Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
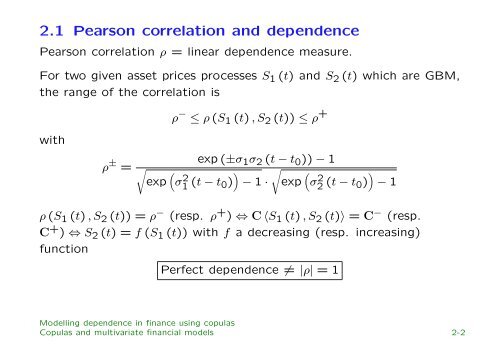
2.1 Pearson correlation and <strong>dependence</strong><br />
Pearson correlation ρ = l<strong>in</strong>ear <strong>dependence</strong> measure.<br />
For two given asset prices processes S 1 (t) and S 2 (t) which are GBM,<br />
the range of the correlation is<br />
ρ − ≤ ρ (S 1 (t) , S 2 (t)) ≤ ρ +<br />
with<br />
ρ ± =<br />
exp (±σ 1 σ 2 (t − t 0 )) − 1<br />
√<br />
exp ( σ1 2 (t − t ) √<br />
0) − 1 · exp ( σ2 2 (t − t 0))<br />
− 1<br />
ρ (S 1 (t) , S 2 (t)) = ρ − (resp. ρ + ) ⇔ C 〈S 1 (t) , S 2 (t)〉 = C − (resp.<br />
C + ) ⇔ S 2 (t) = f (S 1 (t)) with f a decreas<strong>in</strong>g (resp. <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
function<br />
Perfect <strong>dependence</strong> ≠ |ρ| = 1<br />
<strong>Modell<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>dependence</strong> <strong>in</strong> f<strong>in</strong>ance us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>copulas</strong><br />
Copulas and multivariate f<strong>in</strong>ancial models 2-2