You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 6 – Section 2 (5/2/04) Page 6.2-24<br />
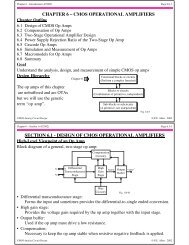
Increasing the Magnitude of the Output Pole †<br />
The magnitude of the output pole , p 2 , can be increased by introducing gain in the Miller<br />
capacitor feedback path. For example,<br />
M10<br />
M11<br />
Fig. 6.2-15B<br />
M8<br />
M12<br />
C c<br />
M9<br />
V Bias<br />
V DD<br />
C gd6<br />
C<br />
r c<br />
M7<br />
ds8<br />
+ +<br />
v OUT<br />
Iin R 1 V 1 Vs8 R 2 C 2<br />
gm8Vs8<br />
- -<br />
M6<br />
V SS<br />
The resistors R 1 and R 2 are defined as<br />
1<br />
R 1 = g ds2 + g ds4 + g ds9<br />
and R 2 =<br />
g m6 V 1<br />
g m6 V 1<br />
+<br />
V out<br />
-<br />
C gd6 C c<br />
+<br />
+<br />
Iin R 1 V1 1<br />
R 2 C 2<br />
gm8 V s8<br />
- g m8 V s8 -<br />
1<br />
g ds6 + g ds7<br />
where transistors M2 and M4 are the output transistors of the first stage.<br />
Nodal equations:<br />
⎛ g<br />
⎜ m8 sC c<br />
⎞<br />
⎡<br />
⎤<br />
⎟<br />
⎢<br />
⎥<br />
I in = G 1 V 1 -g m8 V s8 = G 1 V 1 -⎜<br />
⎟<br />
⎝<br />
g m8 + sC c<br />
V out and 0 = g m6 V 1 + ⎢G ⎥<br />
⎣ 2 +sC 2 + g m8sC c<br />
g m8 +sC c<br />
V out<br />
⎠<br />
+<br />
V out<br />
-<br />
⎦<br />
†<br />
B.K. Ahuja, “An Improved Frequency Compensation Technique for CMOS Operational Amplifiers,” IEEE J. of Solid-State Circuits, Vol. SC-18,<br />
No. 6 (Dec. 1983) pp. 629-633.<br />
CMOS <strong>Analog</strong> Circuit <strong>Design</strong> © P.E. Allen - 2004<br />
Chapter 6 – Section 2 (5/2/04) Page 6.2-25<br />
Increasing the Magnitude of the Output Pole - Continued<br />
Solving for the transfer function V out /I in gives,<br />
V out<br />
I in<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
= ⎜ ⎝<br />
-g m6<br />
⎞<br />
⎟<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
G 1 G 2<br />
⎣<br />
⎢ ⎢⎢⎡<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
⎜<br />
⎝<br />
⎡ C<br />
⎢ c<br />
1 + s⎢<br />
⎣<br />
g + C 2<br />
m8 G + C c<br />
2<br />
⎟<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
1 + sC c ⎞<br />
g m8<br />
⎤<br />
⎥<br />
⎥<br />
⎦<br />
G + g m6C c<br />
2 G 1 G 2<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
+ s2<br />
⎜ ⎝<br />
C c C 2<br />
g m8 G 2<br />
Using the approximate method of solving for the roots of the denominator gives<br />
-1<br />
-6<br />
p 1 = C c<br />
g m8<br />
+ C c<br />
G 2<br />
+ C 2<br />
G 2<br />
+ g m6C c<br />
≈ g m6 r ds<br />
2C c<br />
G 1 G 2<br />
and<br />
p 2 ≈<br />
- g m6r ds<br />
2C c<br />
6<br />
C c C 2<br />
g m8 G 2<br />
= g m8r ds<br />
2G 2<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
6 ⎜ ⎝<br />
g m6<br />
⎞<br />
C 2<br />
⎟<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
⎛<br />
⎜<br />
= ⎜ ⎝<br />
g m8 r ds<br />
⎞<br />
3 |p 2 ’|<br />
where all the various channel resistance have been assumed to equal r ds and p 2 ’ is the<br />
output pole for normal Miller compensation.<br />
Result:<br />
Dominant pole is approximately the same and the output pole is increased by ≈ g m r ds .<br />
⎟<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
⎞<br />
⎟<br />
⎟<br />
⎠<br />
⎦ ⎥⎥⎥⎤<br />
CMOS <strong>Analog</strong> Circuit <strong>Design</strong> © P.E. Allen - 2004