Pharmaceutical botany - Lighthouse Survival Blog
Pharmaceutical botany - Lighthouse Survival Blog
Pharmaceutical botany - Lighthouse Survival Blog
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
HISTOLOGY OF ANNUAL DICOTYL STEM 23<br />
Scaly bulbs have narrow imbricated scales, the outer ones not en-<br />
closing the inner. Ex. : Lily.<br />
Tltbers and corms are annual. Bulbs and Rhizomes are perennial.<br />
Exogenous and Endogenous Stems.— Exogenous stems are typical<br />
of Gymnosperms and Dicotyledons and can increase materially in thick-<br />
ness due to presence of a cambium. Such stems show differentiation<br />
into an outer or cortical region and an inner or central cylinder region.<br />
Endogenous stems are _<br />
typical of Monocotyledons<br />
.««(^^^^^^^5llBfc^ ^<br />
and cannot increase mate- ^4lr7^||^^SjH^|^|£^^ ]-)<br />
rially in thickness due to absence<br />
of cambium. Such<br />
stems show no' differentia-<br />
tion into cortical and central<br />
regions.<br />
Histology of Annual<br />
Dicotyl Stem.— (In both an-<br />
nual and perennial dicotyl-<br />
edonous stems endodermis<br />
and pericambium are rarely<br />
seen since each has become<br />
so similar to cortex through<br />
passage of food, etc.)<br />
1. Epidermis, cutinized,<br />
with hairs.<br />
2. Cortex composed of<br />
three zones : an outer or exo-<br />
cortex, whose cells are thin<br />
walled and contain chloro-<br />
plasts; a middle or medio-<br />
cortex, consisting of cells of<br />
indurated walls giving extreme pliability and strength, an inner or endo-<br />
cortex, a very broad zone of thin and thicked-walled parenchyme cells.<br />
3. The innermost layer of cells of the cortex called the endodermis.<br />
(Not generally distinguishable.)<br />
4. Pericambium. (Not generally distinguishable.)<br />
5. Fibrovascular bundles of open collateral type arranged in a<br />
circle with primary medullary rays between the bundles.<br />
6. Pith.<br />
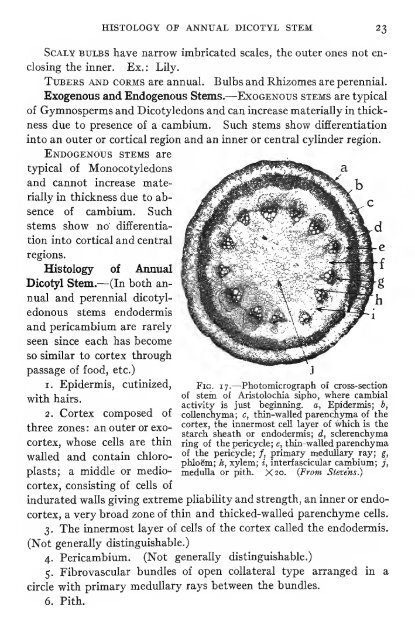
Fig. 17.—Photomicrograph of cross-section<br />
of stein of Aristolochia sipho, where cambial<br />
activity is just beginning, a, Epidermis; b,<br />
collenchyma; c, thin-walled parenchyma of the<br />
cortex, the innermost cell layer of which is the<br />
starch sheath or endodermis; d, sclerenchyma<br />
ring of the pericycle; e, thin-walled parenchyma<br />
of the pericycle; /, primary medullary ray; g,<br />
phloem; h, xylem; i, interfascicular cambium; j,<br />
medulla or pith. X20. {From Stevens.)