multivariate f<strong>in</strong>ancial models 2-7