Bariatric treatments for adult obesity - Institute of Health Economics
Bariatric treatments for adult obesity - Institute of Health Economics
Bariatric treatments for adult obesity - Institute of Health Economics
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
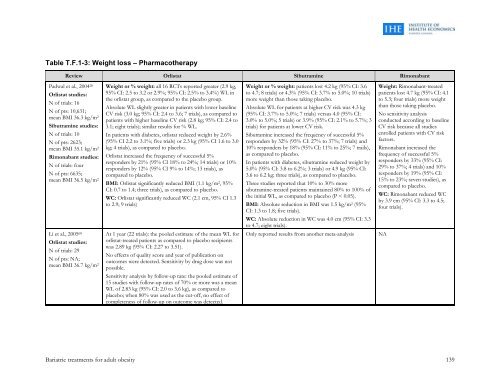
Table T.F.1-3: Weight loss – PharmacotherapyReview Orlistat Sibutramine RimonabantPadwal et al., 2004 20Orlistat studies:N <strong>of</strong> trials: 16N <strong>of</strong> pts: 10,631;mean BMI 36.3 kg/m 2Sibutramine studies:N <strong>of</strong> trials: 10N <strong>of</strong> pts: 2623;mean BMI 35.1 kg/m 2Rimonabant studies:N <strong>of</strong> trials: fourN <strong>of</strong> pts: 6635;mean BMI 36.5 kg/m 2Weight or % weight: all 16 RCTs reported greater (2.9 kg,95% CI: 2.5 to 3.2 or 2.9%; 95% CI: 2.5% to 3.4%) WL inthe orlistat group, as compared to the placebo group.Absolute WL slightly greater in patients with lower baselineCV risk (3.0 kg; 95% CI: 2.4 to 3.6; 7 trials), as compared topatients with higher baseline CV risk (2.8 kg; 95% CI: 2.4 to3.1; eight trials); similar results <strong>for</strong> % WL.In patients with diabetes, orlistat reduced weight by 2.6%(95% CI 2.2 to 3.1%; five trials) or 2.3 kg (95% CI 1.6 to 3.0kg; 4 trials), as compared to placebo.Orlistat increased the frequency <strong>of</strong> successful 5%responders by 21% (95% CI 18% to 24%; 14 trials) or 10%responders by 12% (95% CI 9% to 14%; 13 trials), ascompared to placebo.BMI: Orlistat significantly reduced BMI (1.1 kg/m 2 , 95%CI: 0.7 to 1.4; three trials), as compared to placebo.WC: Orlistat significantly reduced WC (2.1 cm, 95% CI 1.3to 2.9; 9 trials)Weight or % weight: patients lost 4.2 kg (95% CI: 3.6to 4.7; 8 trials) or 4.3% (95% CI: 3.7% to 5.0%; 10 trials)more weight than those taking placebo.Absolute WL <strong>for</strong> patients at higher CV risk was 4.3 kg(95% CI: 3.7% to 5.0%; 7 trials) versus 4.0 (95% CI:3.0% to 5.0%; 5 trials) or 3.9% (95% CI: 2.1% to 5.7%; 3trials) <strong>for</strong> patients at lower CV risk.Sibutramine increased the frequency <strong>of</strong> successful 5%responders by 32% (95% CI: 27% to 37%; 7 trials) and10% responders by 18% (95% CI: 11% to 25%; 7 trails),as compared to placebo.In patients with diabetes, sibutramine reduced weight by5.0% (95% CI: 3.8 to 6.2%; 3 trials) or 4.9 kg (95% CI:3.6 to 6.2 kg; three trials), as compared to placebo.Three studies reported that 10% to 30% moresibutramine-treated patients maintained 80% to 100% <strong>of</strong>the initial WL, as compared to placebo (P < 0.05).BMI: Absolute reduction in BMI was 1.5 kg/m 2 (95%CI: 1.3 to 1.8; five trials).WC: Absolute reduction in WC was 4.0 cm (95% CI: 3.3to 4.7; eight trials).Weight: Rimonabant-treatedpatients lost 4.7 kg (95% CI: 4.1to 5.3; four trials) more weightthan those taking placebo.No sensitivity analysisconducted according to baselineCV risk because all studiesenrolled patients with CV riskfactors.Rimonabant increased thefrequency <strong>of</strong> successful 5%responders by 33% (95% CI:29% to 37%; 4 trials) and 10%responders by 19% (95% CI:15% to 23%; seven studies), ascompared to placebo.WC: Rimonabant reduced WCby 3.9 cm (95% CI: 3.3 to 4.5;four trials).Li et al., 2005 60Orlistat studies:N <strong>of</strong> trials: 29N <strong>of</strong> pts: NA;mean BMI 36.7 kg/m 2At 1 year (22 trials): the pooled estimate <strong>of</strong> the mean WL <strong>for</strong>orlistat-treated patients as compared to placebo recipientswas 2.89 kg (95% CI: 2.27 to 3.51).No effects <strong>of</strong> quality score and year <strong>of</strong> publication onoutcomes were detected. Sensitivity by drug dose was notpossible.Sensitivity analysis by follow-up rate: the pooled estimate <strong>of</strong>15 studies with follow-up rates <strong>of</strong> 70% or more was a meanWL <strong>of</strong> 2.83 kg (95% CI: 2.0 to 3.6 kg), as compared toplacebo; when 80% was used as the cut-<strong>of</strong>f, no effect <strong>of</strong>completeness <strong>of</strong> follow-up on outcome was detected.Only reported results from another meta-analysisNA<strong>Bariatric</strong> <strong>treatments</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>adult</strong> <strong>obesity</strong> 139