- Page 1 and 2:
D Living with Risk A global review
- Page 3 and 4:
Table of Contents Acknowledgements
- Page 5 and 6:
Bastien Affeltranger, France Tom Al
- Page 7 and 8:
Introduction This is a preliminary
- Page 9 and 10:
A more vulnerable world The trend s
- Page 11 and 12:
Journey to a safer world This revie
- Page 13 and 14:
Eruption of Mount Agung, Bali, Indo
- Page 15 and 16:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 17 and 18:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 19 and 20:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 21 and 22:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 23 and 24:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 25 and 26:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 27 and 28:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 29 and 30:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 31 and 32:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 33 and 34:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 35 and 36:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 37 and 38:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 39 and 40:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 41 and 42:
1 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 43 and 44:
Photo: J. Jenkins/PAHO
- Page 45 and 46:
World Map of Natural Hazards Source
- Page 47 and 48:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 49 and 50:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 51 and 52:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 53 and 54:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 55 and 56:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 57 and 58:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 59 and 60:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 61 and 62:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 63 and 64:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 65 and 66:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 67 and 68:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 69 and 70:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 71 and 72:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 73 and 74:
2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 75 and 76: 2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 77 and 78: 2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 79 and 80: 2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 81 and 82: 2 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 83 and 84: Community scale model to identify h
- Page 85 and 86: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 87 and 88: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 89 and 90: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 91 and 92: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 93 and 94: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 95 and 96: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 97 and 98: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 99 and 100: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 101 and 102: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 103 and 104: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 105 and 106: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 107 and 108: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 109 and 110: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 111 and 112: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 113 and 114: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 115 and 116: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 117 and 118: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 119 and 120: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 121 and 122: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
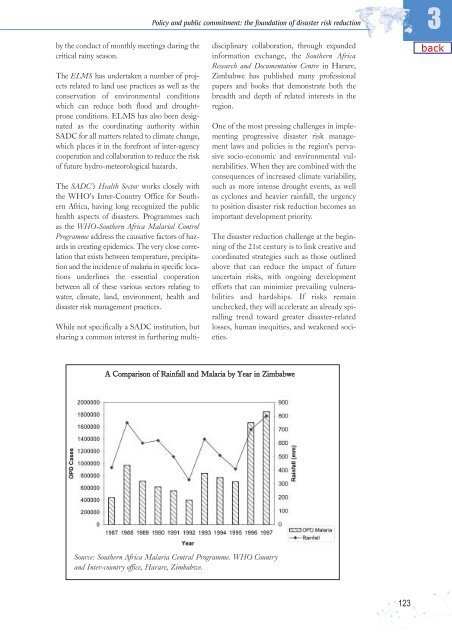
- Page 123 and 124: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 125: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 129 and 130: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 131 and 132: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 133 and 134: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 135 and 136: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 137 and 138: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 139 and 140: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 141 and 142: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 143 and 144: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 145 and 146: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 147 and 148: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 149 and 150: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 151 and 152: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 153 and 154: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 155 and 156: 3 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 157 and 158: Photo: University of Costa Rica
- Page 159 and 160: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 161 and 162: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 163 and 164: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 165 and 166: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 167 and 168: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 169 and 170: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 171 and 172: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 173 and 174: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 175 and 176: 4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 177 and 178:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 179 and 180:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 181 and 182:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 183 and 184:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 185 and 186:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 187 and 188:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 189 and 190:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 191 and 192:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 193 and 194:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 195 and 196:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 197 and 198:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 199 and 200:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 201 and 202:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 203 and 204:
Riskland- a fun way to learn how to
- Page 205 and 206:
4 Living with Risk: A global review
- Page 208 and 209:
A selection of disaster reduction a
- Page 210 and 211:
A selection of disaster reduction a
- Page 212 and 213:
A selection of disaster reduction a
- Page 214 and 215:
development of Africa, deserves att
- Page 216 and 217:
A selection of disaster reduction a
- Page 218 and 219:
ment. Therefore organizational fram
- Page 220 and 221:
A selection of disaster reduction a
- Page 222 and 223:
(NSA) and the System for Environmen
- Page 224 and 225:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 226 and 227:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 228 and 229:
patory approaches: empowering local
- Page 230 and 231:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 232 and 233:
een highlighted and additional asse
- Page 234 and 235:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 236 and 237:
Ways to achieve a safer built envir
- Page 238 and 239:
ture. The following cases demonstra
- Page 240 and 241:
carry out these guidelines. For the
- Page 242 and 243:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 244 and 245:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 246 and 247:
intended to build institutional str
- Page 248 and 249:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 250 and 251:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 252 and 253:
The PRECLIF Project for the Local P
- Page 254 and 255:
It is because these factors, compou
- Page 256 and 257:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 258 and 259:
Combined investment in economic dev
- Page 260 and 261:
mitigation, recovery and reconstruc
- Page 262 and 263:
uilding public and individual asset
- Page 264 and 265:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 266 and 267:
early warning reducing the conseque
- Page 268 and 269:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 270 and 271:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 272 and 273:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 274 and 275:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 276 and 277:
organization-specific requirements.
- Page 278 and 279:
The success of the WMO programmes i
- Page 280 and 281:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 282 and 283:
Selected application of disaster re
- Page 284 and 285:
orological services can provide by
- Page 286 and 287:
Criteria to measure the effectivene
- Page 288 and 289:
Chapter 6 Related international com
- Page 290 and 291:
Related international commitments a
- Page 292 and 293:
These joined the long standing Rams
- Page 294 and 295:
Related international commitments a
- Page 296 and 297:
The Clean Development Mechanism (CD
- Page 298 and 299:
Related international commitments a
- Page 300 and 301:
and production, soil conservation,
- Page 302 and 303:
Related international commitments a
- Page 304 and 305:
Related international commitments a
- Page 306 and 307:
Related international commitments a
- Page 308 and 309:
Division for the Advancement of Wom
- Page 310 and 311:
ECLAC secretariat headquarters Casi
- Page 312 and 313:
The UNDP Drylands Development Centr
- Page 314 and 315:
The foundation of UNICEF action lie
- Page 316 and 317:
Specialized agencies Food and Agric
- Page 318 and 319:
World Health Organization (WHO) WHO
- Page 320 and 321:
international scientific voice on c
- Page 322 and 323:
Disaster Mitigation and Relief Oper
- Page 324 and 325:
an International Training Centre fo
- Page 326 and 327:
the United Nations Secretary-Genera
- Page 328 and 329:
Chapter 7 Challenges for the future
- Page 330 and 331:
Challenges for the future 7 Challen
- Page 332 and 333:
improved disaster risk reduction. T
- Page 334 and 335:
Building performance targets In ord
- Page 336 and 337:
Challenges for the future 7 Methodo
- Page 338:
Annexes 1. Terminology: Basic terms
- Page 341 and 342:
a1 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 343 and 344:
a1 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 345 and 346:
a1 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 347 and 348:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 349 and 350:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 351 and 352:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 353 and 354:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 355 and 356:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 357 and 358:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 359 and 360:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 361 and 362:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 363 and 364:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 365 and 366:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 367 and 368:
a2 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 369 and 370:
a3 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 371 and 372:
a3 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 373 and 374:
a3 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 375 and 376:
a3 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 377 and 378:
a3 UNEP/DEPI UNEP/DEWA UNESCO UNFCC
- Page 379 and 380:
a4 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 381 and 382:
a4 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 383 and 384:
a4 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 385 and 386:
a4 Living with Risk: A global revie
- Page 387:
“In recent years the world has wi