Deliverable D 1.3 RESULTS OF META-ANALYSIS ... - cast-eu.org
Deliverable D 1.3 RESULTS OF META-ANALYSIS ... - cast-eu.org
Deliverable D 1.3 RESULTS OF META-ANALYSIS ... - cast-eu.org
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
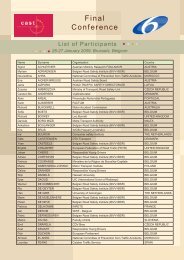
Campaigns and awareness raising strategies in traffic safety — <strong>Deliverable</strong> D-1.1In meta-analysis, then, the odds ratio is treated in two ways: (i) it istransformed to its natural logarithm, and (ii) it assigned a weight. A weight iscalculated for each individual effect using the formula 29 :1/(1/[n before campaign] + 1/[n after campaign] + 1/[control n before campaign] + 1/[control nafter campaign])Thus the greater the number of accident counts the effect is based on, thegreater the weight assigned to the effect. A final weighted effect is thenobtained by simply multiplying the ln odds ratio by the weight.Once a weighted effect has been obtained for each individual effect in a set ofeffects, an overall effect for the set is calculated by dividing the sum of theindividual weighted effects by the sum of the individual weights, and theninversing the natural logarithm to obtain the overall effect in terms of theoriginal odds ratio, which can then be converted to a percentage effect, asdescribed above.In this way, we calculated that the overall weighted effect of road safetycampaigns on accident counts according to the effects extracted from thestudies retrieved is a statistically significant reduction of 10%. The result ispresented in Table 7.17.Table 7.17 Overall effect of road safety campaigns on road accidents according to the effects extractedfrom the studies identified.Groupeffect(%)95%confidenceinterval (%)Significant?(p < 0.05)All accident effects (n = 115) - 10 (- 11 -10) yesStep 2 & 3. Publication biasThe overall effect reported is dependent on the effects extracted from thestudies retrieved. It is a valid concern that these studies do not represent thetrue overall effect. Although we have tried to obtain unpublished studies wherepossible, most of the studies included in the database are published. Theconcern is therefore that our overall effects are influenced by publication bias,a tendency for authors to publish only favourable effects and not to publishunfavourable ones. If there is publication bias, the magnitude of the overalleffects reported here may be too great.One way to observe publication bias is to plot the weight of each effect, whichas we have seen can be considered as the relative number of participants orcounts in that study, against the effect size, as shown in Figure 7.1. It isreasonable to assume that the individual effects in such a plot should be29 The reader might appreciate the anomaly that where there are no control data, greaterweight is assigned. However, an adjustment is made for this by doubling the weightdenominators for non-controlled effects.66