Introducing
IntroducingWindowsServer2016_ebook
IntroducingWindowsServer2016_ebook
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Firewalls<br />
Every container host has a set of firewall rules turned on by default, the firewall rules are configured<br />
with a default set. If you want containers to be pingable (ICMP) or receive an IP Address from DHCP,<br />
you need to ensure that the container host has these rules turned on. To allow different traffic types<br />
into the containers you also will need to configure additional rules.<br />
If you are using NAT and decide to turn on port forwarding for the containers, the firewall rules will be<br />
automatically created for you during configuration.<br />
Troubleshooting<br />
Docker no longer keeps a separate log file; it logs all events to the Application Log in Event Viewer.<br />
You can filter based on source equal to Docker and retrieve all of its events or you can use Windows<br />
PowerShell to review the log, as well, by using the following code:<br />
Get-EventLog -LogName Application -Source Docker<br />
You could also start Docker in debug mode by using this:<br />
Dockerd.exe -D<br />
Or, use the docker configuration file (you can locate this file [or place it if it does not exist] at<br />
C:\ProgramData\docker\config\daemon.json) to start debug mode as follows:<br />
{<br />
}<br />
"debug": true<br />
Installing containers<br />
To use Windows Server Containers, you must first install the Containers feature. Further, if you would<br />
like to also use Hyper-V Containers, you will have to also install the Hyper-V feature.<br />
You will then need to install and set up Docker, which does not come with Windows Server 2016.<br />
More info Follow the URL for details on how to set up these feature and how to install and set up<br />
Docker, go to https://aka.ms/windowscontainers and read the Quick Start guides.<br />
Rules for containers<br />
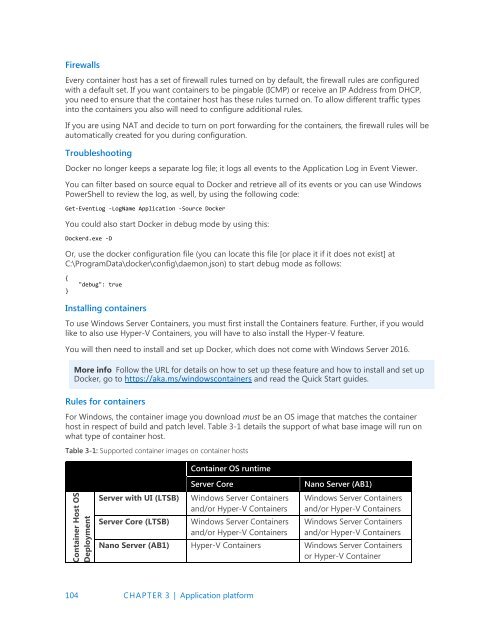
For Windows, the container image you download must be an OS image that matches the container<br />
host in respect of build and patch level. Table 3-1 details the support of what base image will run on<br />
what type of container host.<br />
Table 3-1: Supported container images on container hosts<br />
Container OS runtime<br />
Container Host OS<br />
Deployment<br />
Server with UI (LTSB)<br />
Server Core (LTSB)<br />
Server Core<br />
Windows Server Containers<br />
and/or Hyper-V Containers<br />
Windows Server Containers<br />
and/or Hyper-V Containers<br />
Nano Server (AB1)<br />
Windows Server Containers<br />
and/or Hyper-V Containers<br />
Windows Server Containers<br />
and/or Hyper-V Containers<br />
Nano Server (AB1) Hyper-V Containers Windows Server Containers<br />
or Hyper-V Container<br />
104 CHAPTER 3 | Application platform