ECHINODERMATA - KU ScholarWorks - University of Kansas
ECHINODERMATA - KU ScholarWorks - University of Kansas
ECHINODERMATA - KU ScholarWorks - University of Kansas
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
30 THE UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS PALEONTOLOGICAL CONTRIBUTIONS<br />
differs in that Deltoschisma has a greatly reduced number<br />
<strong>of</strong> hydrospire slits on the anal side, whereas Polydeltoideus<br />
does not. In this respect, Polydeltoideus is considered<br />
more primitive than Deltoschisma, and it would<br />
be natural to assume that Deltoschisma was derived from<br />
Polydeltoideus by reduction in the number <strong>of</strong> hydrospire<br />
slits on the anal side.<br />
23<br />
Occurrence.—Devonian, Calizas de Ferr<strong>of</strong>ies, Asturias,<br />
Spain.<br />
Type.—Topotype, 13,876, one specimen in glass vial<br />
with five other specimens belonging to Pentremitidea,<br />
Gurley collection, Walker Museum, <strong>University</strong> <strong>of</strong> Chicago.<br />
Genus HYPEROBLASTUS Fay, n. gen.<br />
Type-species, by original designation (herein).—Pentremitidea preciosa<br />
REIMANN, 1945.<br />
Generic diagnosis.—Fissiculate blastoids with ten<br />
hidden hydrospire fields, aboral ends <strong>of</strong> outermost<br />
hydrospire slits exposed, however, and pores formed<br />
as gaps between side plates, five spiracles developed as<br />
gaps between deltoid lip, deltoid septum, lancet, and<br />
side plates on each interambulacrum, which includes<br />
anispiracle on the anal side; four anal deltoids, or a<br />
superdeltoid, two cryptodeltoids, and hypodeltoid<br />
present, lancet covered by side plates, club-shaped in<br />
side view. Devonian, North America (New York,<br />
Michigan, Indiana, Kentucky, Wisconsin, Ontario).<br />
Remarks.—The genus Hyperoblastus was probably<br />
derived from Polydeltoideus by closure <strong>of</strong> the<br />
radial and deltoid sinus areas against the side plates,<br />
thus bridging the gap between the Fissiculata and<br />
Spiraculata, by formation <strong>of</strong> pores and spiracles. Two<br />
species, H. filosus and H. preciosus are described in<br />
detail, others being only figured and compared by<br />
means <strong>of</strong> measurements and a few line drawings. The<br />
several species described by REIMANN (1935, 1945) are<br />
probably valid.<br />
HYPEROBLASTUS PRECIOSUS (Rennann)<br />
Plate 7, figures 1-8; text-figs. 26, 27<br />
Pentremitidea preci osa REIMANN, 1945, p. 39, pl. 8, figs. 1-3.<br />
Description.—Calyx calcitic, club-shaped in side view,<br />
' pentagonal in top view, 15.5 mm. long by 10.5 mm.<br />
wide, with periphery near mid-height, vault 11 mm. long,<br />
pelvis 4.5 mm. long, pelvic angle on basal circlet 55 degrees,<br />
and 120 degrees on radial bodies. Basal circlet 4<br />
25<br />
2-1<br />
MSS<br />
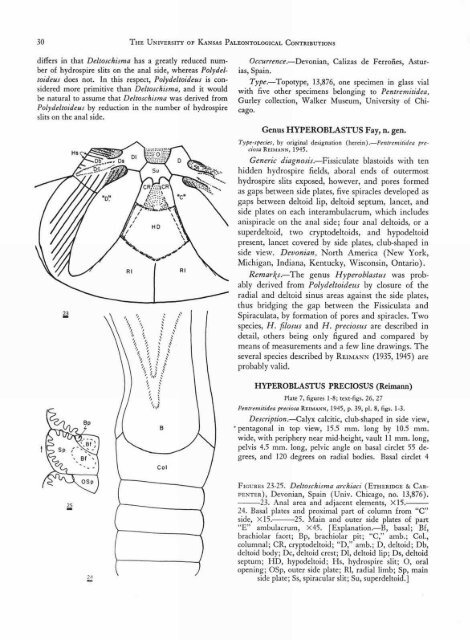
FIGURES 23-25. Deltoschisma archiaci (ETHERIDGE & CAR-<br />
PENTER), Devonian, Spain (Univ. Chicago, no. 13,876).<br />
23. Anal area and adjacent elements, X15.<br />
24. Basal plates and proximal part <strong>of</strong> column from "C"<br />
side, X15. 25. Main and outer side plates <strong>of</strong> part<br />
"E" ambulacrum, X45. [Explanation.—B, basal; Bf,<br />
brachiolar facet; Bp, brachiolar pit; "C," amb.; Col.,<br />
columnal; CR, cryptodeltoid; "D," amb.; D, deltoid; Db,<br />
deltoid body; Dc, deltoid crest; DI, deltoid lip; Ds, deltoid<br />
septum; HD, hypodeltoid; Hs, hydrospire slit; 0, oral<br />
opening; OSp, outer side plate; RI, radial limb; Sp, main<br />
side plate; Ss, spiracular slit; Su, superdeltoid.]