<strong>Cyber</strong> <strong>Security</strong> <strong>Monitoring</strong> and Logging <strong>Guide</strong>Logs and other sources that can be potential indicators of compromise (also known as triggers, alerts or alarms) willbe either (or both):• Precursors, which are signs that an incident may occur in the future• Indicators, which are signs that an incident may have occurred or be occurring now.Examples of possible cyber security incidentsPrecursors can include:• Web server log entries that show the usage of a vulnerabilityscanner• An announcement of a new exploit that targets a vulnerability ofthe organisation’s mail server• A threat from a group stating that the group will attack theorganisation.Indicators (there are many) can include:• A network intrusion detection sensor alerts when a buffer overflowattempt occurs against a database server• Antivirus software alerts when it detects that a host is infected withmalware• A system administrator sees a filename with unusual characters• A host records an auditing configuration change in its log• An application logs multiple failed login attempts from an unfamiliarremote system• An email administrator sees a large number of bounced emails withsuspicious content• A network administrator notices an unusual deviation from typicalnetwork traffic flows.The sources of these signs include…..• <strong>Security</strong> software (eg. IDS, IPS, DLP,SIEM, antivirus and spam software,file integrity checking software,monitoring services (often provided bya third party))• Logs (eg. operating system logs,service and application logs, networkdevice logs and network flows)• Publicly available information(eg. information on new exploits,information exchange groups, thirdparty organisations, governments)• People from within your organisation• Third parties (eg. customers,suppliers, IT providers, ISPs, partners;government bodies).Sources of IOCsThere are many different sources of data that relate to IOCs, which include:• <strong>Security</strong> software (eg. IDS, IPS, DLP, SIEM, antivirus and spam software, file integrity checking software, andmonitoring services (often provided by a third party))• Tools that employ potential malware isolation and investigation techniques (eg. sandboxing or virtualexecution engines)• Logs (eg. operating system logs, service and application logs, network device logs and network flows)• Publicly available information (eg. information on new exploits, information exchange groups, third partyorganisations, governments)• People from within your organisation• Third parties (eg. customers, suppliers, IT providers, ISPs, partners; government bodies).Workshop participants identified a range of publicly available sources of data that can be used in conjunction withcyber security events to help identify indicators of compromise (IOC), evaluating the purpose, likely criticality and costof each source.The results of this analysis are presented in the table on page 31 (in descending order of criticality), together withtheir purpose, criticality and relative cost.30
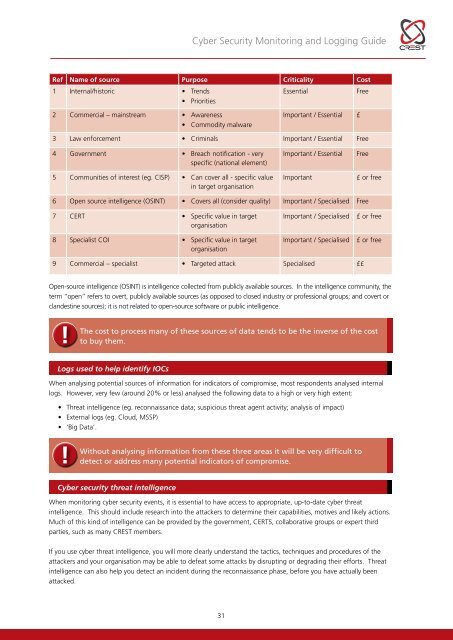
<strong>Cyber</strong> <strong>Security</strong> <strong>Monitoring</strong> and Logging <strong>Guide</strong>Ref Name of source Purpose Criticality Cost1 Internal/historic • TrendsEssentialFree• Priorities2 Commercial – mainstream • Awareness• Commodity malwareImportant / Essential £3 Law enforcement • Criminals Important / Essential Free4 Government • Breach notification - veryspecific (national element)5 Communities of interest (eg. CISP) • Can cover all - specific valuein target organisationImportant / EssentialImportantFree£ or free6 Open source intelligence (OSINT) • Covers all (consider quality) Important / Specialised Free7 CERT • Specific value in targetorganisation8 Specialist COI • Specific value in targetorganisationImportant / SpecialisedImportant / Specialised£ or free£ or free9 Commercial – specialist • Targeted attack Specialised ££Open-source intelligence (OSINT) is intelligence collected from publicly available sources. In the intelligence community, theterm “open” refers to overt, publicly available sources (as opposed to closed industry or professional groups; and covert orclandestine sources); it is not related to open-source software or public intelligence.!The cost to process many of these sources of data tends to be the inverse of the costto buy them.Logs used to help identify IOCsWhen analysing potential sources of information for indicators of compromise, most respondents analysed internallogs. However, very few (around 20% or less) analysed the following data to a high or very high extent:• Threat intelligence (eg. reconnaissance data; suspicious threat agent activity; analysis of impact)• External logs (eg. Cloud, MSSP)• ‘Big Data’.!Without analysing information from these three areas it will be very difficult todetect or address many potential indicators of compromise.<strong>Cyber</strong> security threat intelligenceWhen monitoring cyber security events, it is essential to have access to appropriate, up-to-date cyber threatintelligence. This should include research into the attackers to determine their capabilities, motives and likely actions.Much of this kind of intelligence can be provided by the government, CERTS, collaborative groups or expert thirdparties, such as many CREST members.If you use cyber threat intelligence, you will more clearly understand the tactics, techniques and procedures of theattackers and your organisation may be able to defeat some attacks by disrupting or degrading their efforts. Threatintelligence can also help you detect an incident during the reconnaissance phase, before you have actually beenattacked.31