Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 6 – Section 3 (5/2/04) Page 6.3-8<br />
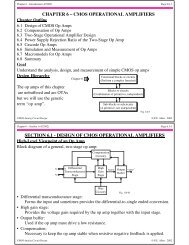
Example 6.3-1 - <strong>Design</strong> of a Two-Stage Op Amp<br />
Using the material and device parameters given in Tables 3.1-1 and 3.1-2, design an<br />
amplifier similar to that shown in Fig. 6.3-1 that meets the following specifications.<br />
Assume the channel length is to be 1µm and the load capacitor is C L = 10pF.<br />
Av > 3000V/V V DD = 2.5V V SS = -2.5V<br />
GB = 5MHz SR > 10V/µs 60° phase margin<br />
V out range = ±2V <strong>IC</strong>MR = -1 to 2V P diss ≤ 2mW<br />
Solution<br />
1.) The first step is to calculate the minimum value of the compensation capacitor C c ,<br />
C c > (2.2/10)(10 pF) = 2.2 pF<br />
2.) Choose C c as 3pF. Using the slew-rate specification and C c calculate I 5 .<br />
I 5 = (3x10-12)(10x106) = 30 µA<br />
3.) Next calculate (W/L) 3 using <strong>IC</strong>MR requirements.<br />
(W/L) 3 =<br />
30x10-6<br />
(50x10 -6 )[2.5 − 2 − .85 + 0.55] 2 = 15 → (W/L) 3 = (W/L) 4 = 15<br />
CMOS <strong>Analog</strong> Circuit <strong>Design</strong> © P.E. Allen - 2004<br />
Chapter 6 – Section 3 (5/2/04) Page 6.3-9<br />
Example 6.3-1 - Continued<br />
4.) Now we can check the value of the mirror pole, p 3 , to make sure that it is in fact<br />
greater than 10GB. Assume the C ox = 0.4fF/µm 2 . The mirror pole can be found as<br />
p -g m3 - 2K’ p S 3 I 3<br />
3 ≈ 2C gs3<br />
= 2(0.667)W 3 L 3 C ox<br />
= 2.81x10 9 (rads/sec)<br />
or 448 MHz. Thus, p 3 , is not of concern in this design because p 3 >> 10GB.<br />
5.) The next step in the design is to calculate g m1 to get<br />
g m1 = (5x106)(2π)(3x10-12) = 94.25µS<br />
Therefore, (W/L) 1 is<br />
(W/L) 1 = (W/L) g m1 2<br />
2 = 2K’ N I 1<br />
= (94.25) 2<br />
2·110·15 = 2.79 ≈ 3.0 ⇒ (W/L) 1 = (W/L) 2 = 3<br />
6.) Next calculate V DS5 ,<br />
V DS5 = (−1) − (−2.5) −<br />
30x10 -6<br />
110x10-6·3 - .85 = 0.35V<br />
Using V DS5 calculate (W/L) 5 from the saturation relationship.<br />
2(30x10-6)<br />
(W/L) 5 = (110x10-6)(0.35)2 = 4.49 ≈ 4.5 → (W/L) 5 = 4.5<br />
CMOS <strong>Analog</strong> Circuit <strong>Design</strong> © P.E. Allen - 2004