C H A P T E R 5 Analytic Trigonometry
C H A P T E R 5 Analytic Trigonometry
C H A P T E R 5 Analytic Trigonometry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
450 Chapter 5 <strong>Analytic</strong> <strong>Trigonometry</strong><br />
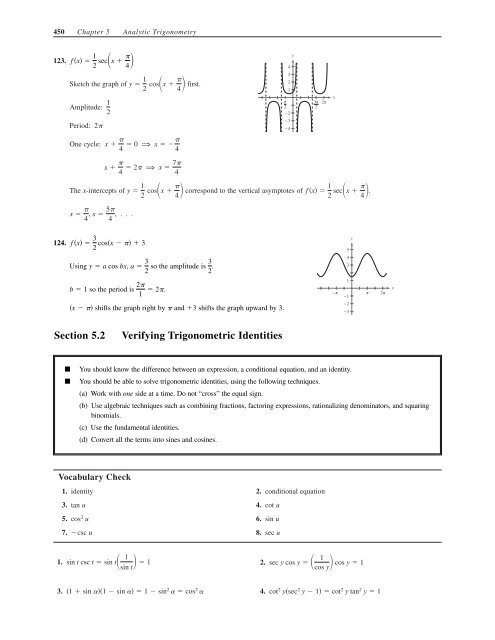
123.<br />
Sketch the graph of y first.<br />
1<br />
f x <br />
<br />
cosx <br />
2 1 <br />
secx <br />
2 4<br />
124.<br />
Amplitude:<br />
Period:<br />
2<br />
One cycle:<br />
1<br />
2<br />
The x-intercepts of correspond to the vertical asymptotes of f x .<br />
1 <br />
y secx <br />
2 1 <br />
cosx <br />
2<br />
x 5<br />
, x , . . .<br />
4 4<br />
Vocabulary Check<br />
x <br />
0 ⇒ x <br />
4 4<br />
x <br />
7<br />
2 ⇒ x <br />
4 4<br />
f x 3<br />
cosx 3<br />
2<br />
2<br />
1. identity 2. conditional equation<br />
3. tan u 4. cot u<br />
5. cos 6. sin u<br />
2 u<br />
7. csc u<br />
8. sec u<br />
4<br />
4<br />
3<br />
Using so the amplitude is<br />
2 .<br />
3<br />
y a cos bx, a <br />
2<br />
b 1 so the period is 2.<br />
1<br />
x shifts the graph right by and 3 shifts the graph upward by 3.<br />
1. sin t csc t sin t 1<br />
sin t 1 2. sec y cos y 1<br />
cos y 1<br />
cos y<br />
3. 1 sin 1 sin 1 sin 2 cos 2 <br />
<br />
Section 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
π<br />
2<br />
−2<br />
−3<br />
−4<br />
y<br />
3π 2π<br />
2<br />
4<br />
4. cot 2 ysec 2 y 1 cot 2 y tan 2 y 1<br />
x<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
1<br />
−2<br />
−3<br />
y<br />
−π<br />
π 2π<br />
−1<br />
■ You should know the difference between an expression, a conditional equation, and an identity.<br />
■ You should be able to solve trigonometric identities, using the following techniques.<br />
(a) Work with one side at a time. Do not “cross” the equal sign.<br />
(b) Use algebraic techniques such as combining fractions, factoring expressions, rationalizing denominators, and squaring<br />
binomials.<br />
(c) Use the fundamental identities.<br />
(d) Convert all the terms into sines and cosines.<br />
x