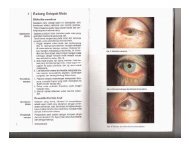
- Page 1 and 2:
CONTEMPORARY ENDOCRINOLOGY Androgen
- Page 3 and 4:
CONTEMPORARY ENDOCRINOLOGY P. Micha
- Page 5 and 6:
© 2003 Humana Press Inc. 999 River
- Page 7 and 8:
vi Preface We hope Androgens in Hea
- Page 9 and 10:
viii Contents 13 Androgens and Body
- Page 11 and 12:
x Contributors RICHARD S. LEGRO, MD
- Page 13 and 14:
2 Winters and Clark
- Page 15 and 16:
4 Winters and Clark chorionic gonad
- Page 17 and 18:
6 Winters and Clark LH REGULATION O
- Page 19 and 20:
8 Winters and Clark These enzymes a
- Page 21 and 22:
10 Winters and Clark -subunit mRNA
- Page 23 and 24:
12 Winters and Clark Fig. 3. A sche
- Page 25 and 26:
14 Winters and Clark Table 1 Factor
- Page 27 and 28:
16 Winters and Clark Table 2 Tissue
- Page 29 and 30:
18 Winters and Clark 11. Thomas JL,
- Page 31 and 32:
20 Winters and Clark 61. Dufau ML,
- Page 33 and 34:
22 Winters and Clark 112. Raivio T,
- Page 35 and 36:
24 Brown Fig. 1. Mechanism for andr
- Page 37 and 38:
26 Brown increase in intracellular
- Page 39 and 40:
28 Brown Fig. 2. Structural and fun
- Page 41 and 42:
30 Brown Fig. 3. Amino acid sequenc
- Page 43 and 44:
32 Brown tions to shuttle the AR th
- Page 45 and 46:
34 Brown Fig. 4. Amino acid primary
- Page 47 and 48:
36 Brown part of an inactive chroma
- Page 49 and 50:
38 Brown the external genitalia is
- Page 51 and 52:
40 Brown tors, as well as the trans
- Page 53 and 54:
42 Brown 49. Williams SP, Sigler PB
- Page 55 and 56:
44 Brown 100. Gregory CW, He B, Joh
- Page 57 and 58:
46 Plymate Table 1 Classification o
- Page 59 and 60:
48 Plymate In addition to the direc
- Page 61 and 62:
50 Plymate LABORATORY FINDINGS In p
- Page 63 and 64:
52 Plymate those manifesting as phe
- Page 65 and 66:
54 Plymate result in some improveme
- Page 67 and 68:
56 Plymate If both testosterone and
- Page 69 and 70:
58 Plymate Persistent Müllerian Du
- Page 71 and 72:
60 Plymate INFERTILITY RESULTING FR
- Page 73 and 74:
62 Plymate unaffected, contralatera
- Page 75 and 76:
64 Plymate SECONDARY HYPOGONADISM H
- Page 77 and 78:
66 Plymate Other syndromes manifest
- Page 79 and 80:
68 Plymate period after the burn. I
- Page 81 and 82:
70 Plymate These findings suggest t
- Page 83 and 84:
72 Plymate 49. Goebelsmann U, Horto
- Page 85 and 86:
74 Plymate 104. Yoshimoto Y, Moride
- Page 87 and 88:
76 Plymate
- Page 89 and 90:
78 Sutton, Amory, and Clark levels
- Page 91 and 92:
80 Sutton, Amory, and Clark cebo in
- Page 93 and 94:
82 Sutton, Amory, and Clark Finaste
- Page 95 and 96:
84 Sutton, Amory, and Clark through
- Page 97 and 98:
86 Sutton, Amory, and Clark 40. The
- Page 99 and 100:
88 Sutton, Amory, and Clark 88. Rob
- Page 101 and 102:
90 Lindzey and Korach Fig. 1. Cellu
- Page 103 and 104:
92 Lindzey and Korach estrogen sign
- Page 105 and 106:
94 Lindzey and Korach TESTIS AND DU
- Page 107 and 108:
96 Lindzey and Korach sufficient to
- Page 109 and 110:
98 Lindzey and Korach Seminal Vesic
- Page 111 and 112:
100 Lindzey and Korach 17. Krege JH
- Page 113 and 114:
102 Lindzey and Korach 68. Chang WY
- Page 115 and 116:
104 McPhaul on the Y chromosome det
- Page 117 and 118:
106 106 McPhaul
- Page 119 and 120:
108 McPhaul number of alleles, dele
- Page 121 and 122:
110 McPhaul The first mutation of t
- Page 123 and 124:
112 McPhaul gene. In vitro studies
- Page 125 and 126:
114 McPhaul risk of impaired sperma
- Page 127 and 128:
116 McPhaul carrying a single mutan
- Page 129 and 130:
118 McPhaul REFERENCES 1. Koopman P
- Page 131 and 132:
120 McPhaul 45. Weidemann W, Peters
- Page 133 and 134:
122 McPhaul 92. Koivisto P, Kononen
- Page 135 and 136:
124 Legro Fig. 1. The spectrum of p
- Page 137 and 138:
126 Legro Virilization presents wit
- Page 139 and 140:
128 Legro Fig. 3. The paradox of an
- Page 141 and 142:
130 Legro small high-density athero
- Page 143 and 144:
132 Legro Table 2 Syndromes or Dise
- Page 145 and 146:
134 Legro Insulin-Sensitizing Agent
- Page 147 and 148:
136 Legro is undetermined according
- Page 149 and 150:
138 Legro 39. Lee O, Farquhar C, To
- Page 151 and 152:
140 Legro
- Page 153 and 154:
142 Wang and Swerdloff PHARMACOLOGY
- Page 155 and 156:
144 Wang and Swerdloff The 17α-alk
- Page 157 and 158:
146 Wang and Swerdloff Table 2 Dose
- Page 159 and 160:
148 Wang and Swerdloff The steroid
- Page 161 and 162:
150 Wang and Swerdloff The inabilit
- Page 163 and 164:
152 Wang and Swerdloff 15. De Lorim
- Page 165 and 166:
154 Wang and Swerdloff
- Page 167 and 168:
156 Marcelli et al.
- Page 169 and 170:
158 Marcelli et al. Differentiated
- Page 171 and 172:
160 Marcelli et al. These coactivat
- Page 173 and 174:
162 Marcelli et al. tigators have e
- Page 175 and 176:
164 Marcelli et al. AR in Prostate
- Page 177 and 178:
166 Marcelli et al. Table 1 Androge
- Page 179 and 180:
168 Marcelli et al. A molecular exp
- Page 181 and 182:
170 Marcelli et al. The above data
- Page 183 and 184:
172 Marcelli et al. up to 9 yr late
- Page 185 and 186:
174 Marcelli et al. Three major pha
- Page 187 and 188:
176 Marcelli et al. vitro model of
- Page 189 and 190:
178 Marcelli et al. yr, survival wa
- Page 191 and 192:
180 Marcelli et al. 26. McKenna NJ,
- Page 193 and 194:
182 Marcelli et al. 78. Isaacs J, C
- Page 195 and 196:
184 Marcelli et al. 126. Watanabe M
- Page 197 and 198:
186 Marcelli et al. 177. Kousteni S
- Page 199 and 200:
188 Marcelli et al. 231. Colombel M
- Page 201 and 202:
190 Marcelli et al.
- Page 203 and 204:
192 Wu and von Eckardstein contrace
- Page 205 and 206:
194 Wu and von Eckardstein beam com
- Page 207 and 208:
196 Wu and von Eckardstein excess o
- Page 209 and 210:
198 Wu and von Eckardstein Endogeno
- Page 211 and 212:
Table 3 Change in Lipids in Hypogon
- Page 213 and 214:
Table 3 (continued) ∆LDL ∆HDL
- Page 215 and 216:
204 Wu and von Eckardstein THE HEMO
- Page 217 and 218:
206 Wu and von Eckardstein In vivo
- Page 219 and 220:
208 Wu and von Eckardstein (uptake
- Page 221 and 222:
210 Wu and von Eckardstein 4. Bhasi
- Page 223 and 224:
212 Wu and von Eckardstein 57. Barr
- Page 225 and 226:
214 Wu and von Eckardstein 107. Fra
- Page 227 and 228:
216 Wu and von Eckardstein 152. Zmu
- Page 229 and 230:
218 Wu and von Eckardstein 201. Cho
- Page 231 and 232:
220 Wu and von Eckardstein 250. Eic
- Page 233 and 234:
222 Kenny and Raisz with a cartilag
- Page 235 and 236:
224 Kenny and Raisz METABOLISM OF A
- Page 237 and 238:
226 Kenny and Raisz The level of th
- Page 239 and 240:
228 Kenny and Raisz REFERENCES 1. G
- Page 241 and 242:
230 Kenny and Raisz 51. Morishima A
- Page 243 and 244:
232 Kenny and Raisz 103. Snyder PJ,
- Page 245 and 246:
234 Basaria and Dobs losses in wome
- Page 247 and 248:
236 Basaria and Dobs 15 dialysis pa
- Page 249 and 250:
238 Basaria and Dobs duced remissio
- Page 251 and 252: 240 Basaria and Dobs hematocrit lev
- Page 253 and 254: 242 Basaria and Dobs 40. Sanchez-Me
- Page 255 and 256: 244 Katznelson in men with testoste
- Page 257 and 258: 246 Katznelson Fig. 1. Body weight,
- Page 259 and 260: 248 Katznelson change during treatm
- Page 261 and 262: 250 Katznelson testosterone or free
- Page 263 and 264: 252 Katznelson disproportionate dec
- Page 265 and 266: 254 Katznelson have been additional
- Page 267 and 268: 256 Katznelson 18. Marin P, Lonn L,
- Page 269 and 270: 258 Katznelson 71. Davis SR, McClou
- Page 271 and 272: 260 Bancroft Androgen Deficiency an
- Page 273 and 274: 262 Bancroft studies had presented
- Page 275 and 276: 264 Bancroft Bagatell et al. (36) g
- Page 277 and 278: 266 Bancroft much larger group of a
- Page 279 and 280: 268 Bancroft In a report of a serie
- Page 281 and 282: 270 Bancroft onset was related to a
- Page 283 and 284: 272 Bancroft Particularly confusing
- Page 285 and 286: 274 Bancroft 4. Studies using place
- Page 287 and 288: 276 Bancroft either E and T or plac
- Page 289 and 290: 278 Bancroft cytotoxic therapy supp
- Page 291 and 292: 280 Bancroft Women with Endocrine A
- Page 293 and 294: 282 Bancroft in response to the fil
- Page 295 and 296: 284 Bancroft Men are much more awar
- Page 297 and 298: 286 Bancroft 22. Morales A, Johnsto
- Page 299 and 300: 288 Bancroft 78. Hyde JS, DeLamater
- Page 301: 290 Bancroft 129. Appelt H, Strauss
- Page 305 and 306: 294 Cherrier and Craft ment of the
- Page 307 and 308: 296 Cherrier and Craft information
- Page 309 and 310: 298 Cherrier and Craft Fig. 3. Wech
- Page 311 and 312: 300 Cherrier and Craft gen excess r
- Page 313 and 314: 302 Cherrier and Craft occurring wi
- Page 315 and 316: 304 Cherrier and Craft gesting that
- Page 317 and 318: 306 Cherrier and Craft 39. Gouchie
- Page 319 and 320: 308 Cherrier and Craft 94. Kelso WM
- Page 321 and 322: 310 Cherrier and Craft
- Page 323 and 324: 312 Matsumoto
- Page 325 and 326: 314 Matsumoto long-term benefits an
- Page 327 and 328: 316 Matsumoto manifestations (7). F
- Page 329 and 330: 318 Formulation Usual adult dosage
- Page 331 and 332: 320 Matsumoto Fig. 1. Mean serum T
- Page 333 and 334: 322 Matsumoto dosage is increased g
- Page 335 and 336: 324 Matsumoto Androgel 5 g (50 mg o
- Page 337 and 338: 326 Matsumoto gen receptor and tiss
- Page 339 and 340: 328 Matsumoto such as hepatic cirrh
- Page 341 and 342: 330 Matsumoto occasionally, more se
- Page 343 and 344: 332 Matsumoto 27. Bhasin S, Bremner
- Page 345 and 346: 334 Matsumoto 77. Dobs AS, Meikle A
- Page 347 and 348: 336 Richmond and Rogol PHYSIOLOGY O
- Page 349 and 350: 338 Richmond and Rogol activity (28
- Page 351 and 352: 340 Richmond and Rogol increase lin
- Page 353 and 354:
342 Richmond and Rogol curve, the h
- Page 355 and 356:
344 Richmond and Rogol Permanent hy
- Page 357 and 358:
346 Richmond and Rogol 46. Stanhope
- Page 359 and 360:
348 Tenover In aging men, the combi
- Page 361 and 362:
350 Tenover Table 1 Changes in Andr
- Page 363 and 364:
352 Tenover studies in which eugona
- Page 365 and 366:
354 Tenover Table 3 Testosterone Th
- Page 367 and 368:
356 Tenover Table 5 ART in Older Me
- Page 369 and 370:
358 Tenover be overcome with either
- Page 371 and 372:
360 Tenover Laboratory tests should
- Page 373 and 374:
362 Tenover 40. Kohrt WM, Malley MT
- Page 375 and 376:
364 Tenover 95. Mooradian AD, Morle
- Page 377 and 378:
366 Davis Table 1 Proposed Androgen
- Page 379 and 380:
368 Davis transdermal testosterone
- Page 381 and 382:
370 Davis increase in circulating t
- Page 383 and 384:
372 Davis (93). Most recently, Zhou
- Page 385 and 386:
374 Davis Table 4 Androgen Replacem
- Page 387 and 388:
376 Davis 8. Vierhapper H, Nowotny
- Page 389 and 390:
378 Davis 60. Simberg N, Titinen A,
- Page 391 and 392:
380 Davis
- Page 393 and 394:
382 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer h
- Page 395 and 396:
384 Table 2 Effects of Testosterone
- Page 397 and 398:
386 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer e
- Page 399 and 400:
388 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer F
- Page 401 and 402:
390 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer t
- Page 403 and 404:
Table 3 Effects of Testosterone Sup
- Page 405 and 406:
Table 4 Effects of Testosterone Sup
- Page 407 and 408:
396 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer c
- Page 409 and 410:
398 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer C
- Page 411 and 412:
400 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer w
- Page 413 and 414:
402 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer 4
- Page 415 and 416:
404 Bhasin, Woodhouse, and Storer
- Page 417 and 418:
406 Amory Fig. 1. The endocrinology
- Page 419 and 420:
408 Amory pregnancies fathered by t
- Page 421 and 422:
410 Amory antagonists can suppress
- Page 423 and 424:
412 Amory 100-mg doses of weekly TE
- Page 425 and 426:
414 Amory FUTURE DIRECTIONS Given t
- Page 427 and 428:
416 Amory 22. Oral contraception. I
- Page 429 and 430:
418 Amory
- Page 431 and 432:
420 Anawalt inadequate androgen eff
- Page 433 and 434:
422 Anawalt few specialty commercia
- Page 435 and 436:
424 Anawalt Fig. 1. (C) Secondary h
- Page 437 and 438:
426 Anawalt Fig. 2. Evaluation and
- Page 439 and 440:
428 Anawalt All men with secondary
- Page 441 and 442:
430 Anawalt anemia (38). With the a
- Page 443 and 444:
432 Anawalt osterone levels achieve
- Page 445 and 446:
434 Anawalt SIDE EFFECTS OF ANDROGE
- Page 447 and 448:
436 Anawalt 7. Rosner W. Errors in
- Page 449 and 450:
438 Anawalt 59. Mackey MA, Conway A
- Page 451 and 452:
440 Index polycystic ovaries, 131 A
- Page 453 and 454:
442 Index lipoid congenital adrenal
- Page 455 and 456:
444 Index women, 254 dihydrotestost
- Page 457 and 458:
446 Index Pituitary adenoma, male h
- Page 459 and 460:
448 Index lipoid congenital adrenal









![SISTEM SENSORY [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/20667975/1/190x245/sistem-sensory-compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)