Pharmaceutical botany - Lighthouse Survival Blog
Pharmaceutical botany - Lighthouse Survival Blog
Pharmaceutical botany - Lighthouse Survival Blog
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
MEDULLARY RAYS 9<br />
Tracheary tissue consists of tracheae (ducts or vessels) and tracheids,<br />
both of which are found in the xylem region of the fibrovascular bundle<br />
and have as their function the conduction of water with mineral salts in<br />
solution from the roots upward. The tracheae or ducts are elongated,<br />
slightly lignefied tubes with occasional cross-walls and having character-<br />
istic thickenings on their inner surface. Tracheae are classified as:<br />
Annular, with ring-like thickenings.<br />
Spiral, with spiral thickenings.<br />
Reticulate, with reticulate thickenings.<br />
Porous or Pitted with spherical or oblique slit pores.<br />
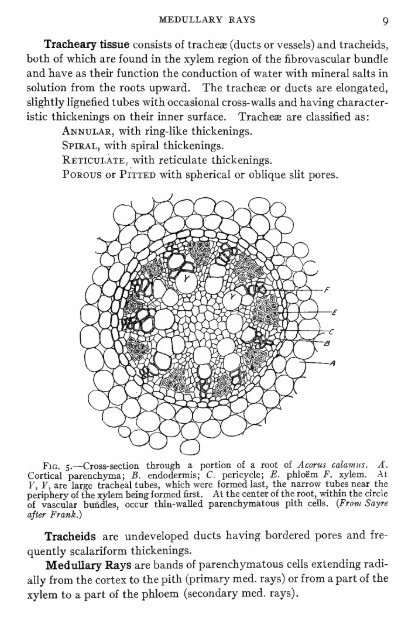
Fig. 5.—Cross-section through a portion of a root of Acorus calamus. A.<br />
Cortical parenchyma; B. endodermis; C. pericycle; E. phloem F. xylem. At<br />
Y, Y, are large tracheal tubes, which were formed last, the narrow tubes near the<br />
periphery of the xylem being formed first. At the center of the root, within the circle<br />
of vascular buiidles, occur thin-waUed parenchymatous pith cells. {From Sayre<br />
after Frank.)<br />
Tracheids are undeveloped ducts having bordered pores and fre-<br />
quently scalariform thickenings.<br />
Medullary Rays are bands of parenchymatous cells extending radi-<br />
ally from the cortex to the pith (primary med. rays) or from a part of the<br />
xylem to a part of the phloem (secondary med. rays).