2.1 Overview of the Proposed Project - Keystone XL pipeline - US ...
2.1 Overview of the Proposed Project - Keystone XL pipeline - US ...
2.1 Overview of the Proposed Project - Keystone XL pipeline - US ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
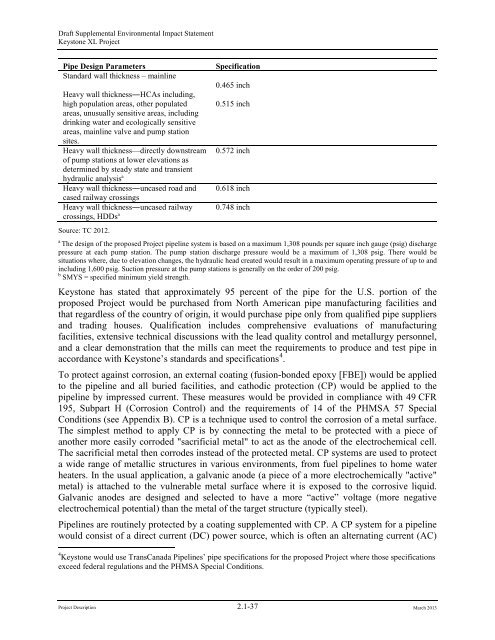
Draft Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement<strong>Keystone</strong> <strong>XL</strong> <strong>Project</strong>Pipe Design ParametersStandard wall thickness – mainlineHeavy wall thickness―HCAs including,high population areas, o<strong>the</strong>r populatedareas, unusually sensitive areas, includingdrinking water and ecologically sensitiveareas, mainline valve and pump stationsites.Heavy wall thickness—directly downstream<strong>of</strong> pump stations at lower elevations asdetermined by steady state and transienthydraulic analysis aHeavy wall thickness―uncased road andcased railway crossingsHeavy wall thickness―uncased railwaycrossings, HDDs aSource: TC 2012.Specification0.465 inch0.515 inch0.572 inch0.618 inch0.748 inchaThe design <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> proposed <strong>Project</strong> <strong>pipeline</strong> system is based on a maximum 1,308 pounds per square inch gauge (psig) dischargepressure at each pump station. The pump station discharge pressure would be a maximum <strong>of</strong> 1,308 psig. There would besituations where, due to elevation changes, <strong>the</strong> hydraulic head created would result in a maximum operating pressure <strong>of</strong> up to andincluding 1,600 psig. Suction pressure at <strong>the</strong> pump stations is generally on <strong>the</strong> order <strong>of</strong> 200 psig.bSMYS = specified minimum yield strength.<strong>Keystone</strong> has stated that approximately 95 percent <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> pipe for <strong>the</strong> U.S. portion <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>proposed <strong>Project</strong> would be purchased from North American pipe manufacturing facilities andthat regardless <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> country <strong>of</strong> origin, it would purchase pipe only from qualified pipe suppliersand trading houses. Qualification includes comprehensive evaluations <strong>of</strong> manufacturingfacilities, extensive technical discussions with <strong>the</strong> lead quality control and metallurgy personnel,and a clear demonstration that <strong>the</strong> mills can meet <strong>the</strong> requirements to produce and test pipe inaccordance with <strong>Keystone</strong>’s standards and specifications 4 .To protect against corrosion, an external coating (fusion-bonded epoxy [FBE]) would be appliedto <strong>the</strong> <strong>pipeline</strong> and all buried facilities, and cathodic protection (CP) would be applied to <strong>the</strong><strong>pipeline</strong> by impressed current. These measures would be provided in compliance with 49 CFR195, Subpart H (Corrosion Control) and <strong>the</strong> requirements <strong>of</strong> 14 <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> PHMSA 57 SpecialConditions (see Appendix B). CP is a technique used to control <strong>the</strong> corrosion <strong>of</strong> a metal surface.The simplest method to apply CP is by connecting <strong>the</strong> metal to be protected with a piece <strong>of</strong>ano<strong>the</strong>r more easily corroded "sacrificial metal" to act as <strong>the</strong> anode <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> electrochemical cell.The sacrificial metal <strong>the</strong>n corrodes instead <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> protected metal. CP systems are used to protecta wide range <strong>of</strong> metallic structures in various environments, from fuel <strong>pipeline</strong>s to home waterheaters. In <strong>the</strong> usual application, a galvanic anode (a piece <strong>of</strong> a more electrochemically "active"metal) is attached to <strong>the</strong> vulnerable metal surface where it is exposed to <strong>the</strong> corrosive liquid.Galvanic anodes are designed and selected to have a more “active” voltage (more negativeelectrochemical potential) than <strong>the</strong> metal <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> target structure (typically steel).Pipelines are routinely protected by a coating supplemented with CP. A CP system for a <strong>pipeline</strong>would consist <strong>of</strong> a direct current (DC) power source, which is <strong>of</strong>ten an alternating current (AC)4 <strong>Keystone</strong> would use TransCanada Pipelines’ pipe specifications for <strong>the</strong> proposed <strong>Project</strong> where those specificationsexceed federal regulations and <strong>the</strong> PHMSA Special Conditions.<strong>Project</strong> Description <strong>2.1</strong>-37 March 2013