- Page 1 and 2:
Investigating carotenoid loss after
- Page 3 and 4:
DECLARATION I certify that this wor
- Page 5 and 6:
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I am deeply gratef
- Page 7 and 8:
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1.! LITERATURE REV
- Page 9 and 10:
4.3.2! Effect of trial and sweet po
- Page 11 and 12:
1.1 BACKGROUND 1.1.1 Introduction C
- Page 13 and 14:
3 1. Literature review It is estima
- Page 15 and 16:
5 1. Literature review food corresp
- Page 17 and 18:
- the leaves that make energy and s
- Page 19 and 20:
9 1. Literature review Uganda and M
- Page 21 and 22:
11 1. Literature review communicati
- Page 23 and 24:
13 1. Literature review soya grains
- Page 25 and 26:
15 1. Literature review Drying is a
- Page 27 and 28:
17 1. Literature review Modelling o
- Page 29 and 30:
19 1. Literature review Other types
- Page 31 and 32:
21 1. Literature review The perform
- Page 33 and 34:
23 1. Literature review degradation
- Page 35 and 36:
25 1. Literature review carotene an
- Page 37 and 38:
27 1. Literature review (Rees, NRI,
- Page 39 and 40:
29 1. Literature review red (>800 n
- Page 41 and 42:
31 1. Literature review Figure 1-17
- Page 43 and 44:
33 1. Literature review induced by
- Page 45 and 46:
35 1. Literature review Enzymatic c
- Page 47 and 48:
37 1. Literature review Volatile pr
- Page 49 and 50:
39 1. Literature review Carotenoid
- Page 51 and 52:
Table 1-5: Effect of type of proces
- Page 53 and 54:
Comparison of losses in drying proc
- Page 55 and 56:
45 1. Literature review observed we
- Page 57 and 58:
47 1. Literature review Different p
- Page 59 and 60:
Oxygen 49 1. Literature review Oxyg
- Page 61 and 62:
51 1. Literature review the storage
- Page 63 and 64:
2.2.2 Root samples 53 2. Assessment
- Page 65 and 66:
2.2.5 Water activity 55 2. Assessme
- Page 67 and 68:
57 2. Assessment of Methods below t
- Page 69 and 70:
59 2. Assessment of Methods !-carot
- Page 71 and 72:
61 2. Assessment of Methods indicat
- Page 73 and 74:
63 2. Assessment of Methods were we
- Page 75 and 76:
65 2. Assessment of Methods Table 2
- Page 77 and 78:
67 2. Assessment of Methods Intra-l
- Page 79 and 80:
69 2. Assessment of Methods Signifi
- Page 81 and 82:
71 2. Assessment of Methods Table 2
- Page 83 and 84:
Content (µg/g) Content (µg/g) Con
- Page 85 and 86:
75 2. Assessment of Methods way-ANO
- Page 87 and 88:
77 2. Assessment of Methods puree.
- Page 89 and 90:
Percentage loss "a" redness 45% 40%
- Page 91 and 92:
CHAPTER 3. 81 3. Preliminary study
- Page 93 and 94:
83 3. Preliminary study Figure 3-1:
- Page 95 and 96:
85 3. Preliminary study Air velocit
- Page 97 and 98:
3.2.10 Statistical analyses 87 3. P
- Page 99 and 100:
89 3. Preliminary study because it
- Page 101 and 102:
Sample area (cm2) 91 3. Preliminary
- Page 103 and 104:
Figure 3-9: UV-Visible spectrum of
- Page 105 and 106:
95 3. Preliminary study Mulokozi an
- Page 107 and 108:
97 3. Preliminary study One hundred
- Page 109 and 110:
99 4. Ugandan field study respectiv
- Page 111 and 112:
Transmittance (%) 101 4. Ugandan fi
- Page 113 and 114:
4.2.5 Total carotenoids extraction
- Page 115 and 116:
105 4. Ugandan field study The dryi
- Page 117 and 118:
107 4. Ugandan field study individu
- Page 119 and 120:
109 4. Ugandan field study values a
- Page 121 and 122:
111 4. Ugandan field study caroteno
- Page 123 and 124:
113 4. Ugandan field study observed
- Page 125 and 126:
115 4. Ugandan field study OFSP chi
- Page 127 and 128:
117 5. Mozambican field study carot
- Page 129 and 130:
119 5. Mozambican field study kg (p
- Page 131 and 132:
121 5. Mozambican field study Table
- Page 133 and 134:
123 5. Mozambican field study carot
- Page 135 and 136: Tot. carotenoid content (!g/g) Tot.
- Page 137 and 138: 127 5. Mozambican field study 5.3.6
- Page 139 and 140: a b c c 129 5. Mozambican field stu
- Page 141 and 142: 131 5. Mozambican field study Table
- Page 143 and 144: 133 5. Mozambican field study #-car
- Page 145 and 146: 135 5. Mozambican field study carot
- Page 147 and 148: CHAPTER 6. 137 6. Effect of pre-tre
- Page 149 and 150: 139 6. Effect of pre-treatment out
- Page 151 and 152: 141 6. Effect of pre-treatment afte
- Page 153 and 154: 143 6. Effect of pre-treatment leve
- Page 155 and 156: 145 6. Effect of pre-treatment Citr
- Page 157 and 158: 147 6. Effect of pre-treatment trea
- Page 159 and 160: 149 6. Effect of pre-treatment inte
- Page 161 and 162: CHAPTER 7. 151 7. Involvement of en
- Page 163 and 164: 7.2.2. pH measurement 153 7. Involv
- Page 165 and 166: 155 7. Involvement of enzymes glyce
- Page 167 and 168: 157 7. Involvement of enzymes Table
- Page 169 and 170: 159 7. Involvement of enzymes carot
- Page 171 and 172: 161 7. Involvement of enzymes carot
- Page 173 and 174: 163 7. Involvement of enzymes Perox
- Page 175 and 176: CHAPTER 8. 165 8. Study under contr
- Page 177 and 178: Kilner jar (with metal lever catch
- Page 179 and 180: Figure 8-2: Storage system for wate
- Page 181 and 182: 8.2.4 Carotenoid analyses 171 8. St
- Page 183 and 184: 8.3 RESULTS & DISCUSSION 8.3.1 Samp
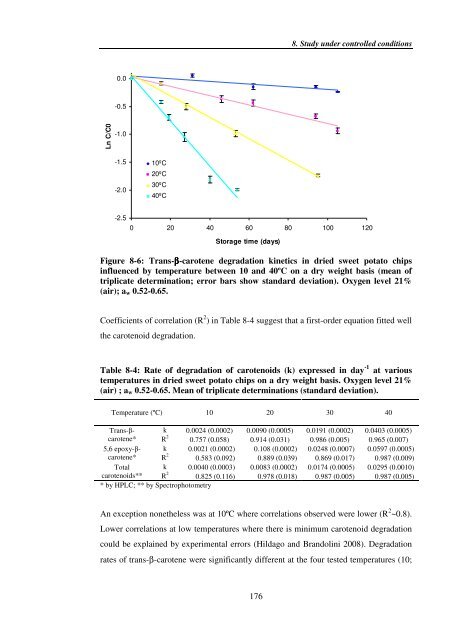
- Page 185: 175 8. Study under controlled condi
- Page 189 and 190: 179 8. Study under controlled condi
- Page 191 and 192: 181 8. Study under controlled condi
- Page 193 and 194: k (day-1) k (day-1) 0.10 0.08 0.06
- Page 195 and 196: 185 8. Study under controlled condi
- Page 197 and 198: 187 8. Study under controlled condi
- Page 199 and 200: 189 8. Study under controlled condi
- Page 201 and 202: 191 8. Study under controlled condi
- Page 203 and 204: 193 8. Study under controlled condi
- Page 205 and 206: CHAPTER 9. GENERAL DISCUSSION AND F
- Page 207 and 208: 197 9. Discussion carotene loss aft
- Page 209 and 210: 199 9. Discussion total carotenoids
- Page 211 and 212: 9.4.2 Varietal influence 201 9. Dis
- Page 213 and 214: 203 9. Discussion 2008). The side e
- Page 215 and 216: 205 9. Discussion Absence of cis-is
- Page 217 and 218: 207 9. Discussion (Chapter 7). Howe
- Page 219 and 220: 209 9. Discussion of these cultivar
- Page 221 and 222: References 211 References Aguayo, V
- Page 223 and 224: 213 References Bechoff, A., Dhuique
- Page 225 and 226: 215 References Chen, H.E., Peng, H.
- Page 227 and 228: DIAS (2006) Semi-Annual and Annual
- Page 229 and 230: 219 References Tropical Agriculture
- Page 231 and 232: 221 References has a positive effec
- Page 233 and 234: 223 References Kamiya N. and Nagamu
- Page 235 and 236: Lee, S.B. and Kim, K.J. (1995) Effe
- Page 237 and 238:
227 References Mills, R.C. and Hart
- Page 239 and 240:
Nestel, P., Bouis, H.E., Meenakshi,
- Page 241 and 242:
231 References Preston, C.M. and Ba
- Page 243 and 244:
Simon, P.W. (1997) Plant pigments f
- Page 245 and 246:
235 References Tran, T.H., Nguyen,
- Page 247 and 248:
237 References Walter, W.M., Purcel
- Page 249 and 250:
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! A
- Page 251 and 252:
Arrhenius model: = ∞ − Ea RT ek
- Page 253 and 254:
242 Appendix 1 B/Calculation of Arr
- Page 255 and 256:
Temperature is integrated for each
- Page 257 and 258:
2) Integration of temperature in Ug
- Page 259 and 260:
Appendix 2b: Dryers cost in Lualua,
- Page 261 and 262:
250 Appendix 2 Technical informatio
- Page 263 and 264:
252 Appendix 2 Technical informatio
- Page 265 and 266:
Open air flat and sloped dryers 254
- Page 267 and 268:
Appendix 3: Total carotenoids metho
- Page 269 and 270:
4. Partition - Pour 40 ml of Petrol
- Page 271 and 272:
Publications: Publications, award a