- Page 14:
Preface xvAcknowledgmentsForeword x
- Page 18:
Chapter 9: Fluoroscopy 2319.1 Funct
- Page 22:
16.3 Transducers 48316.4 Beam Prope
- Page 26:
B.3 Radiological Data for Elements
- Page 32:
We are deeply grateful to that part
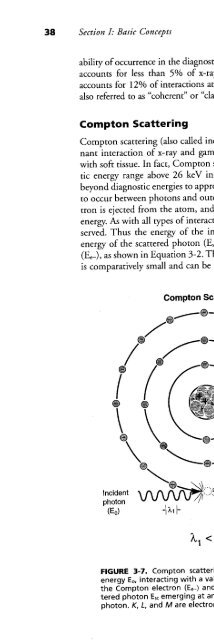
- Page 38:
Can medical physics be interesting
- Page 46:
INTRODUCTION TO MEDICALIMAGINGMedic
- Page 50:
FIGURE 1-2. The chest x-ray is them
- Page 54:
FIGURE 1-4. A computed tomography (
- Page 58:
angles around the patient. These pr
- Page 62:
FIGURE '-8. Sagittal (upper left),
- Page 66: ducer, which records the returning
- Page 70: TABLE 1-1. THE LIMITING SPATIAL RES
- Page 76: WAVELENGTH(nanometers)FREQUENCY(her
- Page 80: The physical properties of the most
- Page 84: The energy required to remove an el
- Page 88: An electron cascade does not always
- Page 92: 160150140130120110100N
- Page 96: The binding energy can be calculate
- Page 102: INTERACTION OF RADIATIONWITH MATTER
- Page 106: x10 3 7becomes electrically neutral
- Page 110: Electrons can undergo inelastic int
- Page 114: The nuclide produced by neutron abs
- Page 120: attenuation differences of the tiss
- Page 124: The probability of photoelectric ab
- Page 128: Pair production can only occur when
- Page 132: As the thickness increases, however
- Page 136: To calculate the linear attenuation
- Page 140: TABLE 3-2. HALF VALUE LAYERS OF TIS
- Page 144: the attenuation coefficient that wo
- Page 148: absorbed dose is the rad (an acrony
- Page 152: gies below 100 keY due to an increa
- Page 156: TABLE 3-5. TISSUE WEIGHTING FACTORS
- Page 160: Bushberg JT. The AAPM/RSNA physics
- Page 164: In the decimal form, the ten digits
- Page 168:
1 kilobyte (kB) = 2'0 bytes = 1024
- Page 172:
o 1 1 1 =71,1 h-> -~~I-~--I~-Time-t
- Page 176:
The digital form facilitates other
- Page 180:
A computer consists of a central pr
- Page 184:
memory can fit only small portions
- Page 188:
oards can be plugged. The boards in
- Page 192:
optical. The recording material of
- Page 196:
Array processor,-~- ~~~~~- ~- ~- -
- Page 200:
10 1=120 PRINT I301=1+140 IF 1
- Page 204:
4.6 STORAGE, PROCESSING, AND DISPLA
- Page 208:
FIGURE 4-10. Effect of number of bi
- Page 212:
y which volumetric data sets are re
- Page 216:
ond) of the beam. The electron beam
- Page 220:
The intensity of each pixel must be
- Page 224:
FIGURE 4-16. Windowing an image wit
- Page 230:
DIAGNOSTICRADIOLOGY
- Page 236:
Heated tungsten filamentcathodeEvac
- Page 240:
Major factors that affect x-ray pro
- Page 244:
TABLE 5-2. K-SHELL CHARACTERISTIC X
- Page 248:
The focusing cup, also called the c
- Page 252:
Anode ConfigurationsX-ray tubes hav
- Page 256:
These and other factors determine t
- Page 260:
The effective focal spot length var
- Page 264:
The heel effect refers to a reducti
- Page 268:
As mentioned earlier, filtration is
- Page 272:
x-ray attenuation) mimics the x-ray
- Page 276:
mary winding") carries the input lo
- Page 280:
A simple autotransformer consists o
- Page 284:
the electron target (anode). The tr
- Page 288:
some x-ray generators, preprogramme
- Page 292:
independent of the polarity of the
- Page 296:
f\f\v~/....•••..••,.\,II
- Page 300:
130 Section II: Diagnostic Radiolog
- Page 304:
Generator~Single-phase 1-pulse(self
- Page 308:
FIGURE 5-34. Automatic exposure con
- Page 312:
Therefore, the ourpur exposure incr
- Page 316:
TABLE 5-4. ROOT-MEAN-SQUAREVOLTAGE
- Page 320:
Energy (J) = Root-mean-square volta
- Page 324:
Previous exposures must also be con
- Page 328:
1,6001,400OJc 1,200'00::::l0 1,000I
- Page 332:
FIGURE 6-1. The basic geometry of p
- Page 336:
Consideration of Equation 6-4 revea
- Page 340:
FIGURE 6-5. A scanning electron mic
- Page 344:
screenx-rays1x-rays1x-rays1emulsion
- Page 348:
the use of dye is to design a phosp
- Page 352:
\20 em Patient ~•...70oUGd2~S ~ .
- Page 356:
emulsion film has a total mass thic
- Page 360:
axis), and the film OD at zero x-ra
- Page 364:
2:' 2.5 ---'w c~ 2.0~ 1.5~ Q.o 1.00
- Page 368:
exposure times the exposure rate is
- Page 372:
.--... 3000?ft::- 1000(J)~C 300 -o(
- Page 376:
504540~35 ..•..•.•en 30jg 25c
- Page 380:
TABLE 6-3. ADDITIONAL PARAMETERS (N
- Page 384:
Most artifacts associated with the
- Page 390:
Film is a unique technology, born o
- Page 394:
and eventually reach the film emuls
- Page 398:
film outdryerFIGURE 7-4. The functi
- Page 402:
ActivatorClearing(hypo)agentHardene
- Page 406:
guide shoes in the developer tank.
- Page 410:
film transportrollerspolygonalmirro
- Page 414:
FIGURE 7-10. The functional compone
- Page 418:
manufacturer and the phosphor emplo
- Page 424:
and craniocaudal views, are routine
- Page 428:
CompressionpaddleGridScreen-filmPho
- Page 432:
Chestwall2:' 100%·00cQ)Cc-§ 50%..
- Page 436:
with little contribution to the ima
- Page 440:
energies not useful in forming the
- Page 444:
120100NE.€80UJc:.90 60.J::.0-'" 4
- Page 448:
40E 35
- Page 452:
ference of 10% to 15% positive (gre
- Page 456:
Scatter to Primary ratio:0.8 - 1.0S
- Page 460:
Grids impose a dose penalty to comp
- Page 464:
ation exposure is also necessary to
- Page 468:
4fastLate 80'spresent~ 3·00 c:Q)0r
- Page 472:
FIGURE 8-23. Film processor testing
- Page 476:
4.54.0Cii 3.5~C 3.08 2.5C:.@ 2.0~ 1
- Page 480:
x-shift2z: receptorto lesiondept.~_
- Page 484:
megabytes, and four times that for
- Page 488:
TABLE 8-7. AVERAGE GRANDUlAR DOSE I
- Page 492:
226 Section II: Diagnostic Radiolog
- Page 496:
FIGURE 8-30. A: The mammography acc
- Page 502:
Fluoroscopy is an imaging procedure
- Page 506:
inputwindowvacuumbottleinputscreenF
- Page 510:
Ii\ !\,-.l,,....,. l'..-t-J..•.vF
- Page 514:
For cardiac imaging, by comparison,
- Page 518:
partial-silveredmirrorinfinitefocus
- Page 522:
local variations in light intensity
- Page 526:
Photo-Spot CamerasA photo-spot came
- Page 530:
Many fluoroscopists practice aggres
- Page 534:
the image constant at the monitor.
- Page 538:
Field of View:cm (inches)14 (5.5)20
- Page 542:
In the angiographic setting, the ta
- Page 546:
50eaJ enaJ::> aJ0 cen -'"len en"0"0
- Page 550:
IMAGE QUALITYImage quality is a gen
- Page 554:
trast in the resultant image) can o
- Page 558:
.a- 2.5.iij~ 2.0c~ 1.5ao 1.02 3Expo
- Page 562:
246 8Tissue Thickness (cm)FIGURE 10
- Page 566:
puter to the display hardware itsel
- Page 570:
FIGURE 10-12. A: An isometric plot
- Page 574:
tor, it will appear life size (magn
- Page 578:
of the resolution performance of th
- Page 582:
wave serves as an input to a hypoth
- Page 586:
11111111 11I1 111I 1111 1111--FIGUR
- Page 590:
c 40f:5!:c 30o'0t 20 .cE:lZ120 140H
- Page 594:
A,0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0Position (
- Page 598:
In all medical x-ray imaging, we wa
- Page 602:
FIGURE 10-30. A circular signal is
- Page 606:
to the calculation of the noise pow
- Page 610:
less than twice per cycle, and it w
- Page 614:
The sine-shaped MTF for a detector
- Page 618:
not just one feature or number, but
- Page 622:
--normal••••• m •••
- Page 628:
for each exposure. The imaging plat
- Page 632:
about 85% BaFBr and 15% BaFI, activ
- Page 636:
charge packetsmove in unisonreadout
- Page 640:
Flat panel detector systems make us
- Page 644:
wires in Fig. 11-8), and the gate i
- Page 648:
scintillator(CSI)~TFT detector elem
- Page 652:
individual images from each camera
- Page 656:
When film-screen image receptors ar
- Page 660:
FIGURE 11-13. The raw and corrected
- Page 664:
If I'(x,y) > Thigh, then I'(x,y) =
- Page 668:
When the 3 X 3 kernel containing al
- Page 672:
same time, and to archive images us
- Page 676:
FIGURE 12-1. The motion ofthe x-ray
- Page 680:
larger tissue volume is exposed. Th
- Page 684:
cient of jivessel, the mask image (
- Page 688:
3E+3 2E+3I3E+3Ẹ E 2E+3~ 2E+3 ~Ql~
- Page 694:
Computed tomography (CT) is in its
- Page 698:
FIGURE 13-2. A pixel (picture eleme
- Page 702:
--I.....Lobject--I.....L-imageacqui
- Page 706:
Pencil BeamGeometryFan BeamGeometry
- Page 710:
ll:llIidlllidlllielltll:llIi:tlloll
- Page 714:
FIGURE 13-11. A schematic diagram o
- Page 718:
FIGURE 13-13. Multiple detector arr
- Page 722:
cally 0.10 to 0.20 mm on each side.
- Page 726:
5 to 10 mm with the same x-ray tech
- Page 730:
Pitch is a parameter that comes to
- Page 734:
FIGURE 13-20. The sinogram is an im
- Page 738:
The raw data acquired by a CT scann
- Page 742:
lesion~CT# I !, ,c... Z ~ominal sli
- Page 746:
esents an individual measurement of
- Page 750:
in the data, but in x-ray images th
- Page 754:
titative CT techniques can be used
- Page 758:
W = 4095, L = 1048 W=600,L=-100 W =
- Page 762:
FIGURE 13-34. A volume-rendered ima
- Page 766:
ent than in radiography, because of
- Page 770:
TABLE 13-1. TYPICAL COMPUTED TOMOGR
- Page 774:
the high SNR detected in the thinne
- Page 778:
Patient motion: If there is involun
- Page 782:
FIGURE 13-40. A: A beam-hardening a
- Page 786:
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is
- Page 790:
conceptualized as the number of mag
- Page 794:
Spinning proton withdipole magnetic
- Page 798:
TABLE 14-3. GYROMAGNETIC RATIO FOR
- Page 802:
FIGURE 14-6. Longitudinal magnetiza
- Page 806:
From the classical physics viewpoin
- Page 810:
ways. A 90-degree angle provides th
- Page 814:
spin-spin interactions by themselve
- Page 818:
:~Med~;:rtV~~OUS:Small, aqueous:~ ~
- Page 822:
FatLiverMuscleWhite matterGray matt
- Page 826:
90 0pulse180 0pulse180 0pulse180 0p
- Page 830:
The equation shows that for the sam
- Page 834:
Mz 1,Longitudinal recovery (T1 )Ima
- Page 838:
TABLE 14-5. SPIN ECHO PULSE SEQUENC
- Page 842:
tization when a short TI is used. T
- Page 846:
FIGURE 14-28. Magnetic resonance se
- Page 850:
generated with smaller flip angles
- Page 854:
FIGURE 14-31. A steady-state gradie
- Page 858:
Even-echo rephasing is a phenomenon
- Page 862:
loss than those of lesser water mob
- Page 866:
Price RR. The AAPM/RSNA physics tut
- Page 872:
Linear changein magnetic fieldSuper
- Page 876:
TABLE 15-1. PRECESSIONAL FREQUENCY
- Page 880:
- 0-40 -30 -20 -10 10 20 30 40(1)-0
- Page 884:
Frequency Encode GradientThe freque
- Page 888:
Position of the spins in the third
- Page 892:
15.2 "K-SPACE" DATA ACQUISITION AND
- Page 896:
RF pulses~ _J!~e_a~ Yd~h_qi!.t~r:e_
- Page 900:
peripheral areas (Fig. 15-16E) isol
- Page 904:
Acquired data:% matrix + 1 lineD-f
- Page 908:
TR180 0excitation90 0readout180 0re
- Page 912:
"effective" echo time occurs at a t
- Page 916:
15.3 THREE-DIMENSIONAL FOURIER TRAN
- Page 920:
Signal·to-NoiseRatioThe signal-to-
- Page 924:
image acquisition. Eddy currents ar
- Page 928:
of the blood. Since the detectable
- Page 932:
YTExcitation I-- I#1TExcitation 1--
- Page 936:
Magnetic susceptibility can be quit
- Page 940:
computeroptimizedprofile"rectangula
- Page 944:
since the evolution of the echo sig
- Page 948:
3-4 ppm difference, fat-5 ppm diffe
- Page 952:
Frequency synthesis of object (harm
- Page 956:
15.7 INSTRUMENTATIONMagnetThe magne
- Page 960:
Permanent magnets rely on the ferro
- Page 964:
Superconductive magnets produce ext
- Page 968:
TABLE 15-2. RECOMMENDED QUALITY CON
- Page 972:
TABLE 15-3. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAG
- Page 978:
Ultrasound is the term that describ
- Page 982:
"Plane-piston"mechanicaldisplacemen
- Page 986:
FIGURE 16-3. Ultrasound wavelength
- Page 990:
Sound energy causes particle displa
- Page 994:
TABLE 16-3. ACOUSTIC IMPEDANCE, Z =
- Page 998:
TABLE 16-4. PRESSURE AND REFLECTION
- Page 1002:
echoes typically have similar echo
- Page 1006:
The echo intensity is one hundredth
- Page 1010:
Equilibrium:No surface chargeEquili
- Page 1014:
i] ,A0.8 0.9 10 1.1flf O"[:f: L~0.5
- Page 1018:
then filled with an epoxy resin to
- Page 1022:
Transducer elementDiameter, dLength
- Page 1026:
and 36.4 cm, respectively. Lateral
- Page 1030:
SummedSignalFIGURE 16-18. Dynamic r
- Page 1034:
amplitude of the peripheral transdu
- Page 1038:
Phased arraytransducerLateral -reso
- Page 1042:
iUnderstanding ultrasonic image for
- Page 1046:
teristics of the transducer element
- Page 1050:
Pre-amplificationand swept gainI Di
- Page 1054:
OJ'0~BeforeTGC 0.E
- Page 1058:
---------_+-Time...................
- Page 1062:
FIGURE 16-33. Articulating arm B-mo
- Page 1066:
eturning echoes. The ultrasound bea
- Page 1070:
apher must consider the compromises
- Page 1074:
Ultrasound Contrast AgentsUltrasoun
- Page 1078:
Harmonics build in relative intensi
- Page 1082:
Linear components(tissue)Non-linear
- Page 1086:
Mechanical:Transducer~Rotating acou
- Page 1090:
(width and height, respectively) of
- Page 1094:
(i\ I)ThroughtransmissionLow _" Hig
- Page 1098:
MirrorimageFIGURE 16-44 (continued)
- Page 1102:
error by neglecting the velocity of
- Page 1106:
shift measurement because a narrow
- Page 1110:
Each Doppler pulse does not contain
- Page 1114:
t IE«-f maxo~ __ Frequency(Velocit
- Page 1118:
AliasingAliasing, as described earl
- Page 1122:
speed of sound. Measured velocity (
- Page 1126:
6E0.s:::. 8-a.low scatter targets d
- Page 1130:
horizontal targets (lateral resolut
- Page 1134:
ultrasound used to enhance image qu
- Page 1138:
Thermal and mechanical indices of u
- Page 1142:
10'" ..!2 ES>-+"'"00 cQ)E+"'0.110 1
- Page 1148:
cylindrical cable with a central co
- Page 1152:
On most networks today, when two no
- Page 1156:
sic (nonswitched) forms of Ethernet
- Page 1160:
lion distinct addresses. The first
- Page 1164:
Typical data transfer rates of mode
- Page 1168:
Picture Archiving and Communication
- Page 1172:
TeleradiologyTeleradiology can prov
- Page 1176:
DigitalImageFIGURE 17-6. Charge-cou
- Page 1180:
serving nuclear medicine, whereas a
- Page 1184:
Multi-terabyteArchiveFIGURE 17-8. R
- Page 1188:
computer or by specialized hardware
- Page 1192:
Standard viewboxMammography viewbox
- Page 1196:
An application program on the works
- Page 1200:
CollimatorlensiBeammodulatorFIGURE
- Page 1204:
An example of a fault-tolerant stra
- Page 1210:
NUCLEARMEDICINE
- Page 1216:
TABLE 18-1. UNITS AND PREFIXES ASSO
- Page 1220:
II25 ~--------20 : :III12.5 . - - -
- Page 1224:
Beta-minus (~-) decay, or negatron
- Page 1228:
When they lose all (or most) of the
- Page 1232:
Each radionuclide's decay process i
- Page 1236:
MOL YBDENUM-99Beta-Minus DecayT1/2
- Page 1240:
FLUORINE-18Electron Capture and Bet
- Page 1244:
Alternating {_Voltage ~Magnetic fie
- Page 1248:
FIGURE 19-3. Hospital-based cyclotr
- Page 1252:
The total energy released by the nu
- Page 1256:
Radiation DetectorsNeutron Beam Hol
- Page 1260:
ProductionmethodNuclear reactor Nuc
- Page 1264:
that shows details of the generator
- Page 1268:
10087.5..•..•.-c::Q)u•..Q)D.-
- Page 1272:
TABLE 19-3. PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTIC
- Page 1276:
septa (see Chapter 21). A radiophar
- Page 1280:
mediated by the energy-dependent Na
- Page 1284:
depending on the solvent, either re
- Page 1288:
(ii) The total dosage (i.e., admini
- Page 1292:
nal. For other applications, photog
- Page 1296:
are often operated in current mode
- Page 1300:
20.2 GAS-FILLED DETECTORSBasic Prin
- Page 1304:
Because gas multiplication does not
- Page 1308:
is extensively used in biomedical r
- Page 1312:
constituent elements and their low
- Page 1316:
visiblelight -...photon+photocathod
- Page 1320:
In crystalline materials, electrons
- Page 1324:
of the diode and the negative polar
- Page 1328:
FIGURE 20-13. Function of asingle-c
- Page 1332:
Nal (TI)crystal..-r--..IIIIPMT...-r
- Page 1336:
Spectrum of Cesium-137The spectrum
- Page 1340:
with the emission of a 140.5-keV ga
- Page 1344:
FIGURE 20-22. Pulse pileup.The dash
- Page 1348:
distance, typically 20 to 25 cm, fr
- Page 1352:
its samples ofI-125 and Co-57 to ac
- Page 1356:
Dose Calibrator Quality AssuranceBe
- Page 1360:
Two measures of the central tendenc
- Page 1364:
4Number of SuccessesFIGURE 20-28. B
- Page 1368:
For example, a counr of 853 is obra
- Page 1372:
entering the standard deviations fr
- Page 1376:
dose to the patient, nearly all nuc
- Page 1380:
PhotomultipliertubesLucite light pi
- Page 1384:
PulsesfromindividualPMTsAnalogJ....
- Page 1388:
the object is moved yet farther fro
- Page 1392:
TABLE 21-1. COMPARISON OF SINGLE·P
- Page 1396:
Some types of collimators magnify (
- Page 1400:
the product of three factors: the c
- Page 1404:
() 0.5c CD"0If=CD.>
- Page 1408:
TABLE 21-3. THE EFFECT OF INCREASIN
- Page 1412:
6.4 mm at 10 cm from the collimator
- Page 1416:
Digital'positionZ correctionlookup
- Page 1420:
two ways that scintillation cametas
- Page 1424:
quency of this testing depends on t
- Page 1428:
ufacturers incorporate a computer f
- Page 1432:
FirstimageSecondimageThirdimageFour
- Page 1436:
pool image sequence, using T c-99m-
- Page 1440:
adionuclides in patients, using a p
- Page 1444:
mator, which never enjoyed wide acc
- Page 1448:
heads of a SPECT system produced id
- Page 1452:
0.50.4CD"0:e0.3c.E 0.2
- Page 1456:
No AttenuationCorrectionAttenuation
- Page 1460:
camera heads that revolve about the
- Page 1464:
In planar nuclear imaging, radioact
- Page 1468:
FIGURE 22-10. Image of a cylinder f
- Page 1472:
TABLE 22-1. RECOMMENDED SCHEDULE FO
- Page 1476:
Design and Principles Of OperationA
- Page 1480:
2 by 2 arrayof PMTs~Slits cut intoB
- Page 1484:
To detect coincidences, the times o
- Page 1488:
DetectorelementsSeptalcollimatorrin
- Page 1492:
J......... ······~~~~~I thiC
- Page 1496:
FIGURE 22-23. Attenuationin PET. Th
- Page 1500:
511-keV collimators and because the
- Page 1504:
A system provided by another vendor
- Page 1508:
Madsen MT. The AAPM/RSNA physics tu
- Page 1514:
It is incumbent upon all individual
- Page 1518:
(5 mrad/hr), which is approximately
- Page 1522:
combustible fuels, including coal a
- Page 1526:
TABLE 23-3. AVERAGE ANNUAL OCCUPATI
- Page 1530:
TABLE 23-6. ANNUAL GENETICALLY SIGN
- Page 1534:
with conventional x-ray film, radia
- Page 1538:
FIGURE 23-3. A small chip of LiF (r
- Page 1542:
Method Measures Useful rangePermane
- Page 1546:
FIGURE 23-6. Portable ion chamber.
- Page 1550:
Inverse Square LawE 2 = E 1 (0 1 /0
- Page 1554:
adherence to the methods in NCRP re
- Page 1558:
espective distances to the point in
- Page 1562:
Exposure per week contributed by th
- Page 1566:
Primary, scatter, and leakage radia
- Page 1570:
IStairwaygQlc..>c19'" 00Waitingarea
- Page 1574:
e the minimal thickness recommended
- Page 1578:
Personnel Protection in Diagnostic
- Page 1582:
TABLE 23-14. EXPOSURE RATE CONSTANT
- Page 1586:
Filtration of the polychromatic x-r
- Page 1590:
out ABC. Some systems have a high e
- Page 1594:
the physician with the ability to m
- Page 1598:
nologist in the correct selection o
- Page 1602:
ination should remove their protect
- Page 1606:
labeled with 1-131. 1-131 decays wi
- Page 1610:
Phosphorus-32 is used for the radio
- Page 1614:
clides are the "Standards for Prote
- Page 1618:
TABLE 23-18. NUCLEAR REGULATORY COM
- Page 1622:
National Council on Radiation Prote
- Page 1628:
section 3.5). The old term for ener
- Page 1632:
TABLE 24-3. ABSORBED DOSES TO SELEC
- Page 1636:
Medical x-ray imaging procedures su
- Page 1640:
mAs, and the distance from x-ray so
- Page 1644:
FIGURE 24-3. The geometry fordeterm
- Page 1648:
FIGURE 24-4. Illustration ofSourceo
- Page 1652:
FIGURE 24-6. The cumulated activity
- Page 1656:
TABLE 24-9. VARIABLES IN THE MIRD S
- Page 1660:
not currently require manufacturers
- Page 1664:
TABLE 25-1. DETERMINANTS OF BIOLOGI
- Page 1668:
Radia~?/ 1'{"l20 H+ ow\ Ionization
- Page 1672:
cific ionization (i.e., ionization
- Page 1676:
chromatid aberrations. Unlike chrom
- Page 1680:
10~n ,,,,,,C), ,,I:Dq'S; 1.0 ------
- Page 1684:
ClC 1.0oS;o~::JCJ)~G)0-0C0:;:;(JCIS
- Page 1688:
mediated through free radical produ
- Page 1692:
Radiationdose~~ANSYS~Dose too---. D
- Page 1696:
to normal within 2 to 3 months. If
- Page 1700:
dose delivered over a protracted pe
- Page 1704:
diseases such as ataxia telangiecta
- Page 1708:
The stages of the neurovascular syn
- Page 1712:
Most of the radiation-induced biolo
- Page 1716:
adiation, such as radiofrequency ra
- Page 1720:
TABLE 25-7. SUMMARY OF MAJOR EPIDEM
- Page 1724:
,.,,. ,,.,,.,,.ỊI"", ,I, IIIIIII"
- Page 1728:
Radiationexposure1-",,II, II,,III,
- Page 1732:
the overall risk and relative proba
- Page 1736:
times greater risk for development
- Page 1740:
Estimating Genetic RiskThe genetica
- Page 1744:
sure, owing principally to the rela
- Page 1748:
1/3 for mice). Nevertheless, develo
- Page 1752:
Numberoccurring fromnatural causesE
- Page 1756:
Prenatal death(Some survivors,no in
- Page 1762:
APPENDICES
- Page 1768:
OriginalVector (V)InternationalSyst
- Page 1772:
PotentialEnergyPotential energy is
- Page 1776:
When a charged particle is placed i
- Page 1780:
The joule is a rather large unit of
- Page 1784:
The band theory of solids explains
- Page 1788:
FIGURE A-7. A spinning charge has a
- Page 1792:
Magnetic field moving towards wire
- Page 1796:
Static magnetic fieldRotating curre
- Page 1802:
PHYSICAL CONSTANTS, PREFIXES,GEOMET
- Page 1806:
Appendix B: Physical Constants, Pre
- Page 1810:
MASS ATTENUATIONCOEFFICIENTS AND SP
- Page 1814:
Appendix C: Mass Attenuation Coeffi
- Page 1818:
Appendix C: Mass Attenuation Coeffi
- Page 1822:
Appendix C: Mass Attenuation Coeffi
- Page 1826:
C.6 MAMMOGRAPHY SPECTRA: Rh/RhTABLE
- Page 1830:
Appendix Co' Mass Attenuation Coeff
- Page 1834:
RADIOPHARMACEUTICALCHARACTERISTICS
- Page 1838:
1251Albumin (ONI) IV N/A -20 mL blo
- Page 1842:
153Sm Lexidronam, also IV over a 1-
- Page 1846:
-90% of dose excreted in 3 hr. Prep
- Page 1850:
99mTc-basedmyocardial perfusion age
- Page 1854:
99mTcMacroaggregated 0.16 ts 0.0161
- Page 1858:
TABLE D-4. ABSORBED DOSE ESTIMATES
- Page 1864:
914 Section V: AppendicesMedical Ph
- Page 1868:
ASCII. See American Standard Code f
- Page 1872:
DDAC. See Digital-to-analog convert
- Page 1876:
Electronic switchltimer, exposure t
- Page 1880:
Image magnification, spatial resolu
- Page 1884:
Magnetic resonance imaging (contd.)
- Page 1888:
Phased array, ultrasound, 490Phosph
- Page 1892:
Radiation detection (contd)gas-fill
- Page 1896:
Shoe marks, processor artifacts, 18
- Page 1900:
Two dimensional multi planar acquis
- Page 1906:
"Nope '" no sign of YOur kitten, Ma