Unified Access Point (AP) Administrator's Guide
Unified Access Point (AP) Administrator's Guide
Unified Access Point (AP) Administrator's Guide
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
D-Link <strong>Unified</strong> <strong>Access</strong> <strong>Point</strong> Administrator’s <strong>Guide</strong><br />
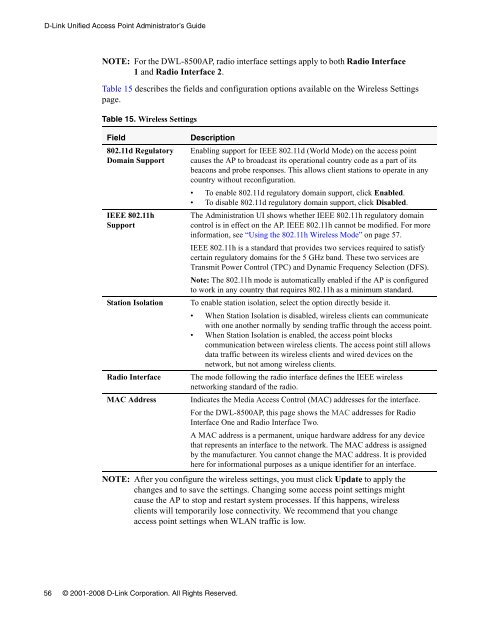
NOTE: For the DWL-8500<strong>AP</strong>, radio interface settings apply to both Radio Interface<br />
1 and Radio Interface 2.<br />
Table 15 describes the fields and configuration options available on the Wireless Settings<br />
page.<br />
Table 15. Wireless Settings<br />
Field Description<br />
802.11d Regulatory<br />
Domain Support<br />
IEEE 802.11h<br />
Support<br />
NOTE: After you configure the wireless settings, you must click Update to apply the<br />
changes and to save the settings. Changing some access point settings might<br />
cause the <strong>AP</strong> to stop and restart system processes. If this happens, wireless<br />
clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that you change<br />
access point settings when WLAN traffic is low.<br />
56 © 2001-2008 D-Link Corporation. All Rights Reserved.<br />
Enabling support for IEEE 802.11d (World Mode) on the access point<br />
causes the <strong>AP</strong> to broadcast its operational country code as a part of its<br />
beacons and probe responses. This allows client stations to operate in any<br />
country without reconfiguration.<br />
To enable 802.11d regulatory domain support, click Enabled.<br />
To disable 802.11d regulatory domain support, click Disabled.<br />
The Administration UI shows whether IEEE 802.11h regulatory domain<br />
control is in effect on the <strong>AP</strong>. IEEE 802.11h cannot be modified. For more<br />
information, see “Using the 802.11h Wireless Mode” on page 57.<br />
IEEE 802.11h is a standard that provides two services required to satisfy<br />
certain regulatory domains for the 5 GHz band. These two services are<br />
Transmit Power Control (TPC) and Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS).<br />
Note: The 802.11h mode is automatically enabled if the <strong>AP</strong> is configured<br />
to work in any country that requires 802.11h as a minimum standard.<br />
Station Isolation To enable station isolation, select the option directly beside it.<br />
When Station Isolation is disabled, wireless clients can communicate<br />
with one another normally by sending traffic through the access point.<br />
When Station Isolation is enabled, the access point blocks<br />
communication between wireless clients. The access point still allows<br />
data traffic between its wireless clients and wired devices on the<br />
network, but not among wireless clients.<br />
Radio Interface The mode following the radio interface defines the IEEE wireless<br />
networking standard of the radio.<br />
MAC Address Indicates the Media <strong>Access</strong> Control (MAC) addresses for the interface.<br />
For the DWL-8500<strong>AP</strong>, this page shows the MAC addresses for Radio<br />
Interface One and Radio Interface Two.<br />
A MAC address is a permanent, unique hardware address for any device<br />
that represents an interface to the network. The MAC address is assigned<br />
by the manufacturer. You cannot change the MAC address. It is provided<br />
here for informational purposes as a unique identifier for an interface.