Lab Manual - eScience Labs
Lab Manual - eScience Labs
Lab Manual - eScience Labs
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Lab</strong> 14: Mendelian Genecs<br />
The law of segregaon states that during<br />
meiosis, homologous (paired) chromosomes<br />
split (Figure 1). The law of independent<br />
assortment states that during<br />
meiosis, each homologous chromosome<br />
has an equal chance of ending up in either<br />
gamete, and alleles for individual<br />
genes segregate with the chromosomes<br />
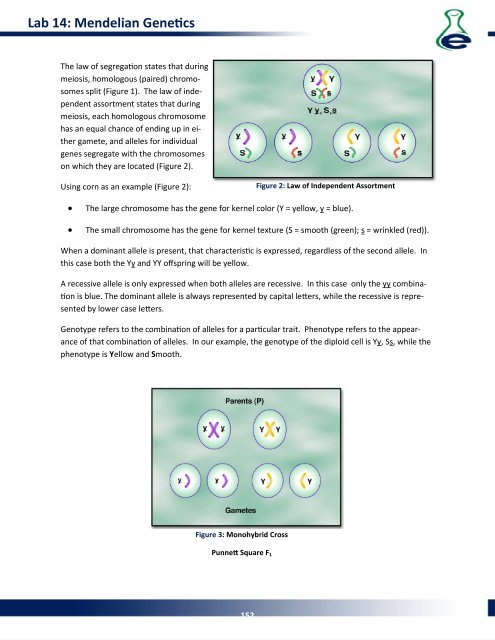
on which they are located (Figure 2).<br />
Using corn as an example (Figure 2):<br />
Figure 2: Law of Independent Assortment<br />
• The large chromosome has the gene for kernel color (Y = yellow, y = blue).<br />
• The small chromosome has the gene for kernel texture (S = smooth (green); s = wrinkled (red)).<br />
When a dominant allele is present, that characterisc is expressed, regardless of the second allele. In<br />
this case both the Yy and YY offspring will be yellow.<br />
A recessive allele is only expressed when both alleles are recessive. In this case only the yy combina-<br />
on is blue. The dominant allele is always represented by capital leers, while the recessive is represented<br />
by lower case leers.<br />
Genotype refers to the combinaon of alleles for a parcular trait. Phenotype refers to the appearance<br />
of that combinaon of alleles. In our example, the genotype of the diploid cell is Yy, Ss, while the<br />
phenotype is Yellow and Smooth.<br />
Figure 3: Monohybrid Cross<br />
Punne Square F 1<br />
152