Scientific Theme: Advanced Modeling and Observing Systems
Scientific Theme: Advanced Modeling and Observing Systems
Scientific Theme: Advanced Modeling and Observing Systems
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Complementary Research: Innovative Research Program<br />
brings together researchers from different disciplines. The ASG was originally designed as a downlooking<br />
instrument for observations of surface reflectance properties. With the use of methods from the atmospheric<br />
sciences, the instrument can be applied to a very different <strong>and</strong> important problem in aerosol <strong>and</strong> climate science.<br />
Research Plan. Radiometric retrievals of atmospheric aerosol properties require observations under cloudless<br />
conditions. In most cases, aerosol characteristics remain constant throughout a given day, though rapid changes are<br />
also possible when dictated by variations in meteorology <strong>and</strong> source strength. In order to incorporate as much of this<br />
variability as possible in our measurements, deployments will be made on clear sky days as often as possible<br />
throughout the year. Full sky-radiance scan will consist of measurements obtained at approximately 100 scattering<br />
angles, either in the principal plane, or at constant zenith viewing angle. This large number of sky-radiance samples<br />
will allow for the identification <strong>and</strong> removal of views contaminated by sub-visual cirrus clouds <strong>and</strong> to correct for<br />
angular pointing errors.<br />
The robot will be programmed to produce up to 10 sky-radiance scans per hour, which is about an order of<br />
magnitude greater than the typical sample rate from AERONET. The availability of several scans per hour will help<br />
differentiate the effects of natural aerosol variation from noise introduced by scene conditions (e.g., sub-visual<br />
cirrus). St<strong>and</strong>ard data products available from the AERONET Cimel sunphotometers are produced from<br />
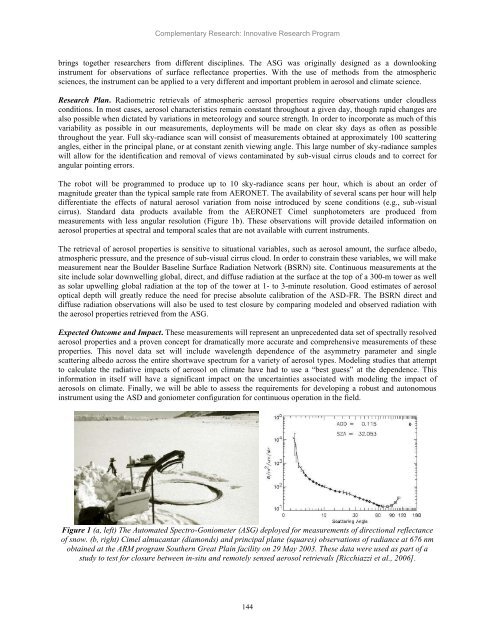
measurements with less angular resolution (Figure 1b). These observations will provide detailed information on<br />
aerosol properties at spectral <strong>and</strong> temporal scales that are not available with current instruments.<br />
The retrieval of aerosol properties is sensitive to situational variables, such as aerosol amount, the surface albedo,<br />
atmospheric pressure, <strong>and</strong> the presence of sub-visual cirrus cloud. In order to constrain these variables, we will make<br />
measurement near the Boulder Baseline Surface Radiation Network (BSRN) site. Continuous measurements at the<br />
site include solar downwelling global, direct, <strong>and</strong> diffuse radiation at the surface at the top of a 300-m tower as well<br />
as solar upwelling global radiation at the top of the tower at 1- to 3-minute resolution. Good estimates of aerosol<br />
optical depth will greatly reduce the need for precise absolute calibration of the ASD-FR. The BSRN direct <strong>and</strong><br />
diffuse radiation observations will also be used to test closure by comparing modeled <strong>and</strong> observed radiation with<br />
the aerosol properties retrieved from the ASG.<br />
Expected Outcome <strong>and</strong> Impact. These measurements will represent an unprecedented data set of spectrally resolved<br />
aerosol properties <strong>and</strong> a proven concept for dramatically more accurate <strong>and</strong> comprehensive measurements of these<br />
properties. This novel data set will include wavelength dependence of the asymmetry parameter <strong>and</strong> single<br />
scattering albedo across the entire shortwave spectrum for a variety of aerosol types. <strong>Modeling</strong> studies that attempt<br />
to calculate the radiative impacts of aerosol on climate have had to use a ―best guess‖ at the dependence. This<br />
information in itself will have a significant impact on the uncertainties associated with modeling the impact of<br />
aerosols on climate. Finally, we will be able to assess the requirements for developing a robust <strong>and</strong> autonomous<br />
instrument using the ASD <strong>and</strong> goniometer configuration for continuous operation in the field.<br />
Figure 1 (a, left) The Automated Spectro-Goniometer (ASG) deployed for measurements of directional reflectance<br />
of snow. (b, right) Cimel almucantar (diamonds) <strong>and</strong> principal plane (squares) observations of radiance at 676 nm<br />
obtained at the ARM program Southern Great Plain facility on 29 May 2003. These data were used as part of a<br />
study to test for closure between in-situ <strong>and</strong> remotely sensed aerosol retrievals [Ricchiazzi et al., 2006].<br />
144