- Page 1: t' 8 ~~~~ottoWorld Development Repo
- Page 4 and 5: Oc 1980 by the International Bankfo
- Page 6 and 7: ivThis report was prepared by a tea
- Page 8 and 9: Text tables2.1 Summary of prospects
- Page 10 and 11: DefinitionsCountry groups in the an
- Page 12 and 13: illion people have barely enough fa
- Page 14: in official aid and other capital a
- Page 17 and 18: production and consumption; in- Tab
- Page 19 and 20: measures can raise efficiency fairl
- Page 21 and 22: adjustment; but the increases pro-
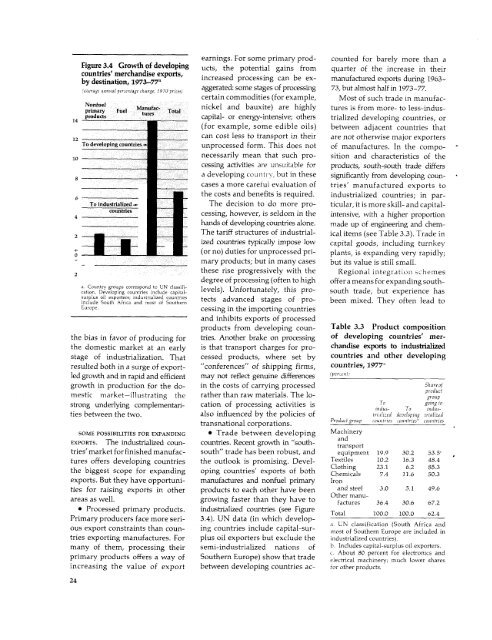
- Page 23 and 24: dustrialized countries' GNP would T
- Page 25 and 26: windfalls, some of their extra cont
- Page 27 and 28: e done to increase the supplies Lat
- Page 29 and 30: exchange-rate depreciation, by perc
- Page 31 and 32: Table 3.2 World merchandise trade,
- Page 33: * Inward-looking policies may exper
- Page 37 and 38: cause individual banks or bank- Tab
- Page 39 and 40: to GNP, of all large industrial na-
- Page 41 and 42: in Chapter 2). Ways of increasing a
- Page 43 and 44: 4 Poverty, growth and human develop
- Page 45 and 46: expectancy was less than 50 years,
- Page 47 and 48: population density (see page 39). e
- Page 49 and 50: ably could not have been achieved c
- Page 51 and 52: ution of income typically is less T
- Page 53 and 54: Table 4.2 Irrigation and income, se
- Page 55 and 56: ment strategies that assume that in
- Page 57 and 58: average 40 percent drop out before
- Page 59 and 60: this may be offset by shifts in the
- Page 61 and 62: UNESCO concluded that the poorUnemp
- Page 63 and 64: A typical finding showed the mean o
- Page 65 and 66: Table5.6 Differences in life tend t
- Page 67 and 68: are more expensive and less critica
- Page 69 and 70: per hos pital and clinic, and to st
- Page 71 and 72: peaks in farm work and widespreadin
- Page 73 and 74: confined to particular places. In A
- Page 75 and 76: Indonesia, Colombia and Chilehave r
- Page 77 and 78: (which respond only gradually to cu
- Page 79 and 80: Contraceptive technologyresearch in
- Page 81 and 82: 6 Implementing human development pr
- Page 83 and 84: probably China-have managed Table 6
- Page 85 and 86:
percent of the development bud- dev
- Page 87 and 88:
members, too, as no bureaucraticRur
- Page 89 and 90:
Private costs of using public servi
- Page 91 and 92:
ut not teachers or health workers,
- Page 93 and 94:
7 Priorities and progress in region
- Page 95 and 96:
literacy and life expectancy); andF
- Page 97 and 98:
to establish the necessary admin-Fi
- Page 99 and 100:
Poverty Figure 7.5 South Asia: life
- Page 101 and 102:
and North Africa cover the spec- gr
- Page 103 and 104:
The high level of urbanization well
- Page 105 and 106:
Chaipter 8 Summary and conclusionsI
- Page 107 and 108:
is high, frequently well above that
- Page 109 and 110:
Stat.istical appendix to Part ITabl
- Page 111 and 112:
Table SA.6 Capital flows and debt o
- Page 113 and 114:
Montgomery survey administra- publi
- Page 115 and 116:
AnnexWorldDevelopmentIndicators
- Page 117 and 118:
Table 13. Balance of Payments and D
- Page 119 and 120:
IntroductionThe World Development I
- Page 121 and 122:
GNP per capitaAverage indexAverageo
- Page 123 and 124:
Average annual growth rate (percent
- Page 125 and 126:
Distribution of gross domestic prod
- Page 127 and 128:
Average annual growth rate (percent
- Page 129 and 130:
Distribution of gross domestic prod
- Page 131 and 132:
Distribution of value added (percen
- Page 133 and 134:
EnergyEnergyconsumptionAverage annu
- Page 135 and 136:
Merchandise tradeAverage annual gro
- Page 137 and 138:
Percentage share of merchandise exp
- Page 139 and 140:
Percentage share of merchandise imp
- Page 141 and 142:
Destination of merchandise exports
- Page 143 and 144:
Destination of manufactured exports
- Page 145 and 146:
Current accountbalance before Inter
- Page 147 and 148:
Public and publicly guaranteed medi
- Page 149 and 150:
External public debtoutstanding and
- Page 151 and 152:
Amount1981a 1982a 1983a 1984a 1985a
- Page 153 and 154:
Average annualHypotheticalgrowth of
- Page 155 and 156:
PercentageCrude Crude Percentage Pe
- Page 157 and 158:
Percentage ofpopulation ofworking a
- Page 159 and 160:
Percentage of urban population Numb
- Page 161 and 162:
Life Infant Childexpectancy mortali
- Page 163 and 164:
PercentageDaily calorie supplyPopul
- Page 165 and 166:
Number Numberenrolled in enrolled i
- Page 167 and 168:
Percentage share of household incom
- Page 169 and 170:
Average index Tables 4 and 5. Growt
- Page 171 and 172:
28 (minerals, crude fertilizers and
- Page 173 and 174:
continues to grow after replacement
- Page 175 and 176:
posttax income and conceptually tic
- Page 180:
-~~~ S-~~~~~ sEuropean Office:66, a