Chapter 1 Minimum Flows and Levels - Southwest Florida Water ...
Chapter 1 Minimum Flows and Levels - Southwest Florida Water ...
Chapter 1 Minimum Flows and Levels - Southwest Florida Water ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
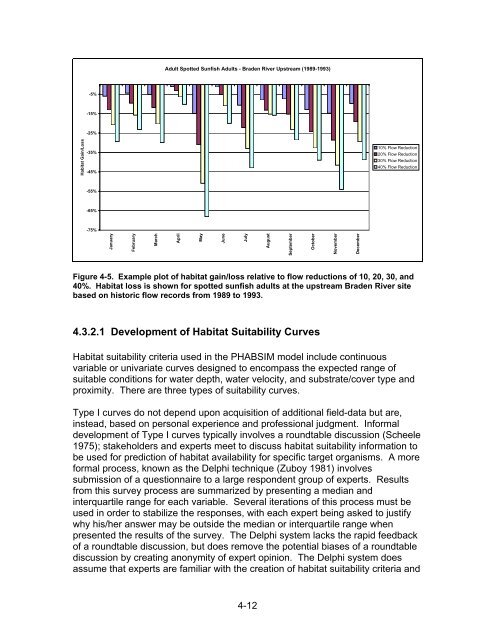
Adult Spotted Sunfish Adults - Braden River Upstream (1989-1993)<br />
-5%<br />
-15%<br />
Habitat Gain/Loss<br />
-25%<br />
-35%<br />
-45%<br />
10% Flow Reduction<br />
20% Flow Reduction<br />
30% Flow Reduction<br />
40% Flow Reduction<br />
-55%<br />
-65%<br />
-75%<br />
January<br />
February<br />
March<br />
April<br />
May<br />
June<br />
July<br />
August<br />
September<br />
October<br />
November<br />
December<br />
Figure 4-5. Example plot of habitat gain/loss relative to flow reductions of 10, 20, 30, <strong>and</strong><br />
40%. Habitat loss is shown for spotted sunfish adults at the upstream Braden River site<br />
based on historic flow records from 1989 to 1993.<br />
4.3.2.1 Development of Habitat Suitability Curves<br />
Habitat suitability criteria used in the PHABSIM model include continuous<br />
variable or univariate curves designed to encompass the expected range of<br />
suitable conditions for water depth, water velocity, <strong>and</strong> substrate/cover type <strong>and</strong><br />
proximity. There are three types of suitability curves.<br />
Type I curves do not depend upon acquisition of additional field-data but are,<br />
instead, based on personal experience <strong>and</strong> professional judgment. Informal<br />
development of Type I curves typically involves a roundtable discussion (Scheele<br />
1975); stakeholders <strong>and</strong> experts meet to discuss habitat suitability information to<br />
be used for prediction of habitat availability for specific target organisms. A more<br />
formal process, known as the Delphi technique (Zuboy 1981) involves<br />
submission of a questionnaire to a large respondent group of experts. Results<br />
from this survey process are summarized by presenting a median <strong>and</strong><br />
interquartile range for each variable. Several iterations of this process must be<br />
used in order to stabilize the responses, with each expert being asked to justify<br />
why his/her answer may be outside the median or interquartile range when<br />
presented the results of the survey. The Delphi system lacks the rapid feedback<br />
of a roundtable discussion, but does remove the potential biases of a roundtable<br />
discussion by creating anonymity of expert opinion. The Delphi system does<br />
assume that experts are familiar with the creation of habitat suitability criteria <strong>and</strong><br />
4-12