Distance Education in Transition - Master of Distance Education ...
Distance Education in Transition - Master of Distance Education ...
Distance Education in Transition - Master of Distance Education ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Visions <strong>of</strong> Autonomous Learn<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� to deal with the great amount <strong>of</strong> messages,<br />
� to exchange <strong>in</strong>formation,<br />
� to follow a discussion that is usually most complex, take an active part <strong>in</strong> it and<br />
concentrate on those aspects <strong>in</strong> which they are <strong>in</strong>terested,<br />
� to try to become “visible” <strong>in</strong> the group and to socialise with other class members<br />
<strong>in</strong> the virtual way,<br />
� to concentrate on preferred aspects <strong>of</strong> the discussion,<br />
� to construct knowledge,<br />
� to cooperate with participants <strong>in</strong> small sub-groups,<br />
� to ask for support and pr<strong>of</strong>it from it.<br />
When the students have experienced a virtual sem<strong>in</strong>ar <strong>of</strong> this k<strong>in</strong>d they will probably<br />
have become better »autonomous« learners.<br />
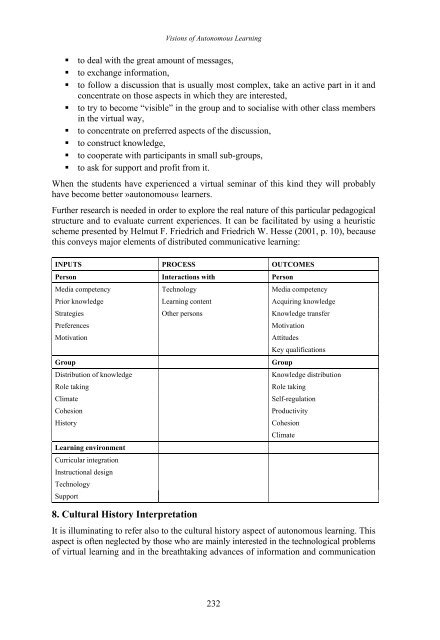
Further research is needed <strong>in</strong> order to explore the real nature <strong>of</strong> this particular pedagogical<br />
structure and to evaluate current experiences. It can be facilitated by us<strong>in</strong>g a heuristic<br />
scheme presented by Helmut F. Friedrich and Friedrich W. Hesse (2001, p. 10), because<br />
this conveys major elements <strong>of</strong> distributed communicative learn<strong>in</strong>g:<br />
INPUTS PROCESS OUTCOMES<br />
Person Interactions with Person<br />
Media competency Technology Media competency<br />
Prior knowledge Learn<strong>in</strong>g content Acquir<strong>in</strong>g knowledge<br />
Strategies Other persons Knowledge transfer<br />
Preferences Motivation<br />
Motivation Attitudes<br />
Key qualifications<br />
Group Group<br />
Distribution <strong>of</strong> knowledge Knowledge distribution<br />
Role tak<strong>in</strong>g Role tak<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Climate Self-regulation<br />
Cohesion Productivity<br />
History<br />
Learn<strong>in</strong>g environment<br />
Curricular <strong>in</strong>tegration<br />
Instructional design<br />
Technology<br />
Support<br />
Cohesion<br />
Climate<br />
8. Cultural History Interpretation<br />
It is illum<strong>in</strong>at<strong>in</strong>g to refer also to the cultural history aspect <strong>of</strong> autonomous learn<strong>in</strong>g. This<br />
aspect is <strong>of</strong>ten neglected by those who are ma<strong>in</strong>ly <strong>in</strong>terested <strong>in</strong> the technological problems<br />
<strong>of</strong> virtual learn<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>in</strong> the breathtak<strong>in</strong>g advances <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>formation and communication<br />
232