World Bank Document
World Bank Document
World Bank Document
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
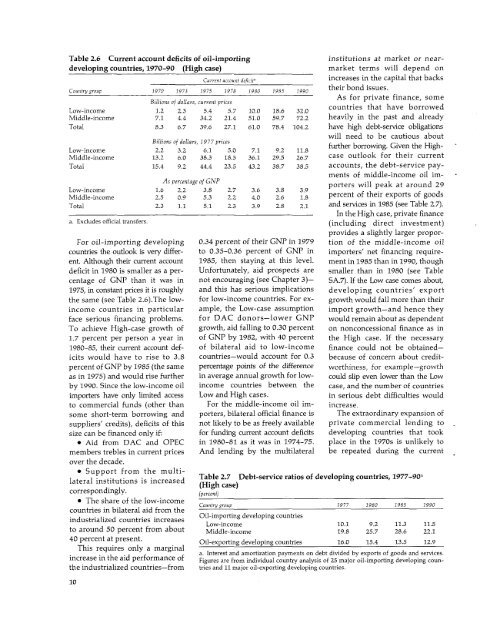
Table 2.6 Current account deficits of oil-importing institutions at market or neardevelopingcountries, 1970-90 (High case) market terms will depend onCurrent account deficit" increases in the capital that backsCountry group 1970 1973 1975 1978 1980 1985 1990 their bond issues.Billions of dollars, current pricesAs for private finance, someLow-income 1.2 2.3 5.4 5.7 10.0 18.6 32.0Middle-income 7.1 4.4 34.2 21.4 51.0 59.7 72.2countries that have borrowedheavily in the past and alreadyTotal 8.3 6.7 39.6 27.1 61.0 78.4 104.2 have high debt-service obligationswill need to be cautious aboutBillions 977 pricesfurther o dollars,borrowing. Given the High-Low-income 2.2 3.2 6.1 5.0 7.1 9.2 11.8Middle-income 13.2 6.0 38.3 18.5 36.1 29.5 26.7 case outlook for their currentTotal 15.4 9.2 44.4 23.5 43.2 38.7 38.5 accounts, the debt-service paymentsAs percentage ofGNP of middle-income oil im-porters will peak at around 29Low-incomeMiddle-income1.62.52.20.93.85.32.72.23.64.03.82.63.91.8 percent of their exports of goodsTotal 2.3 1.1 5.1 2.3 3.9 2.8 2.1 and services in 1985 (see Table 2.7).In the High case, private financea. Excludes official transfers. (including direct investment)provides a slightly larger propor-For oil-importing developing 0.34 percent of their GNP in 1979 tion of the middle-income oilcountries the outlook is very differ- to 0.35-0.36 percent of GNP in importers' net financing requireent.Although their current account 1985, then staying at this level. ment in 1985 than in 1990, thoughdeficit in 1980 is smaller as a per- Unfortunately, aid prospects are smaller than in 1980 (see Tablecentage of GNP than it was in not encouraging (see Chapter 3)- SA.7). If the Low case comes about,1975, in constant prices it is roughly and this has serious implications developing countries' exportthe same (see Table 2.6).The low- for low-income countries. For ex- growth would fall more than theirincome countries in particular ample, the Low-case assumption import growth-and hence theyface serious financing problems. for DAC donors-lower GNP would remain about as dependentTo achieve High-case growth of growth, aid falling to 0.30 percent on nonconcessional finance as in1.7 percent per person a year in of GNP by 1982, with 40 percent the High case. If the necessary1980-85, their current account def- of bilateral aid to low-income finance could not be obtainedicitswould have to rise to 3.8 countries-would account for 0.3 because of concern about creditpercentof GNP by 1985 (the same percentage points of the difference worthiness, for example-growthas in 1975) and would rise further in average annual growth for low- could slip even lower than the Lowby 1990. Since the low-income oil income countries between the case, and the number of countriesimporters have only limited access Low and High cases. in serious debt difficulties wouldto commercial funds (other than For the middle-income oil im- increase.some short-term borrowing and porters, bilateral official finance is The extraordinary expansion ofsuppliers' credits), deficits of this not likely to be as freely available private commercial lending tosize can be financed only if: for funding current account deficits developing countries that took* Aid from DAC and OPEC in 1980-81 as it was in 1974-75. place in the 1970s is unlikely tomembers trebles in current prices And lending by the multilateral be repeated during the currentover the decade.* Support from the multilateralinstitutions lateal nsttutons is s increased icresed Table (High 2.7 case) Debt-service ratios of developing countries, 1977-90ucorrespondingly.(percent)* The share of the low-income Countrygroup 1977 1980 1985 1990countries in bilateral aid from theindustrialized countries increases Oil-importing developing countriesLow-income 10.1 9.2 11.3 11.5to around 50 percent from about Middle-income 19.8 25.7 28.6 22.140 percent at present. Oil-exporting developing countries 16.0 15.4 13.5 12.9This requires only a marginala. Interest and amortization payments on debt divided by exports of goods and services.increase in the aid performance of Figures are from individual country analysis of 25 major oil-importing developing countheindustrialized countries-from tries and 11 major oil-exporting developing countries.10