POLITECNICO
Scarica il PDF (5174KB) - Rivista Politecnico - Politecnico di Milano
Scarica il PDF (5174KB) - Rivista Politecnico - Politecnico di Milano
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Space field research activities<br />
at the aerospace department<br />
of Politecnico di Milano<br />
Moon Exploration<br />
Since a new interest for lunar exploration and exploitation<br />
is risen up in recent years severa1 topics are<br />
under study to better design a mission to the Moon.<br />
Three are the main areas of interest:<br />
WSB Transfer Trajectories. Weak Stability<br />
Boundaries (WSB) are a new and inhiguing altemative<br />
to classica1 Hohmann transfers. Proposed for the<br />
Cst time by Belbmno, this kind of transfer trajectory<br />
exploits regions of transition between stable and<br />
unstable manifolds, providing a meaningful saving of<br />
propellant An efficient procedure to design an optimal<br />
transfer by WSB is under development along with a<br />
stability analysis of the designed trajectory.<br />
Orbit Maintenance. The non-uniform gravity field of<br />
the Moon yields strong periurbiig effects on low perilune<br />
orbits leadig to a hard landing ahr few revolutions.<br />
A siudy of long and medium term effects aimed<br />
Io identify periodic stable solutions and stabilising<br />
minimum Dv manoeuvres has been camed out.<br />
* Optimal Landing. Minimum mass homing trajectory<br />
to a desired target from a given coasting orbit is ofprimary<br />
for the actual reaiisation of the mission. Optiial<br />
control law and optimal initial conditions have been<br />
denved to perform the desii landing trajectory keeping<br />
into account orbita1 and attitude dynamics and<br />
constraints.<br />
Figure I: Periodic solutions<br />
Figure 2: Optirnal thrust program<br />
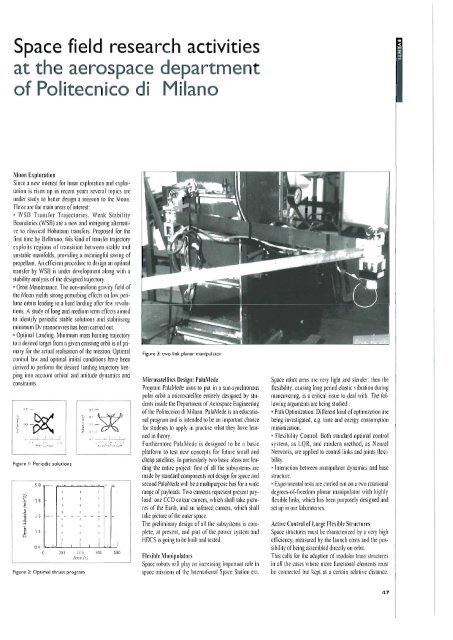
Figure 3: w o link planar manipulator<br />
Microsafeiiites Design: PalaMede<br />
Program PalaMede aims to put in a sun-synchronous<br />
polar orbit a micmsatellite entirely designed by students<br />
inside the Department of Aerospace Engineering<br />
of the Politecnico di Milano. PalaMede is an educati&<br />
nal program and is intended Io be an important chance<br />
for students to apply in practise what they have learned<br />
in theory.<br />
Furthermore PalaMede is designed to be a basic<br />
platform to test new concepts for future small and<br />
cheap satellites. In pariicularly No basic ideas are leadig<br />
the entire project: first of al1 the subsystems are<br />
made by standard components not design for space and<br />
second PalaMede will be a muhipurpose bus fora wide<br />
range of payloads. Two cameras repwmt present payload:<br />
one CCD colour camera, which shaU take pictures<br />
of the Earth, and an infrared wnera, which shaU<br />
take picture of the outer space.<br />
The prehmmy design of al1 the suhystems is complete,<br />
at present, and part of the power system and<br />
HDCS is going to be built and tested.<br />
Fiexible Manipdators<br />
Space robots will play an increasing important role in<br />
space missions of the Intemational Space Station era.<br />
Space robot arms are very light and slender: then the<br />
flexibility, causiig long period elastic vibration during<br />
maneuvering, is a critica1 issue to dea1 with. The foilowing<br />
arguments are being studied :<br />
* Path Optimiition. Different kind of optimization are<br />
beiig investigated, e.g. time and energy consumption<br />
minimintion.<br />
Flexibility Control. Both standard optimal control<br />
system, as LQR, and modern method, as Neural<br />
Networks, are applied to contml links and joints flexibili@.<br />
* Interaction between manipulator dynamics and base<br />
strutture.<br />
Experimental tests are earried out on a two rotational<br />
degrees-of-freedom planar manipulator with highly<br />
flexible links, which has been purposely designed and<br />
set up in our laboratories.<br />
Active Control of hrge Fìexible Struciures<br />
Space struciures must be characterized by a very higb<br />
efficiency, measured by the launch costs and the possibili@<br />
of being assembled directly on orbit.<br />
This calls for the adoption of modular tniss shuctures<br />
in al1 the cases where more functional elements must<br />
be wnnected but kept at a certaii relative distance.