1 Background - mountain.PROJECTS
1 Background - mountain.PROJECTS
1 Background - mountain.PROJECTS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
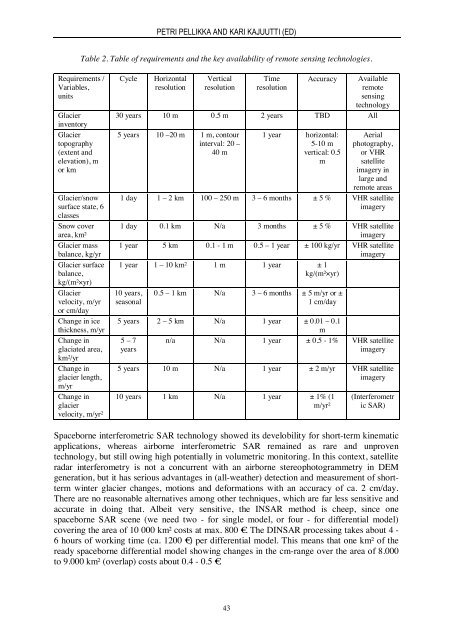
PETRI PELLIKKA AND KARI KAJUUTTI (ED)Table 2. Table of requirements and the key availability of remote sensing technologies.Requirements /Variables,unitsGlacierinventoryGlaciertopography(extent andelevation), mor kmGlacier/snowsurface state, 6classesSnow coverarea, km²Glacier massbalance, kg/yrGlacier surfacebalance,kg/(m²×yr)Glaciervelocity, m/yror cm/dayChange in icethickness, m/yrChange inglaciated area,km²/yrChange inglacier length,m/yrChange inglaciervelocity, m/yr²CycleHorizontalresolutionVerticalresolutionTimeresolutionAccuracyAvailableremotesensingtechnology30 years 10 m 0.5 m 2 years TBD All5 years 10 –20 m 1 m, contourinterval: 20 –40 m1 year horizontal:5-10 mvertical: 0.5mAerialphotography,or VHRsatelliteimagery inlarge andremote areas1 day 1 – 2 km 100 – 250 m 3 – 6 months ± 5 % VHR satelliteimagery1 day 0.1 km N/a 3 months ± 5 % VHR satelliteimagery1 year 5 km 0.1 - 1 m 0.5 – 1 year ± 100 kg/yr VHR satelliteimagery1 year 1 – 10 km² 1 m 1 year ± 1kg/(m²×yr)10 years,seasonal0.5 – 1 km N/a 3 – 6 months ± 5 m/yr or ±1 cm/day5 years 2 – 5 km N/a 1 year ± 0.01 – 0.1m5 – 7 n/a N/a 1 year ± 0.5 - 1% VHR satelliteyearsimagery5 years 10 m N/a 1 year ± 2 m/yr VHR satelliteimagery10 years 1 km N/a 1 year ± 1% (1m/yr²(Interferometric SAR)Spaceborne interferometric SAR technology showed its develobility for short-term kinematicapplications, whereas airborne interferometric SAR remained as rare and unproventechnology, but still owing high potentially in volumetric monitoring. In this context, satelliteradar interferometry is not a concurrent with an airborne stereophotogrammetry in DEMgeneration, but it has serious advantages in (all-weather) detection and measurement of shorttermwinter glacier changes, motions and deformations with an accuracy of ca. 2 cm/day.There are no reasonable alternatives among other techniques, which are far less sensitive andaccurate in doing that. Albeit very sensitive, the INSAR method is cheep, since onespaceborne SAR scene (we need two - for single model, or four - for differential model)covering the area of 10 000 km² costs at max. 800 €. The DINSAR processing takes about 4 -6 hours of working time (ca. 1200 €) per differential model. This means that one km² of theready spaceborne differential model showing changes in the cm-range over the area of 8.000to 9.000 km² (overlap) costs about 0.4 - 0.5 €.43