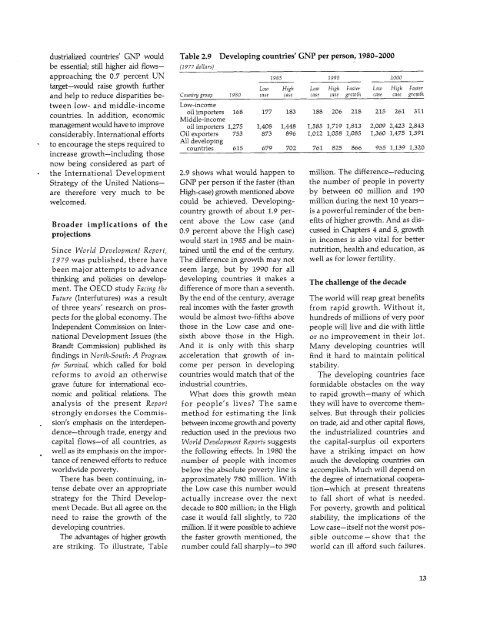
Compared with the industrialized maintain strong growth after 1985. developing countries, the potencountries,growth per person in * The capital-surplus oil ex- tial exists for substantially fasterdeveloping countries will be slightly porters can contribute to efficient growth. While the chances of exlower.The resultant widening in recycling by expanding their ceeding the High case seem slim,income disparities occurs primarily holdings of real and financial it is important that all countriesbecause of slow growth in the foreign assets, by avoiding disrup- recognize the advantages-and thelow-income countries and in the tions in oil supplies or sharp price feasibility-of higher growth.two slowest-growing middle-in- fluctuations, and by extending more What would it require? Onecome groups. Research for this Report direct financial support-conces- important element is more effecsuggeststhat average growth per sional and nonconcessional-to tive adjustment by the industrialpersonof about 1.5 percent a year developingcountries.Andtheycan ized countries, particularly to higherin low-income countries and about help the developing countries to energy costs. Another is a liberal2 percent in middle-income coun- expand foreign earnings by buy- trade environment, with lesstries is needed to prevent the ing more from them and by con- protection for products in whichnumber of people in absolute pov- tinuing to provide employment developing countries have anerty from rising. Thus, for these for their migrant workers. actual or potential cost advantageslow-growing groups (except South * The industrialized countries (this would help to reduce infla-Asia in the High case) the extent can help by avoiding excessive tionary pressures). A third is moreof absolute poverty is likely to in- deflation and by promoting tech- progress by all countries in procreaseduring the decade. nical and policy innovations to ducing and conserving energy, andovercome structural constraints, some reasonable assurance thatPolicy implications by country thus encouraging a rapid resump- supplies would not be suddenlycategories tion of sustained growth. They willassist developing countries (anddisrupted. Improvements in effi-ciency and some further increasesGiven current policies, growth in themselves) by importing more in domestic savings in developingoil-importing developing countries, from them; this requires trade countries would also be valuable.with their total population of 1.8 liberalization as well as economic Finally, capital flows to developingbillion, is likely to be unacceptably growth. The industrialized coun- countries would need to increaselow. The steps needed to move tries should reverse the tendency substantially. Given increases intoward, or beyond, the High case for their aid to fall as a share developing-country exports (andcan be summarized by country of GNP and should encourage thus in debt-servicing capacity)group. prudent expansion in lending and in the efficiency with which* For the oil-importing devel- from their commercial capital capital is used, developing counopingcountries, faster growth markets to developing countries. tries would become increasinglydepends heavily on economic The low-income countries in par- attractive customers to commercialmanagement. This requires efforts ticular need more external finan- lenders. If the industrialized countoincrease exports and invest- cial support than is currently tries grew more rapidly, they wouldment, and to improve the efficiency in prospect. The richer centrally find it easier to provide more aid.with which existing and new in- planned economies also have the With good progress in all thesevestment is used. But increasing capacity to extend considerably areas, GNP per person in thetheir import capacity and their more aid to developing countries developing countries perhapsability to service debt will require and to expand trade with them. could grow 4.3 percent a year inbuoyant export markets, and morethe second half of the 1980s (comcapitalfrom abroad. What would be required for even pared with 3.3 percent in the High* The oil-exporting developing faster growth? case). This would mean growthcountries can grow rapidly; butof 3.9 percent a year in the oiltheymust invest their oil revenues It will take the kind of strong efforts exporting developing countries,productively in the early part of discussed above to reach the High 3.6 percent in the low-income oilthe decade, and ensure that effi- case. But that growth is itself low importers and 4.6 percent in thecient production is encouraged in -measured against that of the 1960s middle-income oil importers.the nonoil as well as oil sectors of and the first part of the 1970s, and Achieving these results wouldthe economy. This will enhance by any reasonable expectations for require much more internationaltheir creditworthiness for the development. Both for the world cooperation than now seems likely.expanded borrowing needed to economy and especially for the Aid of at least 0.5 percent of in-12
dustrialized countries' GNP would Table 2.9 Developing countries' GNP per person, 1980-2000be essential; still higher aid flows- (1977 dollars)approaching the 0.7 percent UN 1985 8990 2000target--would raise growth further Low High Low High Faster Low High Fasterand help to reduce disparities be- Country group 1980 case case case case growth case case growthtween low- and middle-income Low-incomecountries. In addition, economic oil importers 168 177 183 188 206 218 215 261 311Middle-incomemanagement would have to improve oil importers 1,275 1,408 1,448 1,585 1,719 1,813 2,009 2,423 2,843considerably. International efforts Oil exporters 753 873 896 1,012 1,058 1,085 1,360 1,475 1,591to encourage the steps required to All developingcountriesincrease growth-including those615 679 702 761 825 866 955 1,139 1,320now being considered as part ofthe International Development 2.9 shows what would happen to million. The difference-reducingStrategy of the United Nations- GNP per person if the faster (than the number of people in povertyare therefore very much to be High-case) growth mentioned above by between 60 million and 190welcomed. could be achieved. Developing- million during the next 10 yearscountrygrowth of about 1.9 per- is a powerful reminder of the ben-Broader implications of the cent above the Low case (and efits of higher growth. And as disprojections0.9 percent above the High case)would start in 1985 and be maincussedin Chapters 4 and 5, growthin incomes is also vital for betterSince <strong>World</strong> Development Report, tained until the end of the century. nutrition, health and education, as1979 was published, there have The difference in growth may not well as for lower fertility.been major attempts to advance seem large, but by 1990 for allthinkinig and policies on develop- developing countries it makes a The challenge of the decadement. The OECD study Facing the difference of more than a seventh.Future (Interfutures) was a result By the end of the century, average The world will reap great benefitsof three years' research on pros- real incomes with the faster growth from rapid growth. Without it,pects f'or the global economy. The would be almost two-fifths above hundreds of millions of very poorIndependent Commission on Inter- those in the Low case and one- people will live and die with littlenational Development Issues (the sixth above those in the High. or no improvement in their lot.Brandt Commission) published its And it is only with this sharp Many developing countries willfindings in North-South: A Program acceleration that growth of in- find it hard to maintain politicalfor Survival, which called for bold come per person in developing stability.reforms to avoid an otherwise countries would match that of the The developing countries facegrave future for international eco- industrial countries. formidable obstacles on the waynomic and political relations. The What does this growth mean to rapid growth-many of whichanalysis of the present Report for people's lives? The same they will have to overcome themstronglyendorses the Commis- method for estimating the link selves. But through their policiession's emphasis on the interdepen- between income growth and poverty on trade, aid and other capital flows,dence-through trade, energy and reduction used in the previous two the industrialized countries andcapital flows-of all countries, as <strong>World</strong> Development Reports suggests the capital-surplus oil exporterswell as its emphasis on the impor- the following effects. In 1980 the have a striking impact on howtance cf renewed efforts to reduce number of people with incomes much the developing countries canworldwide poverty. below the absolute poverty line is accomplish. Much will depend onThere has been continuing, in- approximately 780 million. With the degree of international cooperatenseclebate over an appropriate the Low case this number would tion-which at present threatensstrategy for the Third Develop- actually increase over the next to fall short of what is needed.ment Decade. But all agree on the decade to 800 million; in the High For poverty, growth and politicalneed to raise the growth of the case it would fall slightly, to 720 stability, the implications of thedeveloping countries. million. If it were possible to achieve Low case-itself not the worst pos-The advantages of higher growth the faster growth mentioned, the sible outcome -show that theare striking. To illustrate, Table number could fall sharply-to 590 world can ill afford such failures.13
- Page 1: t' 8 ~~~~ottoWorld Development Repo
- Page 4 and 5: Oc 1980 by the International Bankfo
- Page 6 and 7: ivThis report was prepared by a tea
- Page 8 and 9: Text tables2.1 Summary of prospects
- Page 10 and 11: DefinitionsCountry groups in the an
- Page 12 and 13: illion people have barely enough fa
- Page 14: in official aid and other capital a
- Page 17 and 18: production and consumption; in- Tab
- Page 19 and 20: measures can raise efficiency fairl
- Page 21: adjustment; but the increases pro-
- Page 25 and 26: windfalls, some of their extra cont
- Page 27 and 28: e done to increase the supplies Lat
- Page 29 and 30: exchange-rate depreciation, by perc
- Page 31 and 32: Table 3.2 World merchandise trade,
- Page 33 and 34: * Inward-looking policies may exper
- Page 35 and 36: inward-looking policies, with high
- Page 37 and 38: cause individual banks or bank- Tab
- Page 39 and 40: to GNP, of all large industrial na-
- Page 41 and 42: in Chapter 2). Ways of increasing a
- Page 43 and 44: 4 Poverty, growth and human develop
- Page 45 and 46: expectancy was less than 50 years,
- Page 47 and 48: population density (see page 39). e
- Page 49 and 50: ably could not have been achieved c
- Page 51 and 52: ution of income typically is less T
- Page 53 and 54: Table 4.2 Irrigation and income, se
- Page 55 and 56: ment strategies that assume that in
- Page 57 and 58: average 40 percent drop out before
- Page 59 and 60: this may be offset by shifts in the
- Page 61 and 62: UNESCO concluded that the poorUnemp
- Page 63 and 64: A typical finding showed the mean o
- Page 65 and 66: Table5.6 Differences in life tend t
- Page 67 and 68: are more expensive and less critica
- Page 69 and 70: per hos pital and clinic, and to st
- Page 71 and 72: peaks in farm work and widespreadin
- Page 73 and 74:
confined to particular places. In A
- Page 75 and 76:
Indonesia, Colombia and Chilehave r
- Page 77 and 78:
(which respond only gradually to cu
- Page 79 and 80:
Contraceptive technologyresearch in
- Page 81 and 82:
6 Implementing human development pr
- Page 83 and 84:
probably China-have managed Table 6
- Page 85 and 86:
percent of the development bud- dev
- Page 87 and 88:
members, too, as no bureaucraticRur
- Page 89 and 90:
Private costs of using public servi
- Page 91 and 92:
ut not teachers or health workers,
- Page 93 and 94:
7 Priorities and progress in region
- Page 95 and 96:
literacy and life expectancy); andF
- Page 97 and 98:
to establish the necessary admin-Fi
- Page 99 and 100:
Poverty Figure 7.5 South Asia: life
- Page 101 and 102:
and North Africa cover the spec- gr
- Page 103 and 104:
The high level of urbanization well
- Page 105 and 106:
Chaipter 8 Summary and conclusionsI
- Page 107 and 108:
is high, frequently well above that
- Page 109 and 110:
Stat.istical appendix to Part ITabl
- Page 111 and 112:
Table SA.6 Capital flows and debt o
- Page 113 and 114:
Montgomery survey administra- publi
- Page 115 and 116:
AnnexWorldDevelopmentIndicators
- Page 117 and 118:
Table 13. Balance of Payments and D
- Page 119 and 120:
IntroductionThe World Development I
- Page 121 and 122:
GNP per capitaAverage indexAverageo
- Page 123 and 124:
Average annual growth rate (percent
- Page 125 and 126:
Distribution of gross domestic prod
- Page 127 and 128:
Average annual growth rate (percent
- Page 129 and 130:
Distribution of gross domestic prod
- Page 131 and 132:
Distribution of value added (percen
- Page 133 and 134:
EnergyEnergyconsumptionAverage annu
- Page 135 and 136:
Merchandise tradeAverage annual gro
- Page 137 and 138:
Percentage share of merchandise exp
- Page 139 and 140:
Percentage share of merchandise imp
- Page 141 and 142:
Destination of merchandise exports
- Page 143 and 144:
Destination of manufactured exports
- Page 145 and 146:
Current accountbalance before Inter
- Page 147 and 148:
Public and publicly guaranteed medi
- Page 149 and 150:
External public debtoutstanding and
- Page 151 and 152:
Amount1981a 1982a 1983a 1984a 1985a
- Page 153 and 154:
Average annualHypotheticalgrowth of
- Page 155 and 156:
PercentageCrude Crude Percentage Pe
- Page 157 and 158:
Percentage ofpopulation ofworking a
- Page 159 and 160:
Percentage of urban population Numb
- Page 161 and 162:
Life Infant Childexpectancy mortali
- Page 163 and 164:
PercentageDaily calorie supplyPopul
- Page 165 and 166:
Number Numberenrolled in enrolled i
- Page 167 and 168:
Percentage share of household incom
- Page 169 and 170:
Average index Tables 4 and 5. Growt
- Page 171 and 172:
28 (minerals, crude fertilizers and
- Page 173 and 174:
continues to grow after replacement
- Page 175 and 176:
posttax income and conceptually tic
- Page 180:
-~~~ S-~~~~~ sEuropean Office:66, a