MacroeconomicsI_working_version (1)
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Fiscal Policy in Details 113<br />
However, the tax cuts also affect aggregate supply. The economists supporting the idea of<br />
deliberate influencing aggregate supply conclude that the aggregate supply curve moves to<br />
the right from AS to AS’ due to tax cuts. This is the domain of supply-side economics.<br />
The supply-side economists suggest three main reasons to explain the impact of reduced<br />
taxes on aggregate supply 2 :<br />
1) Saving and investment. Reduced taxes will increase disposable incomes,<br />
increasing household saving. Tax reductions on businesses will also increase the<br />
profitability of investment. In brief, lower taxes will increase saving and<br />
investment, increasing the rate of capital accumulation. The size of the potential<br />
production capacity of the economy will grow more rapidly.<br />
2) Work motivation. Reduced personal income tax rates also increase after-tax wages<br />
from work and thus increase work incentives. Many people not already in the<br />
labour force will offer their services because after-tax wages are higher. Those<br />
already in the labour force will want to work more hours and take fewer vacations.<br />
3) Risk bearing. Lower tax rates encourage taking risks. Individuals and businesses<br />
will be more motivated and willing to risk their energies and financial capital on<br />
new production methods and new products when lower tax rates ensure a larger<br />
potential after-tax profit.<br />
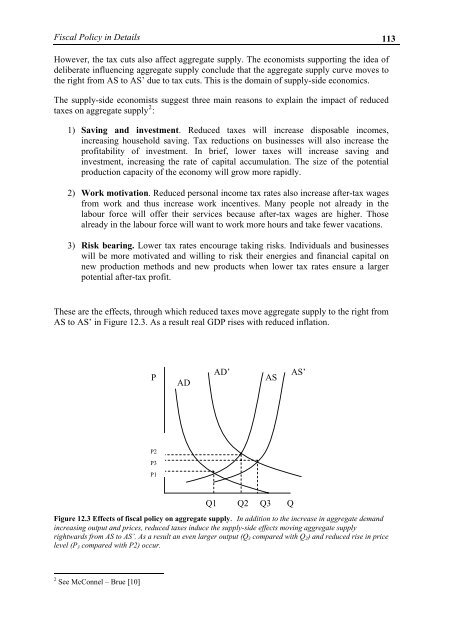
These are the effects, through which reduced taxes move aggregate supply to the right from<br />
AS to AS’ in Figure 12.3. As a result real GDP rises with reduced inflation.<br />
P<br />
AD<br />
AD’<br />
AS<br />
AS’<br />
P2<br />
P3<br />
P1<br />
Q1 Q2 Q3<br />
Figure 12.3 Effects of fiscal policy on aggregate supply. In addition to the increase in aggregate demand<br />
increasing output and prices, reduced taxes induce the supply-side effects moving aggregate supply<br />
rightwards from AS to AS’. As a result an even larger output (Q 3 compared with Q 2 ) and reduced rise in price<br />
level (P 3 compared with P2) occur.<br />
Q<br />
2 See McConnel – Brue [10]