The Art of Practical and Precise Strain Based ... - Webprofile.info
The Art of Practical and Precise Strain Based ... - Webprofile.info
The Art of Practical and Precise Strain Based ... - Webprofile.info
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
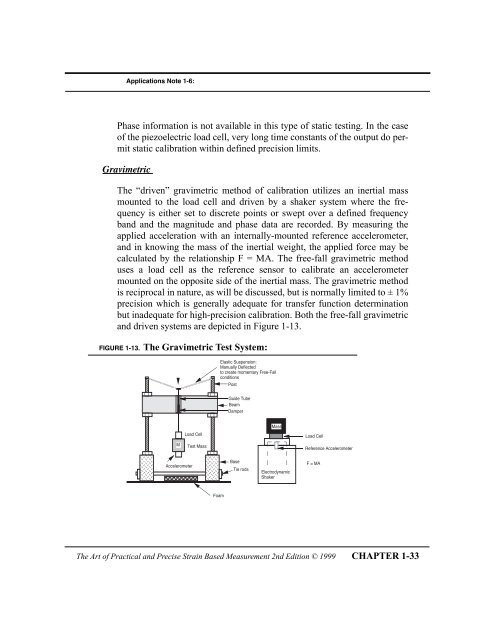
Applications Note 1-6:Phase <strong>info</strong>rmation is not available in this type <strong>of</strong> static testing. In the case<strong>of</strong> the piezoelectric load cell, very long time constants <strong>of</strong> the output do permitstatic calibration within defined precision limits.Gravimetric<strong>The</strong> ÒdrivenÓ gravimetric method <strong>of</strong> calibration utilizes an inertial massmounted to the load cell <strong>and</strong> driven by a shaker system where the frequencyis either set to discrete points or swept over a defined frequencyb<strong>and</strong> <strong>and</strong> the magnitude <strong>and</strong> phase data are recorded. By measuring theapplied acceleration with an internally-mounted reference accelerometer,<strong>and</strong> in knowing the mass <strong>of</strong> the inertial weight, the applied force may becalculated by the relationship F = MA. <strong>The</strong> free-fall gravimetric methoduses a load cell as the reference sensor to calibrate an accelerometermounted on the opposite side <strong>of</strong> the inertial mass. <strong>The</strong> gravimetric methodis reciprocal in nature, as will be discussed, but is normally limited to ± 1%precision which is generally adequate for transfer function determinationbut inadequate for high-precision calibration. Both the free-fall gravimetric<strong>and</strong> driven systems are depicted in Figure 1-13.FIGURE 1-13. <strong>The</strong> Gravimetric Test System: Load Cell M Test Mass Accelerometer Elastic Suspension:Manually Deflectedto create momentary Free-FallconditionsPostGuide TubeBeamDamperBaseTie rodsMassElectrodynamicShakerLoad CellReference AccelerometerF = MAFoam<strong>The</strong> <strong>Art</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Practical</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Precise</strong> <strong>Strain</strong> <strong>Based</strong> Measurement 2nd Edition © 1999 CHAPTER 1-33