DHIJWASv Software FEFLOW 6.1
DHIJWASv Software FEFLOW 6.1
DHIJWASv Software FEFLOW 6.1
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
SK=cáåáíÉJbäÉãÉåí=jÉëÜ<br />
qÜÉ= qêá~åÖäÉ= ãÉëÜ<br />
ÖÉåÉê~íçê= ÉåÖáåÉ= áë<br />
åçí= éêçîáÇÉÇ= ïáíÜ<br />
cbcilt>= cçê= ÇÉí~áäë= ~Äçìí<br />
Üçï= íç= çÄí~áå= íÜÉ= qêá~åÖäÉ<br />
ãÉëÜ= ÖÉåÉê~íçêI= ëÉÉ= íÜÉ<br />
cbcilt=ÜÉäé=ëóëíÉãK<br />
PS=ö=rëÉê=j~åì~ä<br />
is activated before you leave the dialog.<br />
To select the elements to be refined go back to the<br />
Supermesh view and click on Refinement Selection.<br />
Click on all segments of the line and of the edge<br />
that separates the two polygons. The selected edges are<br />
shown in green. Then click on Generate Mesh<br />
again. The resulting finite-element mesh with local<br />
refinement is shown in figure 6.7.<br />
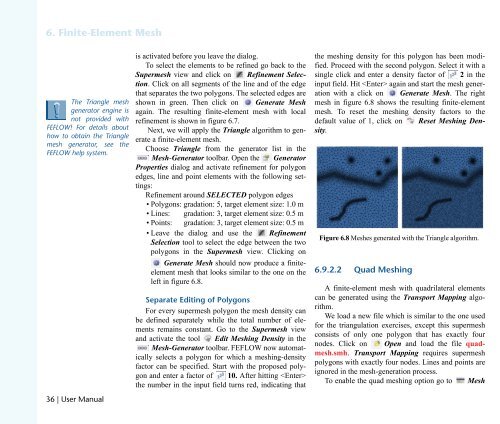
Next, we will apply the Triangle algorithm to generate<br />
a finite-element mesh.<br />
Choose Triangle from the generator list in the<br />
Mesh-Generator toolbar. Open the Generator<br />
Properties dialog and activate refinement for polygon<br />
edges, line and point elements with the following settings:<br />
Refinement around SELECTED polygon edges<br />
• Polygons: gradation: 5, target element size: 1.0 m<br />
• Lines: gradation: 3, target element size: 0.5 m<br />
• Points: gradation: 3, target element size: 0.5 m<br />
• Leave the dialog and use the Refinement<br />
Selection tool to select the edge between the two<br />
polygons in the Supermesh view. Clicking on<br />
Generate Mesh should now produce a finiteelement<br />
mesh that looks similar to the one on the<br />
left in figure 6.8.<br />
pÉé~ê~íÉ=bÇáíáåÖ=çÑ=mçäóÖçåë<br />
For every supermesh polygon the mesh density can<br />
be defined separately while the total number of elements<br />
remains constant. Go to the Supermesh view<br />
and activate the tool Edit Meshing Density in the<br />
Mesh-Generator toolbar. <strong>FEFLOW</strong> now automatically<br />
selects a polygon for which a meshing-density<br />
factor can be specified. Start with the proposed polygon<br />
and enter a factor of 10. After hitting <br />
the number in the input field turns red, indicating that<br />
the meshing density for this polygon has been modified.<br />
Proceed with the second polygon. Select it with a<br />
single click and enter a density factor of 2 in the<br />
input field. Hit again and start the mesh generation<br />
with a click on Generate Mesh. The right<br />
mesh in figure 6.8 shows the resulting finite-element<br />
mesh. To reset the meshing density factors to the<br />
default value of 1, click on Reset Meshing Density.<br />
Figure 6.8 Meshes generated with the Triangle algorithm.<br />
SKVKOKO nì~Ç=jÉëÜáåÖ<br />
A finite-element mesh with quadrilateral elements<br />
can be generated using the Transport Mapping algorithm.<br />
We load a new file which is similar to the one used<br />
for the triangulation exercises, except this supermesh<br />
consists of only one polygon that has exactly four<br />
nodes. Click on Open and load the file quadmesh.smh.<br />
Transport Mapping requires supermesh<br />
polygons with exactly four nodes. Lines and points are<br />
ignored in the mesh-generation process.<br />
To enable the quad meshing option go to Mesh