MacroeconomicsI_working_version (1)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Fiscal Policy in Details 111<br />
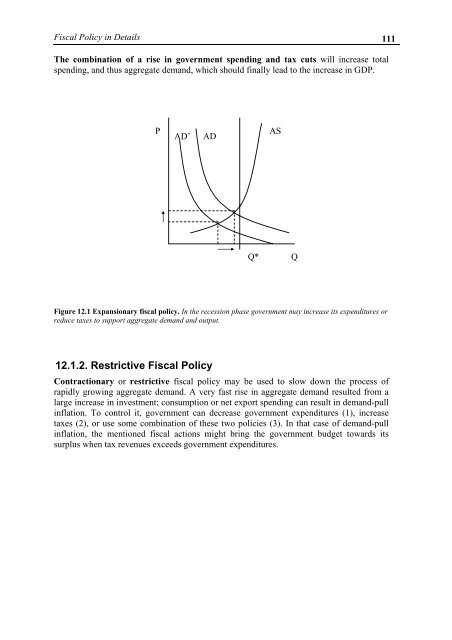
The combination of a rise in government spending and tax cuts will increase total<br />
spending, and thus aggregate demand, which should finally lead to the increase in GDP.<br />
P<br />
AD’<br />
AD<br />
AS<br />
Q*<br />
Q<br />
Figure 12.1 Expansionary fiscal policy. In the recession phase government may increase its expenditures or<br />
reduce taxes to support aggregate demand and output.<br />
12.1.2. Restrictive Fiscal Policy<br />
Contractionary or restrictive fiscal policy may be used to slow down the process of<br />
rapidly growing aggregate demand. A very fast rise in aggregate demand resulted from a<br />
large increase in investment; consumption or net export spending can result in demand-pull<br />
inflation. To control it, government can decrease government expenditures (1), increase<br />
taxes (2), or use some combination of these two policies (3). In that case of demand-pull<br />
inflation, the mentioned fiscal actions might bring the government budget towards its<br />
surplus when tax revenues exceeds government expenditures.