Migrants, Minorities, Belongings and Citizenship. Glocalization and ...
Migrants, Minorities, Belongings and Citizenship. Glocalization and ...
Migrants, Minorities, Belongings and Citizenship. Glocalization and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
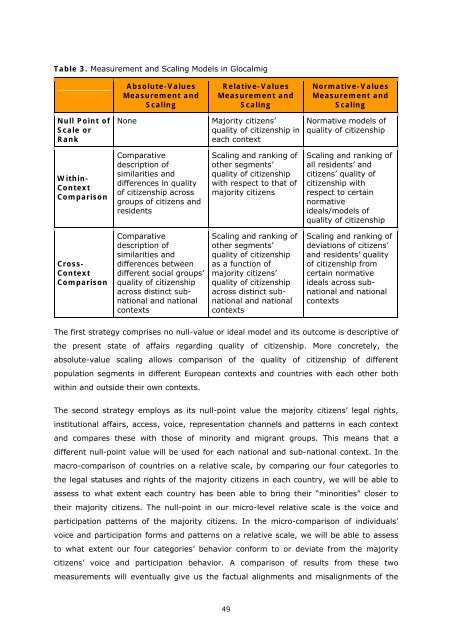
Table 3. Measurement <strong>and</strong> Scaling Models in Glocalmig<br />
Absolute-Values<br />
Measurement <strong>and</strong><br />
Scaling<br />
Relative-Values<br />
Measurement <strong>and</strong><br />
Scaling<br />
Normative-Values<br />
Measurement <strong>and</strong><br />
Scaling<br />
Null Point of<br />
Scale or<br />
Rank<br />
None<br />
Majority citizens’<br />
quality of citizenship in<br />
each context<br />
Normative models of<br />
quality of citizenship<br />
Within-<br />
Context<br />
Comparison<br />
Comparative<br />
description of<br />
similarities <strong>and</strong><br />
differences in quality<br />
of citizenship across<br />
groups of citizens <strong>and</strong><br />
residents<br />
Scaling <strong>and</strong> ranking of<br />
other segments’<br />
quality of citizenship<br />
with respect to that of<br />
majority citizens<br />
Scaling <strong>and</strong> ranking of<br />
all residents’ <strong>and</strong><br />
citizens’ quality of<br />
citizenship with<br />
respect to certain<br />
normative<br />
ideals/models of<br />
quality of citizenship<br />
Cross-<br />
Context<br />
Comparison<br />
Comparative<br />
description of<br />
similarities <strong>and</strong><br />
differences between<br />
different social groups’<br />
quality of citizenship<br />
across distinct subnational<br />
<strong>and</strong> national<br />
contexts<br />
Scaling <strong>and</strong> ranking of<br />
other segments’<br />
quality of citizenship<br />
as a function of<br />
majority citizens’<br />
quality of citizenship<br />
across distinct subnational<br />
<strong>and</strong> national<br />
contexts<br />
Scaling <strong>and</strong> ranking of<br />
deviations of citizens’<br />
<strong>and</strong> residents’ quality<br />
of citizenship from<br />
certain normative<br />
ideals across subnational<br />
<strong>and</strong> national<br />
contexts<br />
The first strategy comprises no null-value or ideal model <strong>and</strong> its outcome is descriptive of<br />
the present state of affairs regarding quality of citizenship. More concretely, the<br />
absolute-value scaling allows comparison of the quality of citizenship of different<br />
population segments in different European contexts <strong>and</strong> countries with each other both<br />
within <strong>and</strong> outside their own contexts.<br />
The second strategy employs as its null-point value the majority citizens’ legal rights,<br />
institutional affairs, access, voice, representation channels <strong>and</strong> patterns in each context<br />
<strong>and</strong> compares these with those of minority <strong>and</strong> migrant groups. This means that a<br />
different null-point value will be used for each national <strong>and</strong> sub-national context. In the<br />
macro-comparison of countries on a relative scale, by comparing our four categories to<br />
the legal statuses <strong>and</strong> rights of the majority citizens in each country, we will be able to<br />
assess to what extent each country has been able to bring their “minorities” closer to<br />
their majority citizens. The null-point in our micro-level relative scale is the voice <strong>and</strong><br />
participation patterns of the majority citizens. In the micro-comparison of individuals’<br />
voice <strong>and</strong> participation forms <strong>and</strong> patterns on a relative scale, we will be able to assess<br />
to what extent our four categories’ behavior conform to or deviate from the majority<br />
citizens’ voice <strong>and</strong> participation behavior. A comparison of results from these two<br />
measurements will eventually give us the factual alignments <strong>and</strong> misalignments of the<br />
49