Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
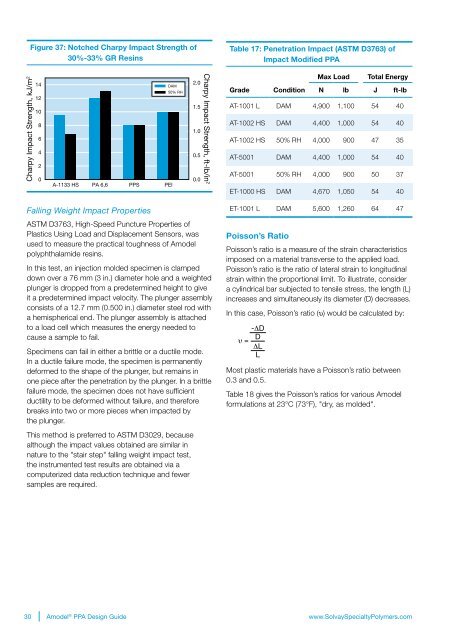
Figure 37: Notched Charpy Impact Strength of<br />
30%-33% GR Resins<br />
Table 17: Penetration Impact (ASTM D3763) of<br />
Impact Modified PPA<br />
Charpy Impact Strength, kJ/m 2<br />
14<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
A-1133 HS PA 6,6 PPS PEI<br />
DAM<br />
50% RH<br />
2.0<br />
1.5<br />
1.0<br />
0.5<br />
0.0<br />
Charpy Impact Strength, ft-lb/in 2<br />
Max Load Total Energy<br />
Grade Condition N lb J ft-lb<br />
AT-1001 L DAM 4,900 1,100 54 40<br />
AT-1002 HS DAM 4,400 1,000 54 40<br />
AT-1002 HS 50% RH 4,000 900 47 35<br />
AT-5001 DAM 4,400 1,000 54 40<br />
AT-5001 50% RH 4,000 900 50 37<br />
ET-1000 HS DAM 4,670 1,050 54 40<br />
Falling Weight Impact Properties<br />
ASTM D3763, High-Speed Puncture Properties of<br />
<strong>Plastics</strong> Using Load and Displacement Sensors, was<br />
used to measure the practical toughness of Amodel<br />
polyphthalamide resins.<br />
In this test, an injection molded specimen is clamped<br />
down over a 76 mm (3 in.) diameter hole and a weighted<br />
plunger is dropped from a predetermined height to give<br />
it a predetermined impact velocity. The plunger assembly<br />
consists of a 12.7 mm (0.500 in.) diameter steel rod with<br />
a hemispherical end. The plunger assembly is attached<br />
to a load cell which measures the energy needed to<br />
cause a sample to fail.<br />
Specimens can fail in either a brittle or a ductile mode.<br />
In a ductile failure mode, the specimen is permanently<br />
deformed to the shape of the plunger, but remains in<br />
one piece after the penetration by the plunger. In a brittle<br />
failure mode, the specimen does not have sufficient<br />
ductility to be deformed without failure, and therefore<br />
breaks into two or more pieces when impacted by<br />
the plunger.<br />
This method is preferred to ASTM D3029, because<br />
although the impact values obtained are similar in<br />
nature to the "stair step" falling weight impact test,<br />
the instrumented test results are obtained via a<br />
computerized data reduction technique and fewer<br />
samples are required.<br />
ET-1001 L DAM 5,600 1,260 64 47<br />
Poisson’s Ratio<br />
Poisson’s ratio is a measure of the strain characteristics<br />
imposed on a material transverse to the applied load.<br />
Poisson’s ratio is the ratio of lateral strain to longitudinal<br />
strain within the proportional limit. To illustrate, consider<br />
a cylindrical bar subjected to tensile stress, the length (L)<br />
increases and simultaneously its diameter (D) decreases.<br />
In this case, Poisson’s ratio (υ) would be calculated by:<br />
-ΔD<br />
D<br />
υ =<br />
ΔL<br />
L<br />
Most plastic materials have a Poisson’s ratio between<br />
0.3 and 0.5.<br />
Table 18 gives the Poisson’s ratios for various Amodel<br />
formulations at 23°C (73°F), "dry, as molded".<br />
30 Amodel ® PPA <strong>Design</strong> <strong>Guide</strong><br />
www.<strong>Solvay</strong>SpecialtyPolymers.com