Barley for Food and Health: Science, Technology, and Products
Barley for Food and Health: Science, Technology, and Products
Barley for Food and Health: Science, Technology, and Products
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
76 BARLEY: GENETICS AND NUTRIENT COMPOSITION<br />
of two hulled <strong>and</strong> two hulless barley cultivars. One of the hulless types was<br />
waxy <strong>and</strong> was grown in a different environment <strong>and</strong> year than the other three<br />
barleys. The concentrations of all T <strong>and</strong> T3 isomers reported in this study were<br />
higher than reported by Wang et al. (1993), Peterson (1994), <strong>and</strong> Ehrenbergerovά<br />
et al. (2006). The greatest differences were in α-T <strong>and</strong> α-T3 concentrations <strong>and</strong><br />
the sum of the eight isomers, which was 2.0 to 2.6 times greater than in the<br />
earlier reports. In contrast to the findings of Ehrenbergerovά (2006), Cavallero<br />
et al. (2004) <strong>and</strong> Moreau et al. (2007) reported higher levels of total tocols in<br />
hulled barley although they also reported that hulless types had higher levels<br />
of α-T3. The results of these four studies indicate variability in concentrations<br />
of the various tocol isomers among different barleys. The differences may be<br />
explained by the different laboratories, genotypes, <strong>and</strong> growing environments.<br />
The one consistent finding in all four studies was the greater concentration of<br />
α-T3 than of the other T <strong>and</strong> T3 isomers (Table 4.4).<br />
There is much less recent in<strong>for</strong>mation on the amounts of the other vitamins in<br />
barley grain. Whole-grain cereals in general are good sources of the B-complex<br />
vitamins. <strong>Barley</strong> contains a range of the B vitamins that act as cofactors or prosthetic<br />
groups <strong>for</strong> various metabolic reactions in animal <strong>and</strong> microbial metabolism.<br />
A summary of the B-complex vitamin concentrations in barley grain is presented<br />
in Table 4.5. The data, which are from different laboratories spanning several<br />
years, are consistent <strong>for</strong> some vitamins but vary widely <strong>for</strong> others. It was suggested<br />
by Briggs (1978) that variation in the concentrations of vitamins reported<br />
in barley may be attributed to differences in analytical procedures <strong>and</strong> techniques<br />
used in different laboratories. Nicotinic acid is the most abundant of the<br />
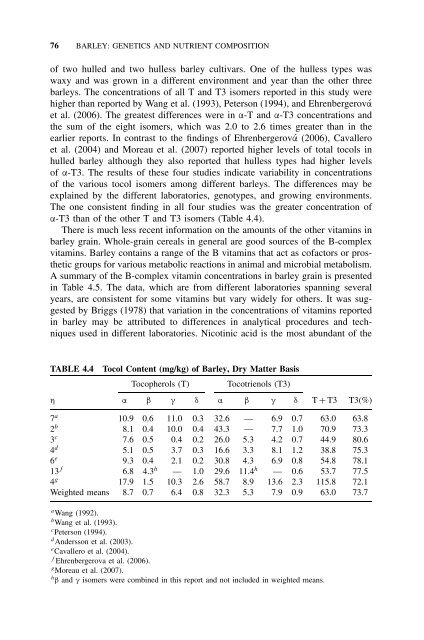
TABLE 4.4<br />
Tocol Content (mg/kg) of <strong>Barley</strong>, Dry Matter Basis<br />
Tocopherols (T) Tocotrienols (T3)<br />
η α β γ δ α β γ δ T + T3 T3(%)<br />
7 a 10.9 0.6 11.0 0.3 32.6 — 6.9 0.7 63.0 63.8<br />
2 b 8.1 0.4 10.0 0.4 43.3 — 7.7 1.0 70.9 73.3<br />
3 c 7.6 0.5 0.4 0.2 26.0 5.3 4.2 0.7 44.9 80.6<br />
4 d 5.1 0.5 3.7 0.3 16.6 3.3 8.1 1.2 38.8 75.3<br />
6 e 9.3 0.4 2.1 0.2 30.8 4.3 6.9 0.8 54.8 78.1<br />
13 f 6.8 4.3 h — 1.0 29.6 11.4 h — 0.6 53.7 77.5<br />
4 g 17.9 1.5 10.3 2.6 58.7 8.9 13.6 2.3 115.8 72.1<br />
Weighted means 8.7 0.7 6.4 0.8 32.3 5.3 7.9 0.9 63.0 73.7<br />
a Wang (1992).<br />
b Wang et al. (1993).<br />
c Peterson (1994).<br />
d Andersson et al. (2003).<br />
e Cavallero et al. (2004).<br />
f Ehrenbergerova et al. (2006).<br />
g Moreau et al. (2007).<br />
h β <strong>and</strong> γ isomers were combined in this report <strong>and</strong> not included in weighted means.