Submitted version of the thesis - Airlab, the Artificial Intelligence ...
Submitted version of the thesis - Airlab, the Artificial Intelligence ...
Submitted version of the thesis - Airlab, the Artificial Intelligence ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
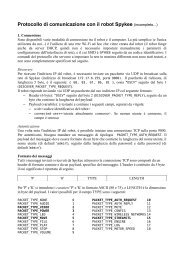
3.7. Hardware Architecture 33<br />
In short, LiPo provide high energy storage to weight ratios in an endless<br />
variety <strong>of</strong> shapes and sizes. The calculation is made to find <strong>the</strong> correct<br />
battery. The motors are consuming 250 mA at free-run and 3300 mA for<br />
<strong>the</strong> stall current. For <strong>the</strong> all three motors we should have <strong>the</strong> following<br />
battery lives:<br />
Battery Capacity/Current Draw = Battery Life<br />
2∗2500mAh/750mA ∼ = 6.6hours<br />
2∗2500mAh/9900mA ∼ = 0.5hours<br />
using <strong>the</strong> 2 batteries each having a capacity <strong>of</strong> 2500 mAh. The battery<br />
life shows changes according to <strong>the</strong> current draw <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> motors. In case,<br />
each motor is consuming 250 mA in free-run current will result 6.6 hours <strong>of</strong><br />
batteries life. On <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r hand, with <strong>the</strong> stall current it will be 0.5 hour<br />
battery life. Since <strong>the</strong> motor will not always work in stall current or <strong>the</strong><br />
free-run current; <strong>the</strong> choice <strong>of</strong> 2500 mA batteries (Figure 3.14) seems to be<br />
enough to power <strong>the</strong> robot for at least 2 hours.<br />
Figure 3.14: J.tronik - Battery Li-Po Li-POWER 2500 mA 2S1P 7,4V 20C<br />
3.7 Hardware Architecture<br />
During <strong>the</strong> development <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> robot, we used several hardware pieces such<br />
as microprocessor, camera, motor control boards, voltage regulator circuit,<br />
voltage divider circuit. Most <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>m were already developed systems and<br />
we did not focus on <strong>the</strong> production details <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>m. We only created <strong>the</strong><br />
voltage regulator and divider circuit, which we used in order to power <strong>the</strong><br />
boards and measure <strong>the</strong> battery level <strong>of</strong> charge.