Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
Modelling dependence in finance using copulas - Thierry Roncalli's ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
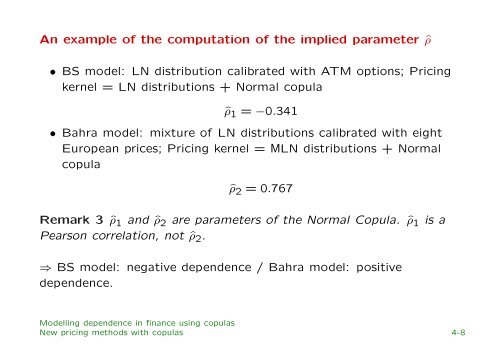
An example of the computation of the implied parameter ˆρ<br />
• BS model: LN distribution calibrated with ATM options; Pric<strong>in</strong>g<br />
kernel = LN distributions + Normal copula<br />
ˆρ 1 = −0.341<br />
• Bahra model: mixture of LN distributions calibrated with eight<br />
European prices; Pric<strong>in</strong>g kernel = MLN distributions + Normal<br />
copula<br />
ˆρ 2 = 0.767<br />
Remark 3 ˆρ 1 and ˆρ 2 are parameters of the Normal Copula. ˆρ 1 is a<br />
Pearson correlation, not ˆρ 2 .<br />
⇒ BS model: negative <strong>dependence</strong> / Bahra model: positive<br />
<strong>dependence</strong>.<br />
<strong>Modell<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>dependence</strong> <strong>in</strong> f<strong>in</strong>ance us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>copulas</strong><br />
New pric<strong>in</strong>g methods with <strong>copulas</strong> 4-8