Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
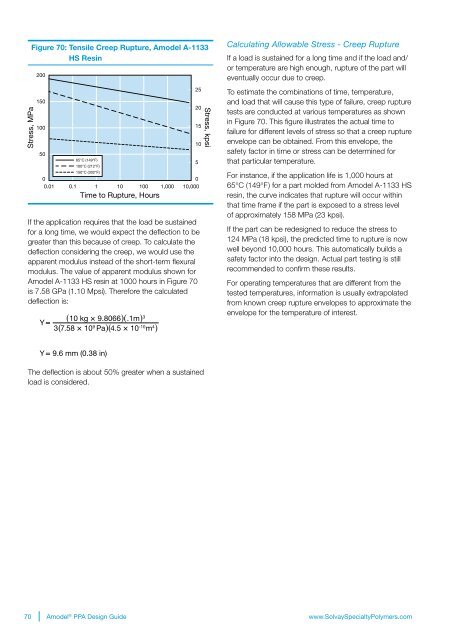
Stress, MPa<br />
Figure 70: Tensile Creep Rupture, Amodel A-1133<br />
HS Resin<br />
200<br />
150<br />
100<br />
50<br />
65°C (149°F)<br />
100°C (212°F)<br />
150°C (302°F)<br />
0<br />
0<br />
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1,000 10,000<br />
Time to Rupture, Hours<br />
If the application requires that the load be sustained<br />
for a long time, we would expect the deflection to be<br />
greater than this because of creep. To calculate the<br />
deflection considering the creep, we would use the<br />
apparent modulus instead of the short-term flexural<br />
modulus. The value of apparent modulus shown for<br />
Amodel A-1133 HS resin at 1000 hours in Figure 70<br />
is 7.58 GPa (1.10 Mpsi). Therefore the calculated<br />
deflection is:<br />
Y=<br />
(10 kg × 9.8066)(.1m) 3<br />
3(7.58 × 10 9 Pa)(4.5 × 10 -10 m 4 )<br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
Stress, kpsi<br />
Calculating Allowable Stress - Creep Rupture<br />
If a load is sustained for a long time and if the load and/<br />
or temperature are high enough, rupture of the part will<br />
eventually occur due to creep.<br />
To estimate the combinations of time, temperature,<br />
and load that will cause this type of failure, creep rupture<br />
tests are conducted at various temperatures as shown<br />
in Figure 70. This figure illustrates the actual time to<br />
failure for different levels of stress so that a creep rupture<br />
envelope can be obtained. From this envelope, the<br />
safety factor in time or stress can be determined for<br />
that particular temperature.<br />
For instance, if the application life is 1,000 hours at<br />
65°C (149°F) for a part molded from Amodel A-1133 HS<br />
resin, the curve indicates that rupture will occur within<br />
that time frame if the part is exposed to a stress level<br />
of approximately 158 MPa (23 kpsi).<br />
If the part can be redesigned to reduce the stress to<br />
124 MPa (18 kpsi), the predicted time to rupture is now<br />
well beyond 10,000 hours. This automatically builds a<br />
safety factor into the design. Actual part testing is still<br />
recommended to confirm these results.<br />
For operating temperatures that are different from the<br />
tested temperatures, information is usually extrapolated<br />
from known creep rupture envelopes to approximate the<br />
envelope for the temperature of interest.<br />
Y=<br />
9.6 mm (0.38 in)<br />
The deflection is about 50% greater when a sustained<br />
load is considered.<br />
70 Amodel ® PPA <strong>Design</strong> <strong>Guide</strong><br />
www.<strong>Solvay</strong>SpecialtyPolymers.com